Posted ,
Reading 3 mins.
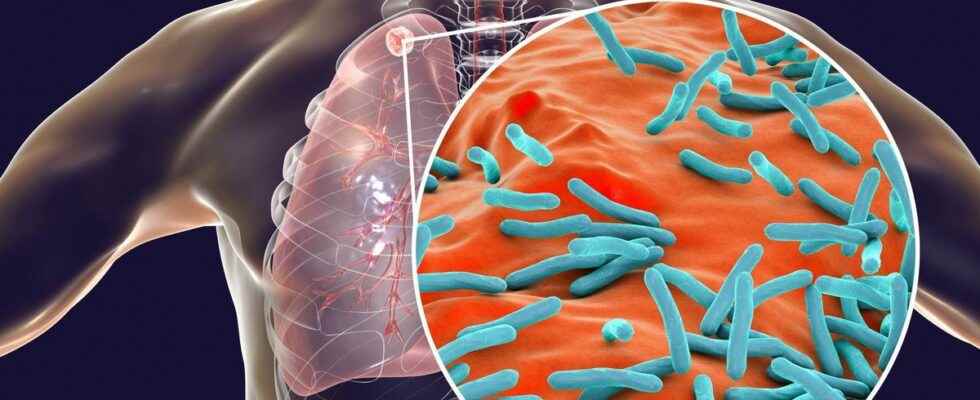
An infectious disease, tuberculosis is caused by a contagious mycobacterium. Children from a school in a commune in Calvados have been in contact with an adult who has declared the disease and must therefore be screened.
The parents of children from a school in Calvados had the bad surprise to discover that their offspring had been in contact with an adult affected by tuberculosis, during extracurricular time. Children must therefore be screened to rule out any risk of contamination with this disease.
What is tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by Koch’s bacillus, named after the man who discovered it, or mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis mainly affects the lungs, but can spread and reach other organs: the lymph nodes , the joints, the urinary tract… in the context of extra-pulmonary tuberculosis. Tuberculosis is transmitted through the air and can infect children and adults. It can lead to death if left untreated.
A latent disease that occurs in 10% of cases
Once the bacillus is in the body, tuberculosis does not declare itself immediately. There is a latency period of two years on average during which the person carries the bacillus within them but does not develop the disease and is not contagious. Then, in 10% of cases and after a certain period of time, the symptoms begin and the disease sets in.
For people who do not show symptoms, the examinations are multiple: a clinical examination, a chest X-ray, a bacteriological examination of sputum (sputum) and/or gene amplification tests.
In the case of latent infection the patient does not produce any signs. The disease is then detected using two types of tests, which will assess the presence of an immune fingerprint:
- Tuberculin Intradermal Reaction (IDR): it is a test that involves injecting a drop of liquid containing the mycobacterial antigen called tuberculin into the dermis on the front of the forearm. The inflammatory reaction obtained should be read 72 hours after the test. It determines whether the subject has previously been in contact with the bacillus or the vaccine, according to the diameter of induration observed. This reaction is not related to a level of protection against the disease.
- IGRA or interferon gamma release tests: these are tests performed on a blood sample. The subject’s blood is brought into contact with specific antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and then the response is evaluated in the form of interferon gamma release.
What are the symptoms and treatment of tuberculosis?
Since 2007, the vaccination obligation has been replaced by a strong recommendation for the “most exposed” children. Tuberculosis is transmitted by microsecretions that the sick person emits when coughing, talking, sneezing or singing… The person also coughs a lot, but may show other signs: weight loss, night sweats, fever…
Antibiotic therapy will then be started for six months, fully covered by Medicare as part of a long-term condition.
A disease in sharp decline
A notifiable disease, tuberculosis remains infrequent in France with 4,606 cases declared in 2020, due to the public health policies carried out in France since the 1970s. However, vigilance remains in order, with regard to “the multiplication of bacterial strains resistant to usually effective treatments” notify the Ministry of Health.
The frequency of tuberculosis is higher in certain territories (Mayotte, Guyana, Île-de-France) and in certain population groups such as homeless people (170 cases/100,000/year), prisoners (64 cases/100,000/year), and people born outside France (34 cases/100,000/year).
Read also


When a treatment is abandoned or poorly conducted, this induces resistance. The bacteria will then not be eradicated by anti-TB drugs. And more seriously, beyond the relapse, the patient is exposed to resistance to treatment.