With the 22H2 update of Windows 11, the Task Manager which had not evolved for years gets a facelift. Featuring a sleeker interface, it remains a must-have tool for monitoring PC activity in real time.
To find out which software takes up most of the RAM available on the computer, which process is involved in the slowdown of the PC or which application is launched at startup, only one direction: the Windows task manager. Integrated into the system for many years, this tool gives an overview or a detailed view of everything that is happening on the computer: occupation rate of random access memory (Ram), utilization of processors, activity of hard disks or SSD, network bandwidth usage, etc. A real control tower that allows you to point out in real time the programs and applications that can cause a problem and fix it.
With version 22H2 of Windows 11, available since the end of September 2022, Task Manager is getting a welcome little facelift. No more unsightly tabs and outdated design. The Task Manager now adopts a much more elegant presentation, in line with apps signed Microsoft, especially in the dark world – finally managed! It also includes some new features such as the Efficiency mode to manage how certain processes use the available resources.
Microsoft has hardly changed the way to display Task Manager in Windows. You can use almost any method we describe in our how-to sheet to get there, including the handy – but little-known – keyboard shortcut CTRL + Shift + Esc (Where Esc) which directly opens the Task Manager, in any circumstance, without going through a menu or a search.
Be careful, however, because with version 22H2, you can no longer open Task Manager by right-clicking on a blank area of the taskbar. This action now leads to the taskbar settings.
Microsoft has not revolutionized the way to use Windows Task Manager but has given it a big brushstroke to see more clearly.
Open Task Manager using one of the methods given above. The new interface is presented. On the left of the window, a column now lists the different items processed by Task Manager that were previously displayed in tabs:
Process displays the list of all processes running on the PC. This is where you can force stop a process or an app if it crashes and slows down the PC, for example.
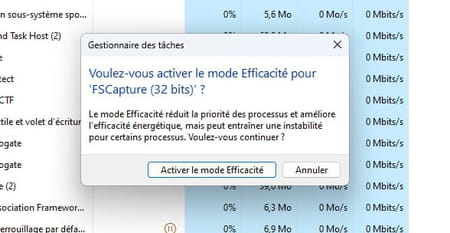
This is also where you can set the Efficiency Mode for one or more processes. For example, if an app is consuming more resources than necessary at the expense of other more important processes, click it to select it, then click Efficiency Mode, at the top right of the window. Then confirm in the window that appears by clicking on the button Enable Efficiency mode. She will see her activity reduced. Please note that this mode is not available for all processes: the option is then grayed out in the function bar.
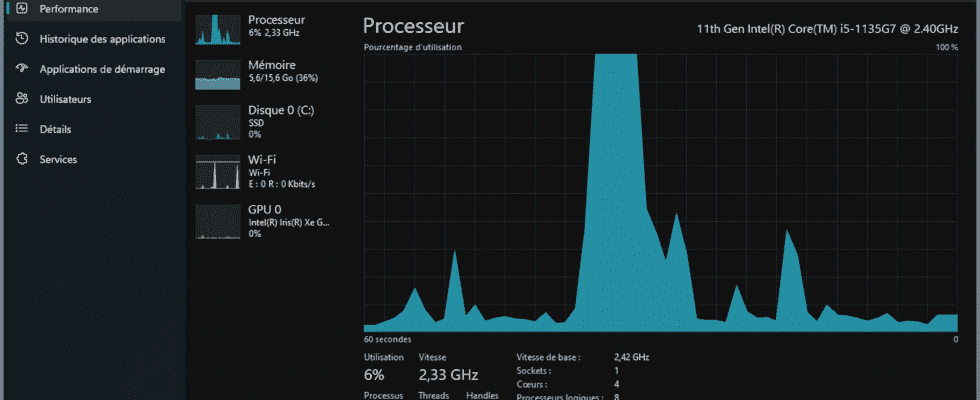
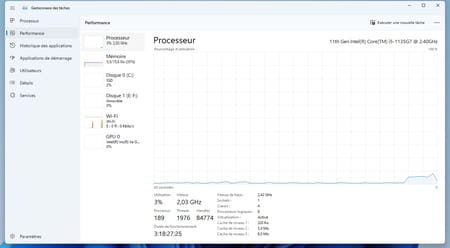
Performance allows you to see at a glance the activity of the processors, the graphics card, the occupation of the RAM, the storage space and the network.
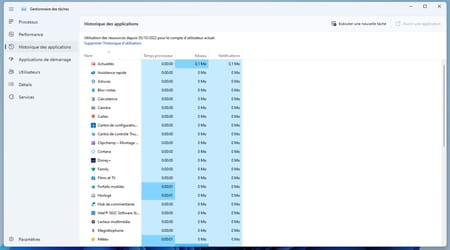
Application history is where you can view the history of launched applications and programs as well as their resource consumption.
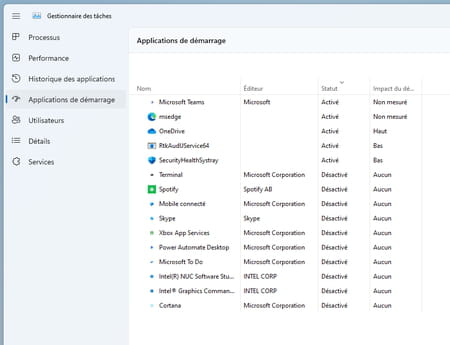
Starter app lists on its side all the programs which start as soon as the active Windows session. Convenient for disabling an application that would have granted itself the right to start at the same time as Windows.
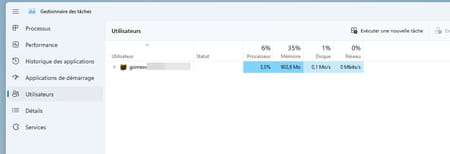
Users allows you to see the user accounts connected at this time on the PC as well as the use of the computer’s resources for each of them.
Details offers, as the name suggests, a very detailed view of all running processes.
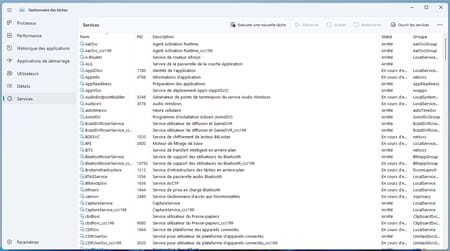
Services lists on its side all active and inactive services in Windows. You can start, stop or restart them if they cause problems.