USSR. Founded in 1922 in the wake of the Bolshevik Revolution of 1917, the USSR disappeared in 1991 after the fall of the Berlin Wall and the dislocation of the Eastern bloc. Which current countries were members and which ones could be coveted by Vladimir Putin to realize his dream of returning to Great Russia?
Vladimir Putin’s ambitions on the international scene and the outbreak of war in Ukraine on February 24, 2022 have revived many questions about the history of the USSR and its fall, Ukraine and Russia being part of it until 1991. of the same state. The dislocation of the Eastern bloc and the end of the USSR are also seen by Vladimir Putin as the “greatest geopolitical catastrophe of the 20th century”, as he admitted according to the documentary “Russia. New history” broadcast on Russian television in December 2021. Eager to find Greater Russia, whose “disintegration” he deplores, can Vladimir Putin go further and target other countries in a return to the borders of the USSR? It should therefore target many countries formed at the fall of the USSR at the end of 1991…
The USSR is the diminutive of Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, the name officially taken by the State formed after the Bolshevik revolution of 1917 in Russia and the fall of the Tsars. The acronym USSR, its English version, has also entered popular culture (for example, the Beatles’ hit “Back in the USSR” released in 1968). Soviet sportsmen lined up under the banner of the USSR, often with outfits marked CCCP, quite simply the Russian language translation from the Cyrillic of the USSR or Союз Советских Социалистических Республик.
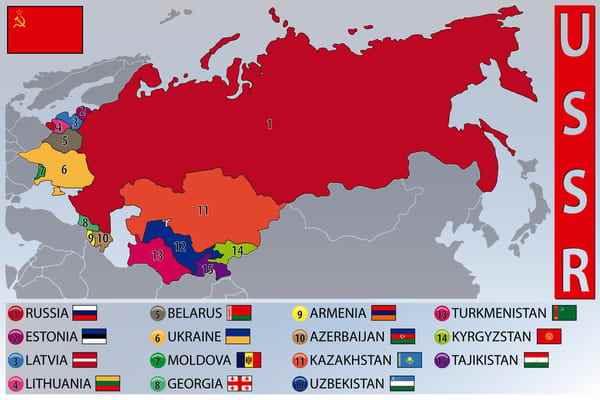
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics or USSR was made up of about fifteen states. Some joined the Soviets voluntarily, but most were annexed by force. The USSR resisted until 1990, when the first states left the union. Among these States, there was of course the Russian Federation, but also:
- Ukraine, which was invaded and integrated into the USSR from its creation in 1922, until its independence on August 24, 1991;
- Belarus, part of whose territory joined the USSR in 1922 and the other was first ceded to Poland. It regains its integrity and independence on August 25, 1991;
- Georgia, which was invaded by the Soviets in 1921. It proclaimed its independence on April 9, 1991;
- Moldavia, which united with Romania in 1918 and was an ally of Nazi Germany during the Second World War. It is recovered by the USSR at the end of the war. It obtained its independence on August 27, 1991;
- Lithuania, which was attacked by Russia in 1940, then occupied by Germany and finally annexed by the USSR in 1944. It gained its independence on March 11, 1990;
- Latvia, which suffered the same fate as Lithuania because of the German-Soviet Pact, until its independence on May 4, 1990;
- Estonia whose history is identical to Lithuania and Latvia. It was incorporated into the USSR from 1944 to August 20, 1991;
- Armenia which believed to obtain its independence after the collapse of the Ottoman Empire and which enters the USSR from its creation. It finally gained independence on September 21, 1991;
- Azerbaijan which was invaded by the USSR in 1920. It affirmed its autonomy on August 30, 1991;
- Uzbekistan which is a territory created by the USSR in 1924. It became a true independent state on September 1, 1991 by separating from the Soviet Union.
- Tajikistan which is also a territory created by the USSR and which proclaimed its independence on September 9, 1991;
- Turkmenistan which, like its neighbors, was conquered by the Russian Empire and which became part of the USSR in 1924. It became autonomous on October 27, 1991;
- Kyrgyzstan, which also came from the Russian conquests of the 19th century. It was incorporated into the USSR from 1936 to August 31, 1991;
- Kazakhstan, whose Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic was associated with the USSR in 1936, like its neighbors. It declared its independence on December 16, 1991.
