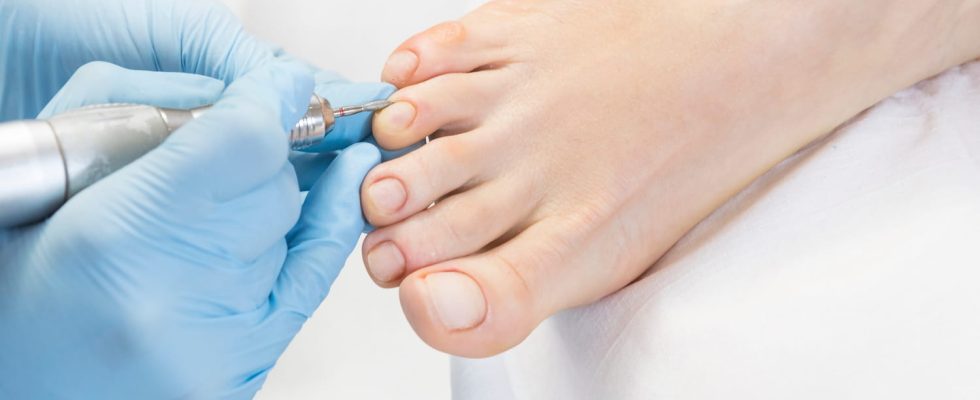
The podiatrist-podiatrist is the specialist of the foot: he can practice hygiene care, treat skin or nail diseases, correct gait disorders. Presentation of an unknown profession.
Soles, corns, foot deformities, plantar warts… This is why it is advisable to consult a podiatrist-podiatrist (commonly called podiatrist). How do we know if we need it? When to consult it? What is the price of a consultation? Is it reimbursed?
What is the definition of a pedicure-podiatrist?
The pedicure-podiatrist is a healthcare professional specializing in foot conditions. It is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous or ungual (nail) pathologies. The pedicure-podiatrist Brigitte Oudet specifies however that it is necessary to distinguish
- pedicure care (corns, ingrown nails, warts, calluses etc.),
- podiatry care
- the manufacture of orthoses intended to help correct certain deformities and pathologies,
- the production of insoles to compensate for static disorders.
What is the difference between a pedicure and a podiatrist?
There are not any. Brigitte Oudet specifies that today “there is only one state diploma in pedicure-podiatry. It is indeed the same profession”. Not to be confused of course with a beautician who can perform a pedicure, which is not a treatment, in an institute and whose training is not medical.
Is the podiatrist-podiatrist a doctor?
THE pedicurist-podiatrist is not a doctor but some doctors may have had training in podiatry (rheumatologist, orthopaedist, sports doctor, etc.)
What does a podiatrist treat?
The pedicure-podiatrist sees patients of all ages, from children to the elderly. He can also intervene with high-level athletes or individuals with disabilities. The conditions and symptoms that can lead to consulting a pedicure-podiatrist are of various types:
- hyperkeratosis (corns, calluses),
- plantar warts,
- Hallux valgus,
- ingrown toenails,
- sweating disorders.
- In the event of gait or balance disorders, the podiatrist is qualified to detect low back pain or another pathology of the joints.
- It also plays a role in monitoring patients with diabetes or arteritis for preventive or therapeutic purposes.
Brigitte Oudet insists on the importance of the interrogation: “This is a very important step to know the patient’s state of health and because many general diseases affect the condition of the foot: neurological diseases, dermatoses, rheumatism, arteritis, diabetes”before continuing: “After the interrogation, a podiatrist carries out an examination of the foot and the statics to eliminate a possible disorder, then only then one begins the treatment.” The professional explains that communication is also essential : “It is necessary to put the person at ease, to reassure him in front of the instruments then to install him comfortably. Too many patients self-medicate and don’t have good habits. So after the treatment, it is important to give them advice on how to put on the right shoes but also take the time to transmit measures and therapeutic education advice to adopt the right foot monitoring and hygiene gestures..”
The pedicure-podiatrist reminds us that it is important to “to take care of the hygiene of the feet before going in consultation by carrying out a rigorous washing”.
What is the price of a session? Is it reimbursed?
Only pedicure-podiatry procedures prescribed by a doctor can give rise to reimbursement by the Health Insurance. Patients with grade 2 or 3 diabetes (presence of a sensory neuropathy requiring regular care, history of ulceration or amputation) can benefit from 4 to 6 sessions per year fully covered.
What studies to become a podiatrist?
To become a pedicure-podiatrist, it is necessary to obtain the state diploma of pedicure-podiatrist which sanctions three years of study after the baccalaureate. 11 establishments in France train students for this diploma: 10 are accessible by competition and one, the Bordeaux school, is accessible only by the Paces competition (common first year of health studies).
Thanks to Brigitte Oudet, podiatrist-podiatrist.