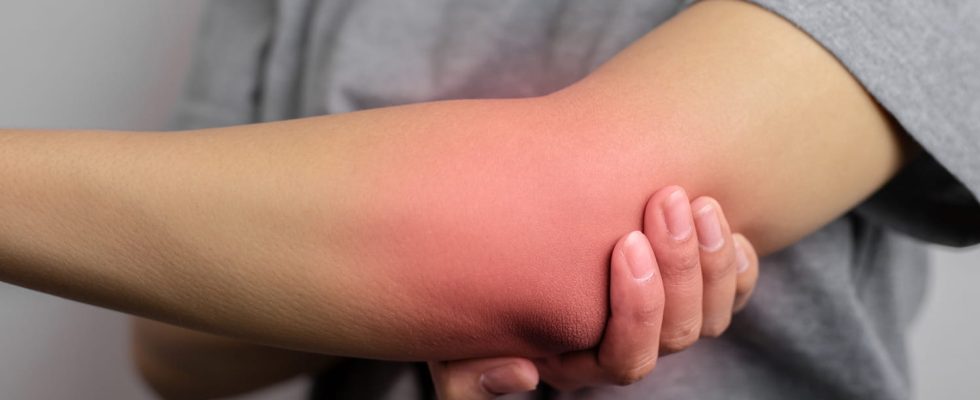
Inflammation is a set of reactions generated by the body in response to an attack (injury, infection, autoimmune disease). Pain and redness are the main signs.
What is the definition of inflammation?
The inflammation is a process of chain reactions, biological and cellular allowing the body to respond to an attack, whether traumatic, infectious or autoimmune. It causes signs mainly sore, identifying its presence. It can be a skin or subcutaneous inflammation (abscess, erysipelas, shock).
What are the 4 signs of inflammation?
Inflammatory reactions are triggered in order to defend the body against aggression.
When the inflammation is external, it is visible and typically manifests as 4 clinical signs:
- A redness
- A pain
- A swelling
- The increase in local heat
When the inflammation is internal, these signs exist but are not visible. Only pain is felt, often increased in intensity during the night.
What are the signs of inflammation in a blood test?
Inflammation is biologically characterized by:
- An increase in C-reactive protein or CRP
- An increase in sedimentation rate
- An increase in the number of white blood cells.
This reflects the establishment of the body’s mechanisms to fight against aggression. At the cellular level, white blood cells have a role in these mechanisms with different cells with well-organized functions.
What does inflammation mean?
The presence of visible inflammation reveals that an attack on the organism has taken place, whether bacterial, traumatic or related to another cause. It may happen that the inflammation is only discovered when carrying out a biological assessment, in the face of signs of fatigue or unexplained pain. The search for the origin of the inflammation must therefore take place in order to adapt the treatment of its cause.
What is chronic inflammation?
Inflammation is a useful reaction since it is the body’s defense against aggression. In some cases, the inflammation may persist until it becomes chronic. The immune system is then overwhelmed by this inflammatory reaction. It is no longer beneficial at all and must be diagnosed and treated with medication. It’s the case chronic inflammatory diseasesas rheumatoid arthritis Or Crohn’s disease.
When should you consult?
When the inflammation becomes chronic, that is, it lasts and no obvious cause is found, it is necessary to consult your doctor to do research to find the cause of this inflammation: search for autoimmune disease, cancer, rheumatic or inflammatory digestive disease…
The inflammatory response is a complex phenomenon, which can sometimes be relieved by the use of anti-inflammatory molecules such as corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. However, these drugs should not be used without medical advice and cannot be prescribed for all inflammatory pathologies. During local inflammation, the application of ice is effective, cold being a powerful natural anti-inflammatory. In any case, chronic inflammatory diseases require regular medical monitoring.