Wave physics studies the deformations that propagate in a medium, whether it is material or not. There are three major wave categories : the gravitational wavesmechanical waves and electromagnetic waves.
The three types of waves
The waves are categorized into 3 main families:
- Gravitational waves which are linked to the concept of relativity and space-time. The editorial staff of Futura devoted an entire dossier to these gravitational waves who carry theenergy to the speed of light. They are particularly at the heart of the study of black holes in astrophysics.
- Mechanical waves are those which propagate in a material medium, whether liquidgas or solid. We find, for example, the swell that forms in water, seismic waves who are in the Earth’s crust or even the sound waves which are invisible to the naked eye but which diffuse thanks toair.
- Electromagnetic waves include both light but also waves radios. What differentiates them from the other two categories are their ability to transport energy but also information. This is why they are at the center of technological progress in matter telecommunications.
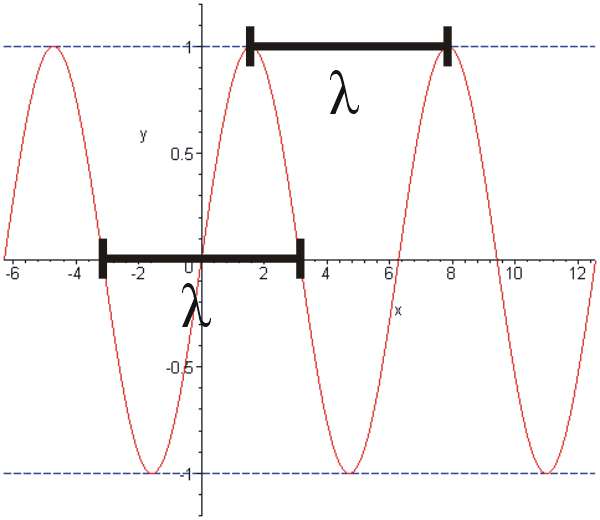
The wavelength is one of the characteristics specific to each wave, whatever its nature. It is noted using the Greek letter lambda: λ. She represents the spatial periodicity oscillations, that is to say the distance between two maxima of the oscillation, for example. The wavelength is also the distance traveled by the wave during one period of oscillation. Thus, it is inversely proportional to the frequency and is expressed in meters.
The wavelength represents the distance traveled by the wave during one period of oscillation. © Schlurcher, Wikipedia, CC by-sa 3.0
To each wave, its wavelength
Note that the wavelength depends on the speed at which the wave propagates through the medium. Thus, when a wave passes from one medium to another by changing speed, its wavelength varies, even if its frequency remains the same. All according to the following relationship: λ = cT = c/f, where c corresponds to the speed of the wave, T to its time period and f to its frequency.
The names given to electromagnetic waves make it possible to locate them on the wavelength scale. Radio waves have wavelengths longer than 30 centimeters. The wavelengths of the visible light are between 400 and 700 nanometers. And every color visible light is characterized by a wavelength range. Thus, green is around 510 nanometers and red around 650 nanometers.
Remember also that the shorter the wavelength of an electromagnetic wave, the greater the energy it carries. The X-rays for example have a wavelength between 10-11 and 10-8 meters. They carry more energy than microwave whose wavelength is between 3 millimeters and 30 centimeters.
You will also be interested
[EN VIDÉO] Interview: Are electromagnetic waves dangerous? We are constantly exposed to electromagnetic waves from a wide variety of sources: high voltage lines, mobile phones, Wi-Fi are among the main sources. But is this overexposure a health hazard? As part of its series of Expert Questions, on physics and astrophysics, the publisher De Boeck asked Olivier Pujol, lecturer at the University of Lille, about this possibility.
Interested in what you just read?