While 90 percent of lung cancers seen in our country are caused by smoking; Being male, having a family history, being exposed to chemicals such as radon and asbestos in occupational and environmental terms, and diseases such as tuberculosis and COPD increase the risk of developing lung cancer.
ATTENTION TO THESE FACTORS INCREASING THE RISK OF LUNG CANCER!
Ex. from the Department of Chest Diseases. Dr. Selda Kaya gave information about lung cancer and risk factors.
EARLY DIAGNOSIS INCREASES TREATMENT SUCCESS
Lung cancer is the uncontrolled proliferation of some cells in the normal lung tissue, forming a mass in the lung. With the progression of the disease, lung cancer, which can spread to the surrounding tissues or other organs through the circulation, is the first cause of cancer-related deaths. While the survival rate is high in lung cancer patients diagnosed at an early stage, this rate decreases in advanced stage cancers. For this reason, it is very critical to make the diagnosis of lung cancer at an early stage.
1 in 7 LONG-TERM Smokers Develops Lung Cancer
Current smokers have a higher incidence of new lung cancer than those who have never smoked or have quit smoking. The risk of developing lung cancer increases as the number of cigarettes smoked per day and the number of years smoked increase. About 1/7 of long-term (average 30 years) smokers develop lung cancer. However, within 10 years of quitting smoking, the risk of developing lung cancer decreases by 50 percent compared to the normal population. In terms of prevalence of cigarette smoking, male gender still predominates in the incidence of lung cancer in our country.
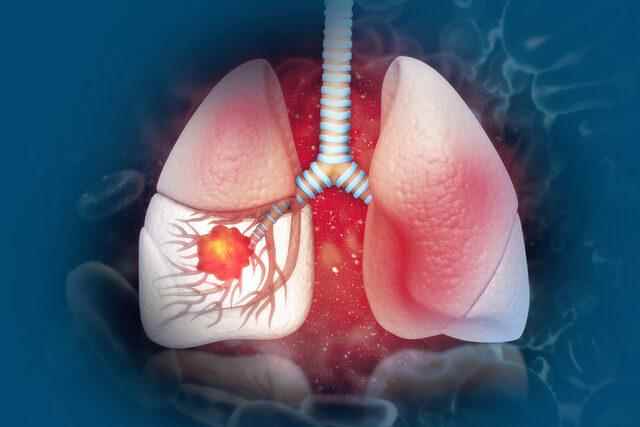
STAGE OF CANCER DEFINES TREATMENT
For the diagnosis of lung cancer, first of all, a physical examination is performed by a physician specialized in chest diseases. Along with the examination, diagnostic tests such as chest X-ray, computed tomography, sputum cytology, bronchoscopy, fine needle aspiration, thoracentesis, thoracoscopy, and thoracotomy may be requested. Determining the stage of lung cancer is important in determining the treatment modality and determining the severity of the disease. Whether the disease has spread to other organs, the patient’s effort capacity and mobility in daily life also affect the success of treatment as well as staging.
May increase the risk of lung cancer
General risk factors for lung cancer include genetic and environmental factors. The groups at high risk for lung cancer can be listed as follows:
As announced by the Ministry of Health, 90 percent of lung cancers seen in our country are caused by smoking. When effective tobacco control is provided, approximately 110 thousand deaths due to tobacco use, including lung cancers, will be prevented each year.
Although the male gender is at the forefront, the gender gap has been decreasing as a result of the prevalence of smoking among women in recent years. Lung cancer; It has an annual incidence of 61.2 per hundred thousand for both sexes in our country.
Having a family history of lung cancer increases the risk of developing lung cancer compared to other individuals in the community.
A history of occupational or environmental exposure to chemicals doubles the risk for lung cancer. However, there is a risk increase of 8-11 percent in radon gas exposure caused by environmental radiation, and 1.5-5.4 times in asbestos exposure. Radon gas is the most important factor in lung cancer after smoking and is responsible for 3 to 15 percent of lung cancer.
Having diseases that may be in the high risk group such as tuberculosis, pulmonary fibrosis or COPD in terms of cancer increases the risk of lung cancer.
Excessive alcohol consumption increases the risk of lung cancer.
