Researchers have managed to create a camera with a depth of field beyond anything that exists. Thanks to an optical metasurface and a neural network, they can create images where all objects are perfectly sharp, whether they are placed a few centimeters away or almost two kilometers away.
You will also be interested
Depth of field is one of the basic elements in photography. A shallow depth of field helps achieve the bokeh effect on selfies, while a deeper depth of field allows you to capture both foreground and background elements simultaneously. Researchers from National Institute of Standards and Technology in the United States succeeded in setting a new record for depth of field by taking inspiration from trilobites.
These old arthropods sailors, extinct 250 million years ago, had compound eyes particularly complex. L’species Dalmanitina socialishad eyes bifocals, in other words that could simultaneously focus close on their prey and far away to monitor the presence of predators. The researchers took inspiration from their eyes to create a camera capable of simultaneously focusing on objects three centimeters away and 1.7 kilometers away.
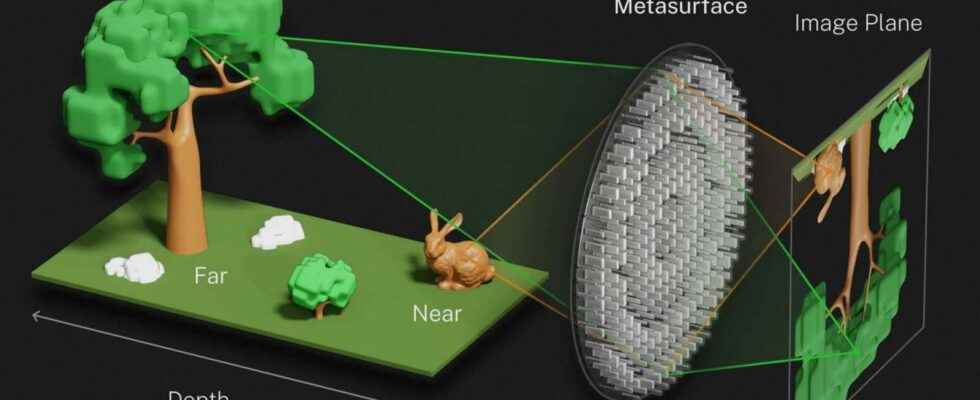
An optical metasurface to simultaneously create two images
In their article published in the journal NatureCommunicationsthey detail how they integrated a optical metasurface in a plenoptic camera, a camera that records the direction of light rays, in addition to the light intensity like a conventional device. The metasurface is covered with pillars in titanium dioxide nanoscale, each specifically designed to manipulate the light. Thanks to the particular geometry of this optical metasurface, they were able to separate the light according to its polarization, and thus create two images. One focused at a few centimeters and the other at almost two kilometres.
For objects between these two distances, the researchers used an algorithm based on a convolutional neural network. This corrects the aberrations induced by the metasurface and allows to create a sharp image over the entire depth of field. This system could one day be used in cameras, optical microscopes or even computer vision.
Interested in what you just read?