Researchers have created robots from the stem cells of frogs, capable of reproducing by stacking new stem cells which in turn will give rise to robots. And so on over several generations. A fascinating experience that could tell us about the origins of life.
You will also be interested
[EN VIDÉO] The fantastic power of stem cells Eternal youth seems to be a quest as old as humanity. It could be that this coveted fountain of youth is located at the very heart of our body, within stem cells. Discovery Science takes us to the discovery of these amazing cells in video.
For several years, researchers have been trying to develop xenobots made up of living cells. By 2020, a team from the University of Vermont and Tufts University had successfully created robots from stem cells frogs, able to move around independently and organize themselves to perform different tasks (read below). Today, a new step has just been taken with xenobots that can produce new generations of robots and therefore reproduce like a living organism.
Stacks of stem cells that become robots
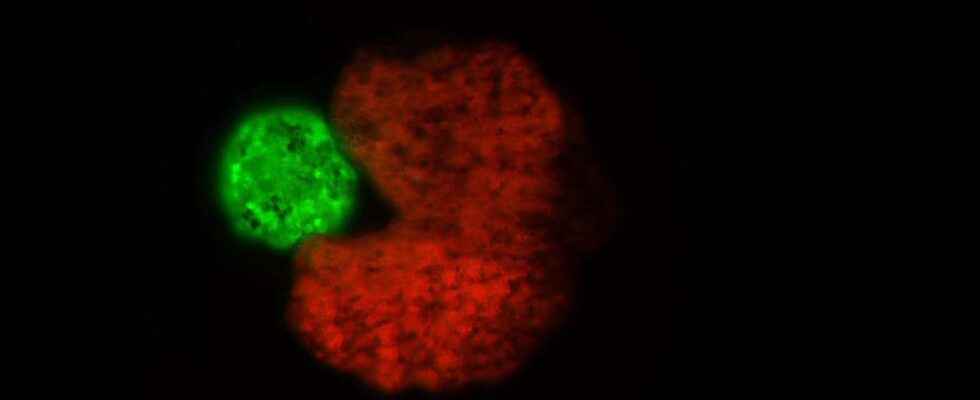
Initially, as before, we have xenobots formed from clusters of frog stem cells Xenopus laevis (smooth xenopus). Each cluster, about half a millimeter in diameter, contains around 3,000 stem cells. These xenobots are then immersed in a “bath” of 60,000 new stem cells, and there, surprise: they begin to create “stacks” of stem cells, large enough so that they in turn become autonomous. Reproduction is stopped when we stop adding new stem cells.
Each cycle of replication However, it produces smaller offspring, so after a while the new robots are no longer viable (below 50 cells). To solve this problem, the researchers turned toArtificial intelligence to determine if there is an optimal form of assembly. Using an algorithm, they were able to determine in advance which initial configuration was likely to give the greatest number of generations. Verdict: Pac-Man shaped robots are the most efficient, with “children” on average 149% larger than spherical shaped robots. By testing this hypothesis, the researchers found that Pac-Man robots produced four generations of xenobots, against only two for spherical robots.
Create made-to-measure robots using living “kits”
” THE’analogy that I use is that of computer hardware and software, illustrates Michael Levin, co-author of the study published in PNAS. What the geneticis to provide the material. It tells each cell exactly what components it can have. The rules governing the operation of newly arranged cells are akin to software “. The researchers are now planning to build a “library” of modules from which we would draw functionality to create a “super robot” with all the desired characteristics.
The beginning of life on Earth?
” This is the first time that multicellular organisms have self-replicated in a way that does not involve the growth of the body’s cells Enthuses Michael Levin. This biological process could however be involved in the appearance of life on Earth. ” It has been shown that the components ofRNA can assemble and act like enzymes to help assemble more RNA. […] Other non-biological chemicals also create copies of themselves in this way. “, Says the researcher.
A living robot made from cells
Article by Celine Deluzarche published on 01/19/2020
Researchers have created robots from frog stem cells, able to move around autonomously and self-organize to perform different tasks. However, the creation by humans of organisms that do not exist in nature gives rise to fears of misappropriation and ethical questions.
The man cyborg is not yet for tomorrow, but the first living robot created from frog stem cells has just seen the light of day. ” This is not a traditional robot nor a new one species animal, but a whole new fully programmable life form », Welcomes Joshua Bongard, engineer in robotic at the University of Vermont and co-designer of the project. These xenorobots, as the researchers called them, are less than a millimeter in length and are able to move around independently, survive for weeks without food, and work together.
This is not the first attempt to create artificial life. In April 2019, researchers at Cornell University announced that they had created robots in DNA endowed with a artificial metabolism. Other approaches have attempted to build flexible robots, inspired by animals (snakes, cockroaches, bird, turtle, eel, caterpillar, fish, astonished, insect, dog). ” But for the first time, we have created biological machines from the ground up “, Congratulate the researchers in their study reported in the journal PNAS.
The xenorobot is a programmable living organism, designed from stem cells. © University of Vermont
A lifespan of 10 days to several weeks
These xenorobots do not look much like traditional animals or robots. They are more like a embryo informs, the cells being organized according to how they were programmed. Stem cells are first taken from a frog embryo african Xenopus laevis (hence their name). An evolutionary algorithm generates thousands of possible combinations with “passive” cells (skin cells) and “active” cells (heart cells), the latter ensuring the mobility of the biorobot thanks to their contractions. After incubation, the cells are assembled according to the models drawn by thecomputer. It is thus possible to modify the characteristics depending on the desired task. Researchers have, for example, found that certain configurations are more or less fast or that they cause robots to self-organize to collect materials or manipulate objects.
Each xenorobot has enough energy to survive on its own for 10 days, but their lifespan could extend for several weeks in a rich environment. nutrients, say the researchers. Xenorobots are also able to “heal” wounds themselves.
Robots made from nerve cells, endowed with cognitive abilities
The potential of these xenorobots is something to dream about: they could for example carry medication in the human body or clean the plaques ofatheroma in the arteries before degrading naturally. They could also collect plastic in the ocean, digest toxic substances or radioactive or to identify molecules in environments inaccessible to humans. But this technology offers even more dizzying prospects. By building them from nerve and sensory cells, xenorobots could thus be endowed with cognitive capacities and become “intelligent”.
Are the robots going to turn against us?
Perceptives that have something to raise concerns, some alarming at the possible hijacking of such robots (fear fueled by the fact that the project is partly funded by Darpa, the research arm of the American army). Even if they are not yet able to reproduce or evolve, we can imagine colonies of robots deciding by themselves to invade an organism, to spread a deadly virus or destroy objects. For now, their behavior is driven by design, which is itself determined by algorithms. Except that artificial intelligence is a real black box, the ins and outs of which escape us more and more. The creation of entirely new organisms outside all biological evolution also raises many ethical questions. What to feed the next science fiction films.
Did you know ? Futura launches its very first paper magazine ! A review of more than 200 pages, 4 files on Science which will mark 2022, zero fake news, just Science !
For this adventure to succeed, Futura needs you. Meeting on Ulule to support the project and participate in its launch. The objective is to reach the threshold of 2,500 presales in order to be able to print the magazine with enriched formats (comics, photo reports, etc.)
It is high time to stop fake news, and to make Science accessible to as many people as possible. #LeMagFutura
So, are you ready to embark on the Mag Futura?
Interested in what you just read?
.
fs3