After weeks of hectic campaigning, D-Day has almost arrived. Sunday June 9, the French are called to the polls to elect the 81 French European deputies who will sit for five years in the Strasbourg Parliament.
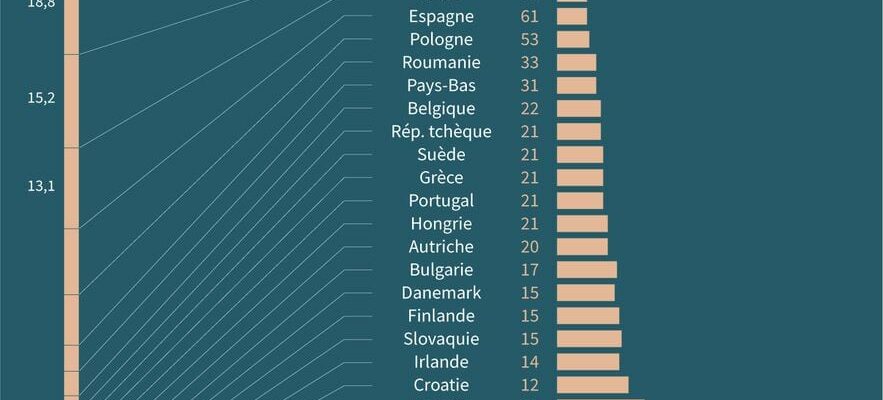
In total, citizens of the 27 member countries will elect 720 representatives, by proportional representation, to modify and vote on laws. The distribution of seats by state takes into account the population of each country, but this advantage decreases with the increase in population.
Number of Members of the European Parliament, per million inhabitants for each EU country, and the percentage of the overall EU population that it represents
© / AFP
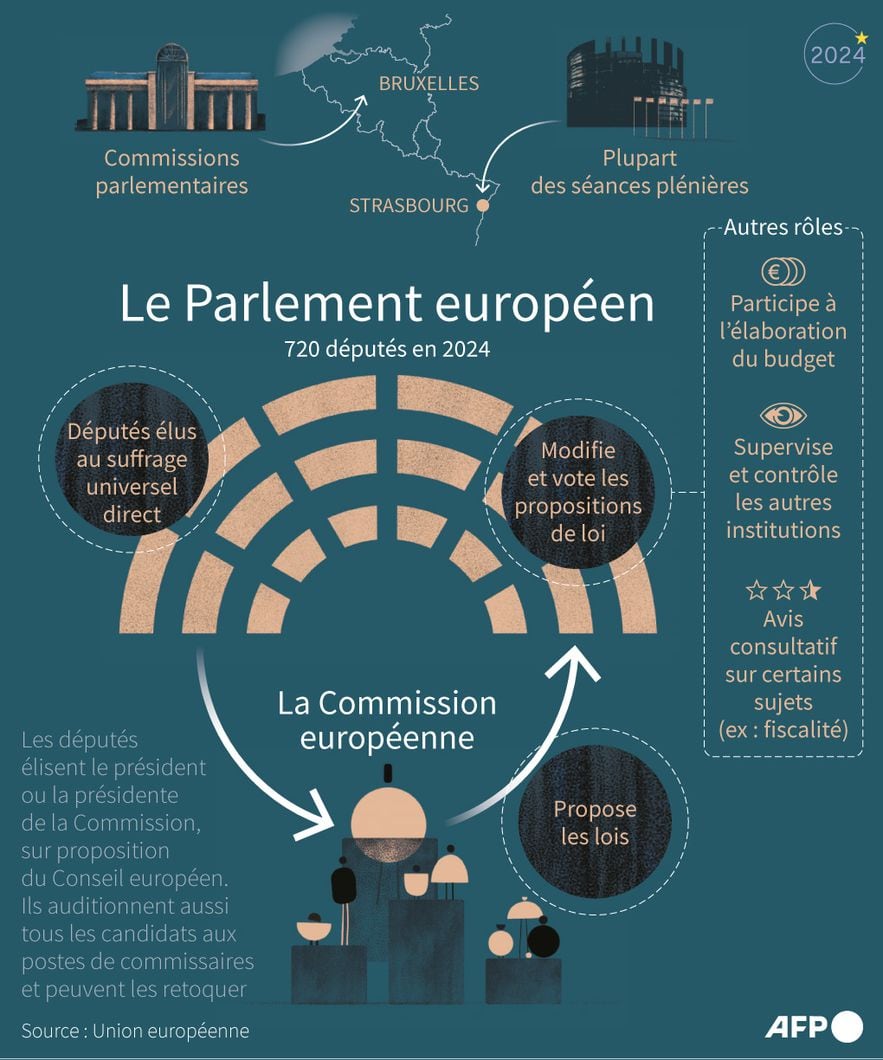
The only institution of the European Union elected directly by citizens, the European Parliament is involved in the adoption of legal acts of the European Union. The 2007 Treaty of Lisbon established the “co-decision” procedure, today called the ordinary legislative procedure, as the main European decision-making method.
After the election of MEPs, the European Parliament elects the president of the European Commission, the institution responsible for proposing laws. On each proposal, the European Parliament decides at first reading, then submits its position to the European Council. If the latter approves all (possible) amendments from MEPs, the act can be adopted. But if the Council adopts another position, Parliament has three months (which can be extended by one month on request) to react. It then decides on second reading and decides either to accept the Council’s position, or to amend it again (it then returns to the Council), or to reject it and the proposal is not adopted.
Unless otherwise provided for by the treaties, a text cannot therefore be adopted in the event of disagreement between the Council and the European Parliament. In the event of persistent disagreement, the act is examined by a conciliation committee, also called a “trilogue”.
Main characteristics and responsibilities of the European Parliament
© / AFP
Budgetary and control power
In addition to drafting the law, the European Parliament is also responsible, in collaboration with the Council, for voting on the annual budget of the European Union. With the entry into force of the Lisbon Treaty, the Commission prepares a draft budget which it presents to the two institutions which share the legislative procedure. The Council then adopts a position, which it transmits to the European Parliament. If it approves the position of the Council or abstains from ruling, the budget is adopted; but if Parliament adopts amendments, the draft budget is sent again to the Council and the Commission.
The European Parliament finally has a role of monitoring the institutions, via its power of censorship of the Commission – which must resign if the majority of two thirds of the votes cast and the majority of the members of the Parliament are in favor -, but also by constituting temporary commissions of inquiry, in the event of infringements or poor application of Community law.
It can, if it wishes, ask written or oral questions to the Council and the Commission, and has a right of appeal to the Court of Justice of the European Union, which ensures the proper application of the treaties.