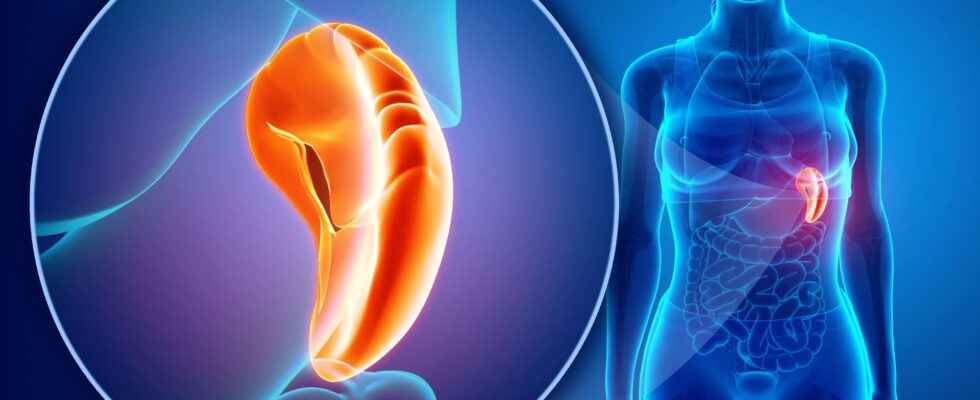
Splenomegaly is a significant increase in volume of the missed which is not palpable in the normal state. The perception of a splenomegaly is therefore a reflection of a dysfunction, of an underlying pathology. It can be observed in an acute, subacute or chronic context.
Diagnosis of splenomegaly
In most cases, splenomegaly is asymptomatic, so it is sought in a suggestive clinical context. It is generally painless but can generate by phenomenon of compression, a feeling of tension, pain in the left part of the abdomen or back.
It may be associated with hepatomegaly (increased volume of the liver). This is called hepatosplenomegaly.
The clinical examination by palpation makes it possible to evaluate the degree of increase in the volume of the spleen according to five stages ranging from stage 0 (spleen of normal size, not palpable even in deep inspiration) to stage 5 (spleen which is palpable in the left iliac fossa).
L’medical imaging is not necessary to characterize a splenomegaly, but a ultrasound or a TDM (computed tomography) can be contributory in case of doubt.
Causes of splenomegaly
The spleen has different functions in the body:
- storage role of blood cells;
- role in the regulation of blood flow;
- role of filter (macrophages, elimination of Red cells abnormal);
- role inimmunity (production ofantibody).
Also, an increase in its volume can be induced by various diseases. Additional medical and laboratory examinations will determine the causes of the splenomegaly. Different pathologies can be involved:
- infectious pathologies of parasitic origin (malaria), viral (hepatitis), bacterial (endocarditis);
- hyperdestruction of red blood cells;
- liver damage which may lead to vascular compression (hypertension portal);
- Cancer some blood : lymphoma, leukemia ;
- overload disease: linked to deficits enzymatic ;
- system disease: lupus, sarcoidosis.
The treatment will therefore be specific to the disease concerned and, if it is effective, the spleen may decrease in size.
Complications of splenomegaly are hypersplenism (blood cells stagnate in the spleen instead of circulating), heart attack, and rupture which can lead to death without surgery. In rare cases, it will be necessary to perform a splenectomy (ablation spleen) which will expose by immunosuppression to infections by bacteria.
You will also be interested
Interested in what you just read?
.
fs7