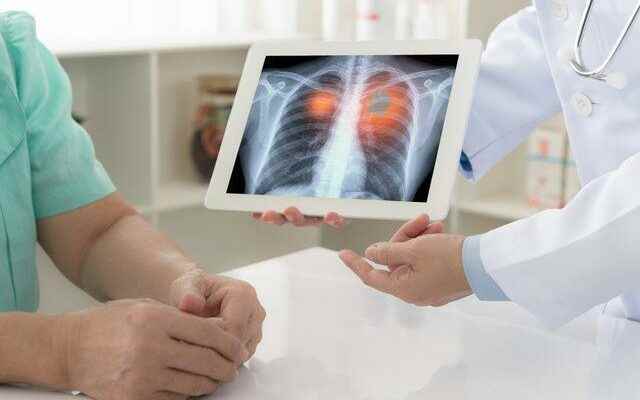
The biggest proven cause of lung cancer is the use of tobacco products such as cigarettes and cigars. However, among the causes of lung cancer, there are many reasons that we are exposed to every day but are not aware of. Lung cancer starts in the lung cells and spreads to other parts of the body by forming a tumor due to abnormal cell growth.
LUNG CANCER SYMPTOMS
- Cough that does not go away or gets worse
- coughing up blood or bloody sputum
- Chest pain that worsens when breathing deeply, coughing, or laughing
- Loss of appetite, weakness, fatigue and weight loss
- hoarseness
- Shortness of breath
- Recurrent or persistent lung infections such as bronchitis or pneumonia
Many causes other than cancer can also cause these symptoms. However, if any of these are common and do not go away, it is absolutely necessary to consult a specialist.
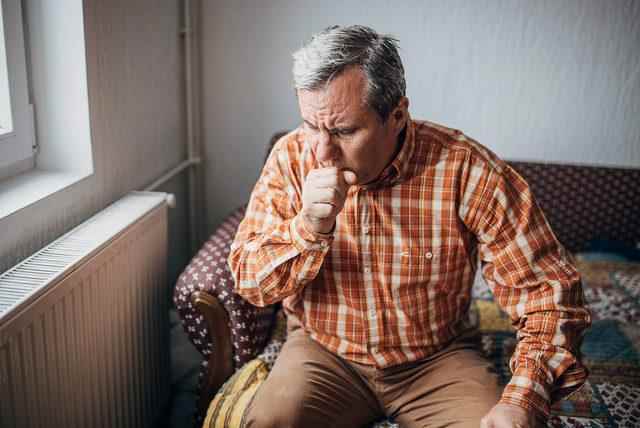

If you have any of the above symptoms, have a family history of lung cancer, or have different risk factors, you may need to have a screening test for lung cancer.
If the diagnosis of lung cancer is confirmed, further examinations are required to find possible spreads throughout the body. The doctor may then order, for example, bone scintigraphy, liver ultrasound, endoesophageal ultrasound, an angiography to visualize possible damage to the aorta and pulmonary vessels, and a test to look for damage to the lymph nodes.
IS THERE A LUNG CANCER TREATMENT?
Quitting smoking is always a prerequisite for treatment. The treatments then chosen depend on the type of lung cancer defined as non-small cell or small cell, the stage of development, and the patient’s general condition.

For non-small cell lung cancers, surgery to remove the tumor is usually considered. Removal of a lobe of the lung or the entire lung can be performed.
Then, chemotherapy with or without radiotherapy is often recommended, depending on the situation. In large types of cancer, chemotherapy is sometimes used before surgery to reduce tumor volume. In some cancers with very large metastases, surgery cannot be performed. The progression of the disease is tried to be controlled with a treatment that combines chemotherapy, radiotherapy and targeted therapies.
Small cell lung cancer is a lung cancer known for its tendency to spread very quickly throughout the body. In non-invasive forms, treatment is based on chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Immunotherapy is a new treatment that aims to stimulate the patient’s immune defense against cancer cells. This therapy is now integrated into various therapeutic treatments.
It is known that smoking increases the risk more than other factors in lung cancer, which is one of the deadliest cancers. However, in some cases, lung cancer also affects people who have never smoked. It is thought that factors such as environment, radon and passive smoking may be associated with lung cancer in non-smokers.
RADON
Few people are aware of the risk of radon. Radon exposure can cause lung cancer deaths in people who have never smoked. It is estimated to be responsible for many deaths among smokers or people who have smoked before. Radon is an invisible radioactive gas that escapes from certain soil types.

Radon can infiltrate and accumulate in your home. Sources of radon exposure can be your workplace, school, and indoor places where you spend a lot of time. Therefore, if you are in doubt, you can have radon tests done indoors.
PASSIVE SMOKE
Being around smokers exposes you to the same carcinogens in cigarettes, but with a lower toxic dose. Men and women who smoke are 13 and 23 times more likely to develop lung cancer, respectively, and passive smoking increases the risk of developing lung cancer by 20 to 30 percent.

If you live with a smoker, avoiding secondhand smoke can be difficult. For your own health, stay away from cigarette smoke.
AIR POLLUTION
Research shows that air pollution, especially fine particles such as PM2.5 produced by car exhaust, power plants and forest fires, can increase the risk of lung, breast and other cancers. While air pollution triggers health problems such as asthma, it also contains high levels of toxic substances that can increase the risk of developing lung cancer.
ASBESTOS
Asbestos is among the factors that increase the risk of developing lung cancer. However, this effect on health requires a long and intense exposure and is usually only seen in individuals exposed to asbestos in a professional setting. People working in the construction, demolition, auto mechanic and military industries are at risk of exposure to asbestos because buildings and brake linings can contain asbestos. Most products containing asbestos are banned or restricted.

Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a group of lung diseases such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema, increases the risk of developing lung cancer. Lung cancer and COPD have similar risk factors, such as smoking and exposure to radon or asbestos. Smoking is the biggest risk factor for COPD.
Inflammation associated with COPD is thought to increase the risk of lung cancer. People with COPD should try to quit and have lung cancer screenings if they still smoke.
FAMILY STORY
People with a family history of lung cancer are at higher risk of developing the disease, especially if they have a close relative who developed lung cancer at a young age. No genetic testing is available in lung cancer because no gene responsible for the disease has yet been identified.
It is recommended that people with a family history have a lung cancer screening test.
ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE
Although electronic cigarettes are seen as a safe alternative to cigarettes, they are not. The dangers about electronic cigarettes are becoming more and more obvious. It is thought that the use of electronic cigarettes will lead to a high risk of increase in the number of lung cancer deaths that will occur in older ages. Research shows that lung disease caused by e-cigarettes can lead to an increased risk of lung cancer.