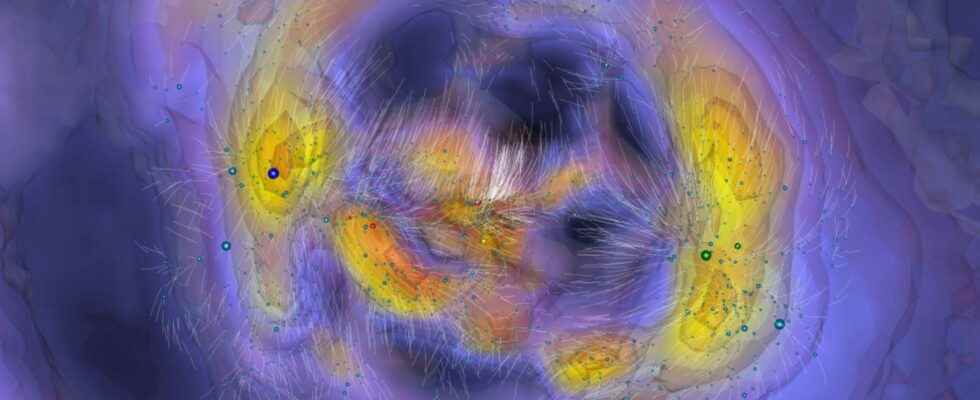
Retracing the path traveled by galaxies since the Big Bang is not easy. Because they are not guided simply by expansion. Gravity also comes into play. And researchers have managed to combine all these parameters to give us a glimpse of what the movements of 10,000 galaxies within a radius of 350 million years may have been over the last 11.5 billion years- light around the Milky Way. Captivating…
In our Universe, nothing is forever. Nothing is static either. The comets come and go. The Earth revolves around the Sun. The stars are moving in the Milky Way. And even the galaxies have trouble keeping up. From movements which often exceed the time scales to which our modest human lives have accustomed us.
What we are offering today researchers from the University of Hawaii (United States), the University of Maryland (United States) and the University of Paris-Saclay, is to trace the movements of 10,000 galaxies and cluster of galaxies. To discover the history of the formation of these structures by unraveling the threads of gravitational interactions that have shaped them over the last 11.5 billion years.
The astronomers calculated the trajectories of the galaxies according to their brightness, their current position and movement. All based on what researchers know about expansion rate of our universe. Of the speed at which distant galaxies move away from each other. And taking into account that over time, the gravity exerts its influence to form filaments, walls or clusters on the one hand and emptying certain regions on the other hand.
The movements of galaxies, from past to future
With the passing millions of years, the movement of the galaxies moves away from that which it would be under the sole influence of the expansion of the Universe. In the densest regions, orbits get complicated. Collisions may even occur. And the researchers, precisely, put forward several of them.
So the one they call ” the great attractor»the core of the supercluster of Laniakea. It is a supercluster which contains that of Virgo, of which the Milky Way . The simulation shows galaxies heading towards an area in the middle of a cluster of four clusters. “For more than 30 years, astronomers have considered this ‘great attractor’ to be the main source of gravity that causes the whole region near us to move with a particularly high speed compared to the uniform cosmic expansion, but nature from this source has remained obscurecomments Brent Tully, astronomer, in a press release from the university of hawaii. Our orbit reconstructions have provided the first good insight into this enigmatic region.”
The other advantage of the work carried out by the researchers is that it allows us to project ourselves into the future. To confirm that with expansion dominating motion, most galaxies are moving away from each other. However, collisions will continue to occur. Even if at the large scales of this simulation, only a few mergers major ones may appear in the next 10 billion years. All in very dense areas.
In video: maps of the universe in motion
An international research team, involving in France the Institute of physicalLyon nuclear facility and the CEA-Irfu 2, has just established a dynamic cartography of the nearby universe. These new maps of the cosmos are available as a movie showing the velocities associated with galaxies in the environment of the Milky Way. The maps drawn confirm the standard cosmological model.
CNRS article published on 06/28/2013
Our planet is located in a spiral arm on the outskirts of a large galaxy: the Milky Way. Our galaxy is itself part of a supercluster of 100,000 galaxies . At this scale, the universe looks like a moussesoap bubbles: very large voids are connected by filaments and superclusters of galaxies.
An international team, involving the Institute of Nuclear Physics of Lyon (Claude-Bernard Lyon 1 University, CNRS), the CEA-Irfu, the Institute of Astronomy of the University of Hawaii and the Racah Institute of Physics of the University of Jerusalem, has just published results allowing to describe more precisely the movements of the structure of our local universe.
This video shows velocity maps of the galaxies around the Milky Way and their motions. Such maps can be compared to predictions from simulations of the observable universe based on the model of standard cosmology with dark matter and dark energy. © HeleneCourtois, YouTube
Tools for studying dark matter and energy
Results of the scientific project Cosmic Flows(cosmic fluxes), the work of the researchers aims to disseminate to the entire scientific community the dynamic cartography of the near universe, thanks to sophisticated visualization tools. The area covered extends up to 300 millionlight years . For the first time, a film accompanying this publication presents maps that incorporate the movements of large galaxy structures. As the study of tectonic plates makes it possible to go back to the properties of the depths of the Earth, the overall movements of the galaxies make it possible to study and map the dominant components of the universe:dark energyand the black matter . The film thus reveals maps of the distribution of visible matter, the galaxies, directly compared to maps of the black matter invisible (a mysterious matter which would constitute more than 80% of the matter of our universe, and which would make it possible to explain in particular the movements of the galaxies).
Accurately map in 3D the total matter (dark and light) in such a large volumeis a first. The correspondence between dark matter sinks and the position of galaxies is clearly identified, providing direct confirmation of the standard model of the cosmology. By means of zooms and successive displacements of the point of view, this film makes it possible to follow the structures and their movements in three dimensions and on different scales. Thus, the scientific community now has a better representation of the universe around us: a valuable tool for future research.
Interested in what you just read?