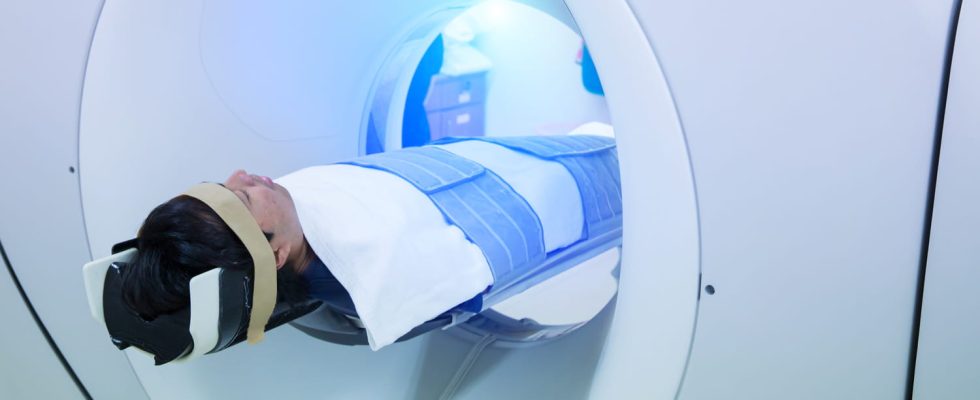
A PET-Scan (or PET scan) is a medical imaging examination mainly used in the diagnosis and monitoring of cancers, but also in neurology or cardiology.
The PET-Scan (or PET scan in French for Position Emission Tomography) is an imaging test to study the metabolic activity of tissues. This is an essential examination in oncologyto refine a diagnosis and monitor progress of the disease. It can also be recommended in cardiology to see the heart and in neurology for examine the brain. What does it allow see ? How does it go a PET scan? Explanations with Dr Franck Lacoeuille, head of the nuclear medicine and biophysics department of the CHU d’Angers.
PET scan or PET scan?
It’s the same thing. PET scan is the English name given this exam for Position Emission Tomography. PET scan is the French term which characterizes the Position Emission Tomography.
What is the definition of a PET-Scan?
THE PET scan is a medical imaging examination based on the injection of a tracer (For example [18F]-FDG, choline (prostate cancer), iodine (thyroid cancer), L-Dopa (neurological cancers) weakly radioactive in the body. One hour after the injection, the patient is installed in a machine which looks like a x-ray scanner with a large ring. Different detectors placed inside this device then pick up the radiation emitted by the tracer in the body and display it on a screen.
What do you see on a PET-Scan?
The tracer injected intravenously into the patient makes it possible to detect in the body the binding sites of this tracer in the form of luminous points. In oncology, the PET scan can detect the presence of tumor cells (tumors) and metastases.
How long does a PET-Scan take?
It takes approximately 2h30 between arrival for the exam and departure.
Do you have to be fasting to do a PET-Scan?
This examination requires you to be on an empty stomach and not to smoke. 5 to 6 hours before the exam. Only drinking water is allowed.
Why do a PET-Scan?
“The PET scan is recommended in the diagnosis and monitoring of tumoral, infectious or inflammatory pathologies”, explains Dr. Franck Lacoeuille.
► The PET-Scan is mainly used in oncology : the concentration of the tracer in certain zones indeed reveals the presence, the activity and the extent of the cancerous tumours. It can also be done repeatedly to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment or to look for possible metastases invisible on an image obtained by another imaging technique.
► This exam is also used in cardiology to analyze blood flow in the coronary arteries or heart chambersand visualize the extent of lesions after myocardial infarction.
► In neurology, it makes it possible to evaluate cerebral functions in certain neurodegenerative pathologies such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease. Finally, it can detect certain abnormalities inaccessible to other imaging techniques.
Is there a risk of false negatives?
Yes, the PET-Scan can give false negatives, in other words, it does not always detect existing tumours. And this for many reasons :
- Some tumors do not fix the isotope and therefore go unnoticed on imaging. .
- The isotope does not reach certain parts of the body and the tumor cannot be visualized.
- Very small tumors (less than approximately 5-10 mm) are undetectable because their mass is less than the minimum size of the elements that can be viewed on the image.
Conversely, the PET-Scan can also give false positives and detect a tumor where there is none.
First of all, the patient must be fasting for at least 6 hours. “When he arrives in the service, check your blood sugar and if this is correct he is injected with the tracer. The patient is then left to rest for an hour, the time that the drug is distributed in the organism and is taken up by the cells which consume the sugar. After this time, it passes under the camera for about ten minutes“, says the specialist.
What side effects after a PET-Scan?
“PET scan has no side effects since the quantities of drug that are injected are really very small. There are no allergic reactions or nausea or vomiting“, reassures Dr. Franck Lacoeuille.
Does the PET-Scan tire?
“There is no fatigue or drowsiness effect, you can drive afterwards. The only downside is the exam time that goes spread over two hours in total and then the time under the camera during which you won’t have to move. However, these are devices that look like scanners so it’s not at all oppressive like an MRI can be“continues the specialist.
What is the price of a PET-Scan? Is it reimbursed?
The PET scan is an exam fully paid for by Social Securityso there is no cost to the patient.
Thanks to Dr Franck Lacoeuille, head of the nuclear medicine and biophysics department of the CHU d’Angers.