Peeling skin on the hands, face, back… Why is it ragged? Update on the causes and solutions to peeling skin with Dr Jean-Luc Rigon, dermatologist-venerologist in Nancy.
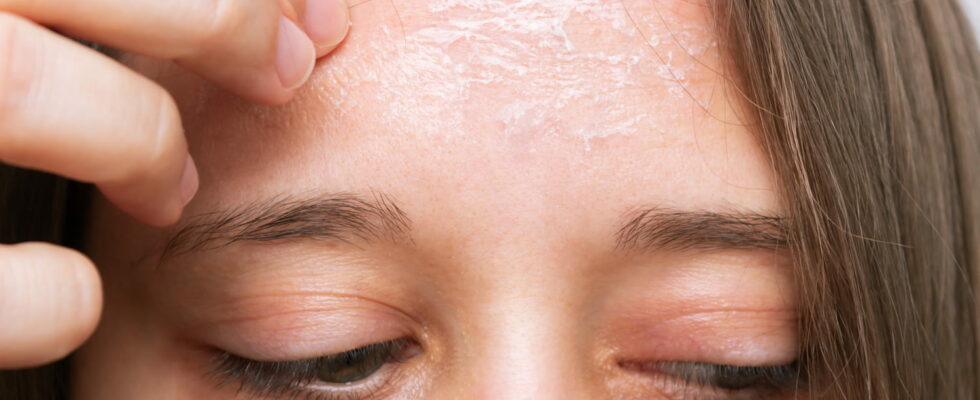
There peeling skin, or flaking, corresponds to the loss of the superficial layers of the epidermis. The skin comes off in the form of small shreds. This is a natural regeneration process of the epidermis whether on the face, neck, hands or any part of the body. Explanations and advice from Dr Jean-Luc Rigon, dermatologist-venerologist in Nancy.
Definition: why does the skin peel?
There peeling skinOr desquamationEast a frequent phenomenon, with multiple causes. This is a detachment of the upper layer of the epidermis, which occurs when cells regenerate. Dead skin comes off in pieces similar to more or less large dandruff. “It is a way for the skin to heal after having suffered external aggression (overexposure to the sun, very often) or internal aggression (medicinal poisoning, for example). Peeling skin is a good sign!“, explains Dr. Jean-Luc Rigon, dermatologist-venerologist in Nancy. Desquamation can occur in patches on more or less extensive surfaces depending on its cause.
What are the causes of peeling skin?
► Very often, the skin peels following a chemical burnthermal or due to light rays, the most classic cause of which is sunburn. In this case, the peeling affects the part of the skin that has burned. The phenomenon is irreversible: the parts of the skin that begin to peel off will eventually come off.
► An unsuitable toilet can cause peeling skin. “Taking showers that are too long or too hotapplying stripping soaps, rubbing too vigorously (it’s better to dab to dry yourself!), all of this can attack the skin and cause it to peel“, says Dr. Rigon.
► An allergy to a substance applied to the skin, contained in a beauty product or a perfume, is sometimes involved. But in this case there is usually a strong itch.
► Skin damaged by the cold, Winter in particular, can peel, as well as dehydrated skin, or even when it has just undergone a tattoo.
► Rarer, drug poisoning (e.g. anti-inflammatories or antibiotics) can cause the skin to peel.
► Finally, dermatological diseases such as psoriasisa local infection of the skin by a fungus or other germ can cause desquamation.
Peeling skin due to dermatitis or seborrheic eczema
The skin may peel due to seborrheic dermatitis, a common condition in adults, which causes red patches and flaking, in oily areas of the face (namely the wings of the nose, between the eyebrows, the scalp, the folds of the ears…). Seborrheic dermatitis can go unnoticed. “Most patients come to us thinking they have peeling and dry skin.“, explains Jean-Luc Rigon. Moreover, “it is not always easy to distinguish a significant seborrheic dermatitis from a small psoriasis“, he adds.
What are the symptoms of peeling skin?
Desquamation appears as loss of clumps of skin called scales. When the skin peels off the scalp, this leads to dandruff, which are neither more nor less than scales attached to the scalp by the hair. Desquamation can affect more or less extensive areas of the skin.
Location: peeling skin on the face, hands, back…
All parts of the body can be affected, depending on the attacked zone. We frequently find scales on the hands, on the back, on the feet, on the face. Desquamation can also reach the scalp: it is then at the origin of dandruff and is linked to the renewal of the tissue. “This is a normal process; simply, the hair retains these skins“, underlines Dr. Jean-Luc Rigon. Factors such as stress and fatigue, too aggressive shampoos, an allergy to hairdressing products (dyes, permanents) or too hot drying can reinforce this phenomenon.
People at risk: what about babies with peeling skin?
“Anyone can have peeling skin, but those who have naturally dry skin (elderly people, eczematous children are more at risk“, specifies Dr. Rigon. should be worn on infants, whose skin is in prolonged contact with products and diapers. “Specific products must be used to avoid attacking the skin of babies.“.
To treat, but also prevent, desquamation, you have to stay hydrated, it’s the only way to accelerate the healing of the skin : “apply cream twice a day, drink lots of water (we are all 2/3 water)“, advises the dermatologist. After exposure to the sun, it is recommended to apply an after sun milk, which soothes and nourishes the skin. Finally, it is necessary avoid tearing off the flaps of dead skin by pulling on them: these will naturally go away when you take your shower, for example. Likewise, it is not not advisable to exfoliate the skin at the risk of irritating him further. In effect, “it’s necessary prohibit any product that could further attack the epidermis, especially excessively repeated scrubs“, concludes the dermatologist.
Thanks to Dr Jean-Luc Rigon, dermatologist venerologist in Nancy (Meurthe-et-Moselle), for his details.