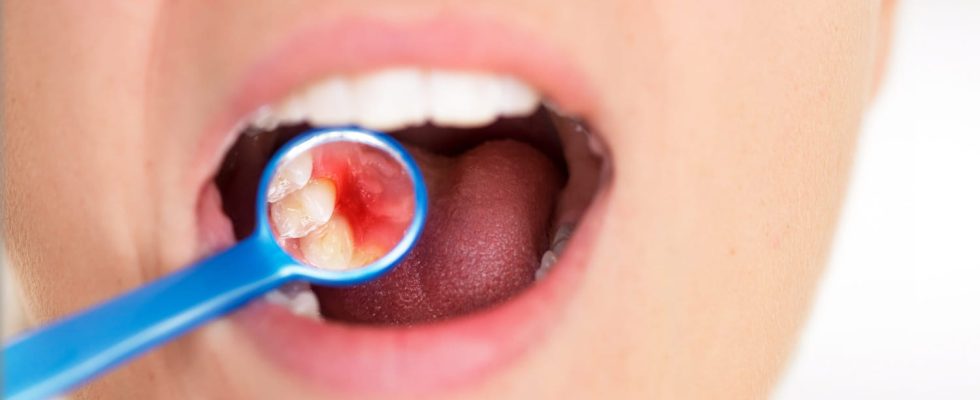
Tongue, lips, gums, palate… 70% of oral cancers are diagnosed too late, which reduces the chances of cure.
Cancer is a disease that causes uncontrolled proliferation of cells and tissues responsible for the appearance of tumors. Tongue, gums, tonsils, palate, inside of the lips… It can affect the mouth or oral cavity, especially in smokers and alcohol drinkers. “The incidence of lip cancer-mouth-pharynx is moreover higher in certain northern departments and of the westwhere consumption alcohol is also higher” underlined the Inca in his Panorama of cancers 2023. Nearly 10,000 of these cancers are detected each year in humans and 4000 for women. L’middle age cancers of the oral cavity is 62 years old.
What is oral cancer?
Oral cancer is a condition that affects the oral mucous membranes, it can be:
- tongue cancer
- gum cancer
- hard palate cancer
- cancer of the floor of the mouth
- tonsil cancer
- of cancer of the inner surfaces of the days and lips
“90 to 95% of oral cancers are squamous cell carcinomas which develop in the epithelium or lining tissues of the mucous membranes. The tumor grows in place and in depth” specifies Dr Philippe Gorphe, ENT surgeon at the Gustave Roussy Institute. first distant invasion of this type of cancer is the neck with lymph node involvementarea.
What are the causes of oral cancer?
The main cause is exposure of mucous membranes to tobacco and alcohol. “A third of cases are linked to smoking, a third of cases to alcohol consumption and the last third of cases are not linked to risk factors“, explains the ENT surgeon. The combination of tobacco and alcohol potentiates the risks of oral cancer. Men are the most affected by these cancers but the incidence increases in women due to their consumption of tobacco and alcohol .
“The symptoms of oral cavity cancers can vary depending on the location. answers straight away Dr Philippe Gorphe. A lymph node in the neck, voice abnormalities, pain when swallowing… Everything unusual sign persisting for more than 10/15 days should lead you to consult a GP or dental surgeon.
What are the different stages of oral cancer?
Four stages are defined for oral cavity cancers:
- stage 1 designates a tumor less than or equal to 2 cm in large diameter,
- stage 2 a tumor larger than 2 cm and less than or equal to 4 cm,
- stage 3 a tumor larger than 4 cm,
- stage 4 (T4) a tumor invading adjacent structures.
The diagnosis of oral cancers is made with a clinical examination and a biopsy, most often performed under endoscopy to look for other possible tumors of the upper aerodigestive tract (AVDS). When the biopsy confirms cancer, an imaging assessment (CT scan and MRI) is carried out to assess the extent of the disease. Rapid detection and early therapeutic treatment can improve the prognosis.
“In 90 to 95% of cases of oral cancer, the disease remains localized and accessible to curative treatment”
What is the life expectancy with oral cancer?
“The 5-year survival rate for oral cavity cancers at all stages is 50%. But the rate depends on the stage of the disease and we must not forget that we are mainly talking about smoking patients, who may have other tobacco-related diseases and are of a certain age, informs Dr Philippe Gorphe. 5-year survival from oral cavity cancer stage 1 is 70%5-year survival from cancer stage 4 by 25%“. The location of the cancer also influences survival:
- the net 5-year survival of people with lip cancer is 88%
- the 5-year net survival for head and neck cancers (which include the oral cavity, tongue, oropharynx, nasopharynx and hypopharynx does not exceed 40%.
The treatment of cancers of the oral cavity is very often based on surgery followed by radiotherapy. When the surgery is extensive, reconstructive surgery may be performed afterwards. Chemotherapy can be associated with radiotherapy when the analysis of the tumor (biopsy) has shown serious factors. “In 90 to 95% of cases of oral cancer, the disease remains localized and accessible to curative treatment” informs Dr. Philippe Gorphe.
Thanks to Dr Philippe Gorphe, ENT surgeon at the Gustave Roussy Institute.
- National estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in mainland France between 1990 and 2018, INCA, 2019
- Cancers in France in 2018 – Essential facts and figures (2019 edition), INCA