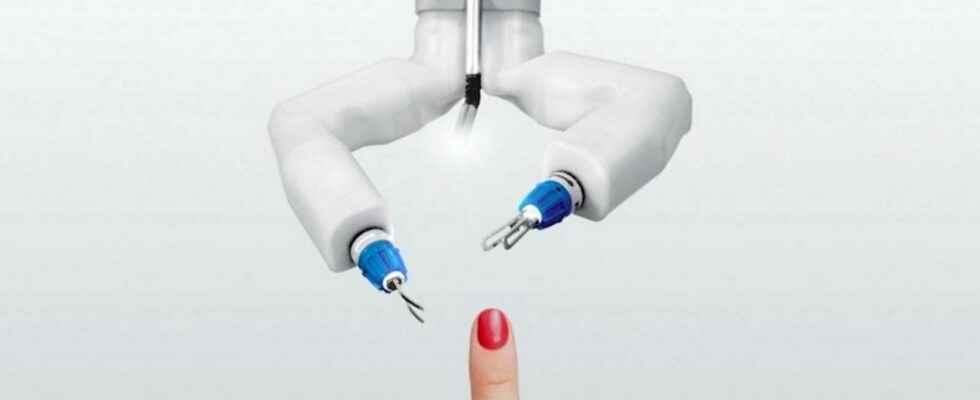
In order to develop robotic surgery in space, NASA will send the Mira robot for experiments aboard the International Space Station. The device, which has performed operations on Earth before, has two arms with a surgical tool at each end.
You will also be interested
[EN VIDÉO] Can a medical robot operate on the spine? The robot surgeon Rosa has already been accompanying neurosurgeons for several years for brain operations. It has been adapted to another medical field: back surgery, in particular that of the spine.
One of the difficulties facing the astronauts, and which will become a major problem in the future during long space voyages, for example to Mars, is access to healthcare. For this reason, the Nasa account send a robot surgeon aboard the international space station (ISS).
Virtual Incision, a start-up from the University of Nebraska at Lincoln, has just been awarded a budget of $100,000 to prepare its Mira robot for a stay in space. The firm has been working on this robot for almost 20 years. Mira is made up of two articulated arms each with a small clamp at the end, and surgeons have already used it for a colectomy.
Discover the Mira robot surgeon in this presentation video. © Virtual Incision
Launch planned for 2024
However, the robot will not operate on the astronauts. He will have to cut rubber bands and move rings with movements reproducing those used in surgery. The purpose of this project is to be able to test the device without the gravity earthly. ” We expect that the robot behaves differently in spacesaid Shane Farritor, co-founder of Virtual Incision. Any force or play in the joints will lead to inaccuracy in weightlessness “.
Researchers will need to ensure that the robot is sufficiently solid to survive the launch. They will also have to program the robot to carry out the tests autonomously in order to limit the use of the bandwidth of the ISS as well as the time the astronauts will have to pass over it. They will normally only need to turn it on, then turn it off two hours later.
Nasa plans to send the robot to the ISS in 2024. This is a long-term project, since Shane Farritor does not expect it to be able to perform autonomous operations for 50 or more years. 100 years.
Rheem, a robocop in Dubai This is Rheem, a rolling humanoid developed by Pal Robotics. Rheem — 1.70 meters tall for 100 kilos of electronics, mechanical and plastic parts — was the first robot hired in the police! It was in Dubai in May 2017. So, admittedly, he does not quite have the profile of Robocop and he is more likely to do local policing by helping and informing, initially, tourists in the shopping centers. © Pal Robotics
Roméo, a robot that listens and helps the elderly This is Romeo, another member of Pepper’s family. From the height of its 1.40 meters, the humanoid robot is developed with a view to helping the elderly or those with loss of autonomy. © Softbank Robotics
Motobot, soon to be a motorcycle champion Presented in 2015, Motobot returned in 2017 in a more optimized version, without support wheels for turns and capable of reaching 228 km/h. Yamaha’s humanoid robot hasn’t (yet) managed to beat Grand Prix world champion Valentino Rossi against whom it measured (1’57.504 against 1’25.740) but that’s only a question of time. ©Yamaha
Pepper, a humanoid that sells well At 1.20 meters tall, Pepper is a very popular robot. Designed in 2012, it is now mass-produced and sold worldwide. The humanoid is very available and well mannered, always prompt, as far as possible, to answer your questions. In the years to come, Pepper will have brothers and sisters, no doubt equally kind, who can do a little housework and walk around on their legs. © Softbank Robotics
Valkyrie, future space explorer The R5 or Valkyrie robot was designed by engineers at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. He is 1.88 meters tall and weighs around 140 kilograms. Initially developed to respond to disasters, R5 could become the first humanoid robot to explore the Solar System and beyond. © Nasa, Bill Stafford, James Blair, Regan Geeseman
Murata Boy and Girl Thanks to gyroscopic sensors, Murata Boy and Girl can perform some pretty incredible balance tricks. While Murata Boy rides a bicycle, Murata Girl can ride on curved paths (even on a 2 centimeter wide beam). When they encounter a person, their ultrasonic sensors alert them. They then automatically go to sleep. © Murata
Qrio “Quest for cuRIOsity”, Quest for cuRIOsity in French, this robot is a prototype developed between 2003 and January 2006 by Sony. This small robot, 58 centimeters tall, is capable of voice and facial recognition. He can carry on a conversation as long as you speak English or Japanese. He can sing too! It locates objects in space using its stereoscopic vision. He climbs stairs, walks on difficult floors (inclined or cluttered) © Sony
Asimo Asimo is a humanoid robot developed by Honda. Its name means “Advanced Step in Innovative MObility”. We pronounce “ashimo” (which is reminiscent of Asimov) which in Japanese means “legs too”. This robot is not intended for marketing since it is a search robot but large companies like IBM have monopolized it to make it a host. Asimo may, in the future, help elderly people or carry out tasks that are dangerous for human beings. © Wikipedia, GNU Free Documentation License
Albert Hubo Direct competitor of Asimo or Qrio, Hubo is less advanced than these last two but it has the big advantage of having cost only one million dollars of investment against 300 for the development of Asimo. Albert Hubo is an improved version of Hubo (with Albert Einstein’s mask). Thirty-one servo motors allow him to express different emotions. © Wikipedia, GNU Free Documentation License
wakamaru This small yellow humanoid robot measures 1 meter in height and 30 centimeters in width. The robot recognizes its owner’s face and voice. Equipped with a mobile phone, he can call in case of emergency (if his master has an accident for example). He obeys his master’s daily schedule. © Wikipedia, GNU Free Documentation License
Nao Nao is 100% French. Its use is not yet defined. It could be used in the future as a companion robot, this playmate looks strangely like Aibo but more human. And for good reason, it replaced it in 2007, as the standard RoboCup platform. © DR
Robovie-R Robovie (version 3) is a small humanoid robot made to help people with disabilities or the elderly. It is indeed a commercialized model but watch out for your wallet. At the moment, it costs 41 million dollars. © Vstone
Interested in what you just read?