Need to configure boot options or Windows services? Learn how to do it quickly with the MSConfig system tool. An old utility, but still present in Windows 10 and 11… and still just as effective!
Introduced in 2001 with the XP version, MSConfig – by its full name, System Configuration – is a Microsoft tool still present in Windows 10 and 11. Although it has lost some functions over time, it remains extremely valuable because it has many options related to Windows startup and services. It can be used, for example, to manage the system to be launched when the PC is started or to deactivate certain services in the event of a problem. Its handling is relatively simple, as long as you know its operating principle. And we know where to find it!
Like other Windows system tools, MSConfig is somewhat hidden. It can be found by browsing the list of installed applications in the menu To start upin the file Windows administrative toolsunder the name of System Configuration. But the easiest way is still to launch it via a command in the window Execute.
- Simultaneously press the keys Windows+R to access the window Execute.
- Come in msconfig in the field Open, then click OK.
On Windows 10 and 11, you can also use the taskbar search engine.
- Open the search field then enter msconfig.
- Click on System Configuration at the top of the result window.
The MSConfig window has several tabs – five for Windows 10 and 11, and four in previous versions – each devoted to particular functions, detailed below. Depending on your needs, you will therefore have to refer to a specific tab.
Of course, you should do your homework before making any changes in MSConfig because, as with all system tools, some settings can cause problems if they are not correct. Be careful, then…
Select Windows Boot Modes with MSConfig
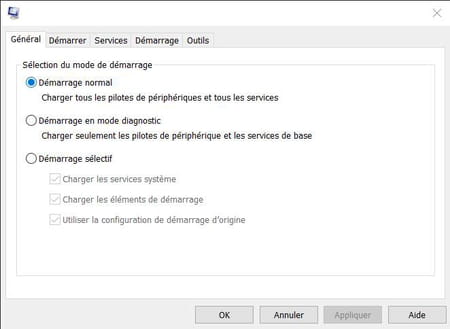
The General tab lets you choose how Windows starts. Three options are available:
- Normal start: automatically checked, this is the default Windows boot mode with all services and device drivers enabled.
- Starting in diagnostic mode: this mode corresponds to starting in “safe mode” of Windows. Only essential services and device drivers are enabled. This option is useful if you need to diagnose and fix a problem on your PC or if you need to remove software or a file that you cannot uninstall or delete in normal mode.
- Selective start: This option allows you to start Windows by selecting the system services and programs to activate. It is in this mode that you can make your choice and fine-tune the behavior of Windows at startup. If you use it, the PC will automatically start in this mode every time – it will be the default mode. It will be necessary to return to normal mode to start with all the services activated or to choose the diagnosis.
- To change the boot mode, check the corresponding button, then click the button Apply.
Set Windows Boot Options with MSConfig
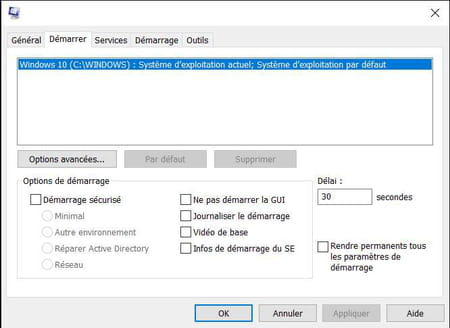
The Start tab allows you to manage everything related to Windows startup, and in particular the menus that the system offers when starting the PC. This is where you can manage choosing a system to boot to, if you have more than one, or options related to safe mode. Several possibilities are available in the section Boot Options but, again, you have to know what you are doing…
- Secure Boot: starts Windows in one of four available modes:
- Minimal: opens Windows in safe safe mode, without network support.
- Other environment: opens secure Windows command prompt and critical services.
- Repair Active Directory: opens Windows in safe safe mode, with support for critical services and Active Directory.
- Network : opens Windows in safe safe mode with networking.
- Don’t start the GUI: launch Windows without GUI
- Log startup: logs boot process info to the Ntbtlog.txt file.
- Basic video: loads the system with a basic, standard VGA driver instead of that of the PC’s graphics card.
- OS boot info: displays the names of the drivers loaded during startup.
- The button Advanced options opens another window allowing in particular to limit the number of processors or the maximum memory used by Windows.
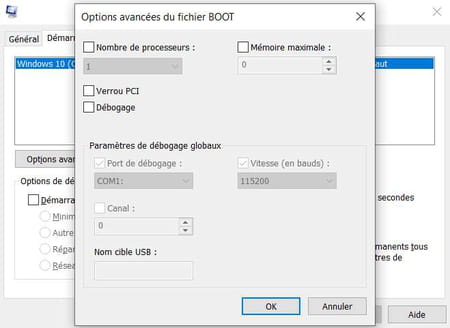
- Click on the button Apply to confirm and apply your settings in this tab.
Managing Windows Services with MSConfig
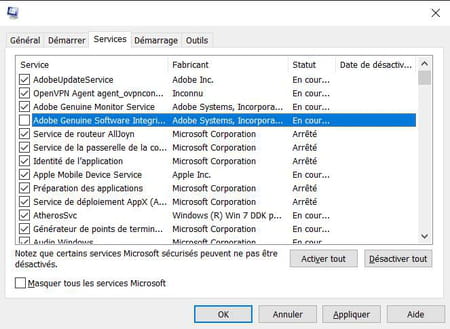
The Services tab is particularly useful because it displays all the services launched when Windows starts, or which are regularly run by the system. Each line gives the name of the service, its origin (curiously called “manufacturer”…), its status (stopped or running), and its deactivation date if applicable.
- To deactivate a service, simply uncheck the box to the left of its name, then click the button Apply. To enable it, check the box. Keep in mind, however, that disabling certain services may cause various malfunctions.
- If you check the box Hide all Microsoft services at the bottom of the window, instances of Windows services and Microsoft software (such as Windows Defender) will no longer be displayed. This allows you to see only the services of third-party programs, which can help identify the possible presence of malware.
- Note that if you disable one or more services, then you automatically switch to selective startup in the General tab.
Manage programs that run at startup with MSConfig
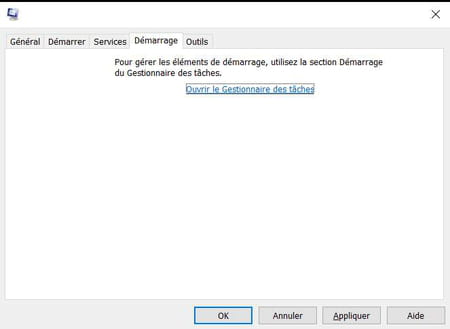
The French name of this tab is misleading, because it actually deals with programs that launch at Windows startup, and not system startup. Up to Windows 7, this tab displays the list of programs launched at the opening of the Windows session and allows them to be deactivated in one click. It is still present in Windows 10 and Windows 8, but it refers to Task Manager. It is now to this tool that you will have to turn to manage the programs launched at Windows startup.
Access System Tools with MSConfig
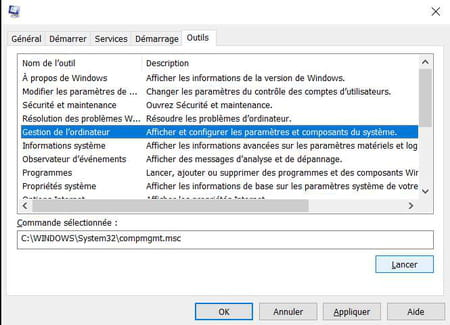
The Tools tab only exists in Windows 10 and 11, so you won’t find it in previous versions of the system. Contrary to what its name suggests, it does not include any tools. It simply allows you to launch various Windows system tools such as Command Prompt, Performance Monitor, Resource Monitor, Internet Options or Task Manager, which avoids having to look for them elsewhere – it is the only interest of this tab. To open a tool, select it in the list, then click the button Throw.
