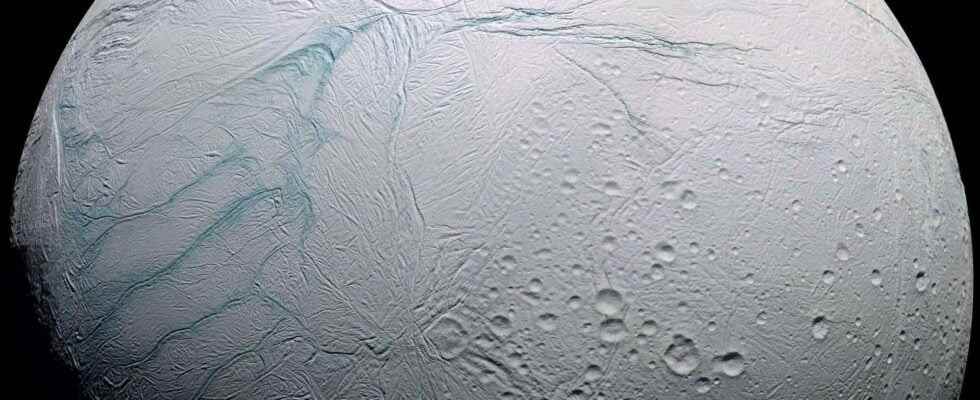
The search for life today is focused on the moons of the giant planets Saturn and Jupiter, which are known to harbor subterranean oceans. During his press conference at the beginning of the year, Josef Aschbacher, the director general of the European Space Agency recalled his plan to send a probe to Enceladus in order to bring back to Earth samples from this moon which it is assumed that it could harbor a form of life in its underground ocean. An excellent initiative.
You will also be interested
[EN VIDÉO] Neptune, such a mysterious blue planet It is blue like the Earth but it is not because of the water. It is giant, they very far, installed just before the Kuiper belt, another world. Let’s discover Neptune, visited only once, by Voyage-2, in 1989, and which we know so little about. We just know that in his heart, perhaps, it is raining diamonds…
Since the Galileo and Cassini probes showed that Mars might not be the only body in the Solar system to have been able to harbor extraterrestrial life, the search for a form of life focuses beyond the habitable zone of our star.
It has long been speculated that Mars may be home to a primitive form of life. But, today, it is difficult to imagine any of them on the surface of this planet due to the very oxidizing soil and the radiation UV jointly which is not strongly attenuated by one ozone layer — exerting a protective effect on Earth — so that all molecules organisms would be rapidly destroyed.
But if, today, life on the surface is not possible, it may not have been the case throughout the history of the planet. Scientists are convinced that 4 to 3.5 billion years ago, Mars could harbor ecosystems analogous to those of theArchean earthly. The existence of life forms, at least very simple on Mars, during the 4.5 billion years of its history, is therefore a conceivable principle according to many researchers.
But if life on the surface is impossible, scientists assume that its deep subsoil, below five kilometers, could host endogenous life similar to that of the Earth’s subsoil. However, so far, if thehabitability of Mars proven, no evidence of extinct or active life on Mars has been found. While waiting to be able to sink that deep, scientists are more busy discovering the remains of an extinct primitive life form, which could take the form of fossils or induced effects on the environment, rather than detecting an active life form.
To discover a form of life in the Solar System, scientists are now aware that they must look for it far beyond the habitable zone from Sun, and venture to the giant planets Jupiter and Saturn. Some of moons The ice caps of these two planets are known to harbor liquid oceans located several kilometers below their surface. These oceans, warmed by the heat dissipation of the effects of tide, would sustainably combine the three intrinsic and necessary factors for the appearance of life that are water in the form liquid, a chemistry organic and a source of heat. The idea of finding live shrimp at the bottom of this underground ocean isn’t as far-fetched as it sounds.
Is the ocean of Enceladus, presumably habitable, inhabited?
It is therefore in this context that Josef Aschbacher, the Director General of the European Space Agency, again mentioned, during his back-to-school conference, the European project to send a probe aroundEnceladus and one lander who would land there to bring back samples of its surface to Earth. He recalled that the icy moons of Jupiter and Saturn are the ” best places in the solar system to search for a primitive form of life “. He made a point of specifying that, if there is a form of primitive life under the surface of these moons, it could be located in the underground oceans which they shelter, or even in the layer of ice which covers them.
A precision that is important because the underground ocean of Enceladus is located several kilometers below the surface. And the idea of drilling to this depth is technically impossible today. It is assumed that faults frequently form on the surface of Enceladus and are filled in by water from the depths. The idea would be to drill into these faults hoping that primitive organisms will have been trapped in this water that is instantly frozen on contact with the surface.
The best places in the solar system to look for a primitive form of life
The choice of Enceladus as a target for a sample return mission is explained by the latest scientific advances in knowledge of this moon. Since the Cassini mission of the Nasa, the presence of methane,hydrogen molecular and organic molecules, which can allow the synthesis ofamino acids, of the basics of life, was known. Added to this is that, recently, we know that the Enceladus “geysers” expel water ice particles containing organic molecules, salt, silica and dihydrogen, attesting to hydrothermal reactions. Finally, despite this array of strong clues, we do not know whether life could have emerged in the ocean of Enceladus or that of Europe.
For the moment, this mission is not officially approved by the member states of theESA let alone funded. That said, it is nevertheless an excellent initiative on the part of the European Space Agency. As Josef Aschbacher points out, the ” The search for an extraterrestrial life form is a very fundamental question that would impact not only science but also human psychology, philosophy and religion. “.
This mission, scheduled to last three or four decades, from its development to its return to Earth, is a ” opportunity to encourage the younger generation to take an even greater interest in space “. We therefore hope that ESA delegations and Member States will follow and take into account the following observation: ” dreaming, meeting challenges and answering big questions pays off much more in the long term than the cost of the missions that allow this, would like to highlight Patrick Michel. If only because it helps to inspire younger generations who have important challenges ahead of them, including for our survival. “.
As a reminder, the European community interested in sample returns fought for seven years in vain to pass a mission to return a sample ofasteroid between 2007 and 2014 with the MarcoPolo and MarcoPolo-R projects in ESA’s Cosmic Vision program.
Unprecedented technological and scientific ambitions
The idea that ESA is embarking on an even more ambitious return of samples (than the two abandoned MarcoPolo missions) can therefore only delight this community, including Patrick Michel, CNRS research director at the Côte d’Observatory. ‘Azur and principal investigator and co-investigator of numerous international missions to asteroids.
The first ambition is scientific because “ a return of samples from an icy moon will make it possible to answer a number of completely incredible fundamental questions, in particular in connection with theexobiology, life, its origin and its presence in theUniverse “. The second is technological vsar finally, we are talking again about innovation and taking risks, because it will be necessary to succeed in a mission whose scientific return is certain !
At a time when there is a tendency to separate innovation from scientific knowledge when the two are intimately linked because the major scientific questions require increasingly complex missions and require the demonstration of new technologies, ” I can only be delighted that ESA understands this by proposing such an ambitious project, both scientifically and technologically “.
The European Space Agency will be able to rely on the legacy of the Huygens mission, which succeeded in landing on titan in 2005, ExoMarch 2022 which will be able to take samples up to 2 meters deep and Martian sample return mission NASA and ESA scheduled for the end of this decade.
No timetable exists but, between the time to develop the technologies necessary for this return trip to Enceladus as well as the instruments and equipment for drilling and preserving the samples, this sample return mission is not possible. before the 2050s.
Interested in what you just read?