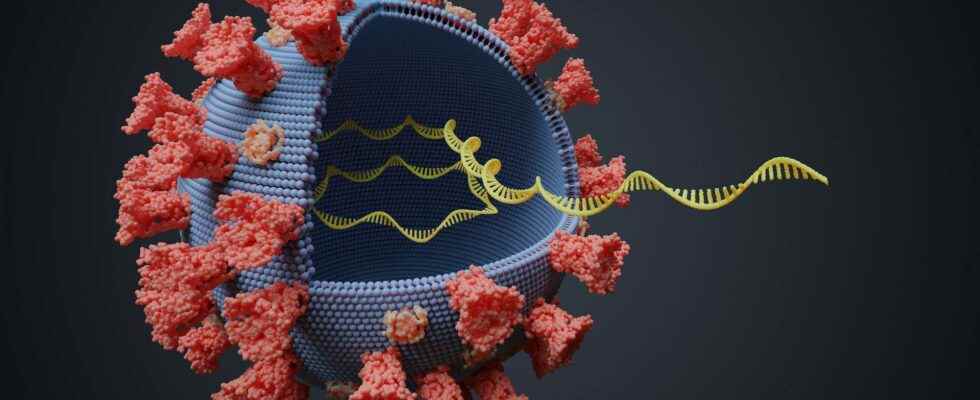
Being part of the family of nucleic acidsL’RNA messenger is a macromolecule responsible for copying and transmitting the information contained in our genome to allow the manufacture of protein. Discovered in 1961 by scientists from the Institut Pasteur, its identification has made it possible to explain the ” genetic regulation of the synthesis of enzymes and viruses (Nobel Prize in Medicine, 1965).
Structure and synthesis of messenger RNA
Chemically, messenger RNA is a polymer of elementary units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of three elements: a sugar (the ribose), a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base such asadeninethe guaninethe cytosine or theuracil. These nucleotides are connected by chemical bonds called phosphodiester bonds. With a linear, single-stranded structure, messenger RNA has three functional regions: the 5′ region (the cap), the 3′ region (the polyA tail) that is not translated and the cistron(s) coding for a protein.
In the cell eukaryotic, messenger RNA is synthesized in the nucleus through various complex steps. Thanks to an enzyme, theRNA polymeraseone or more regions of theDNA coding for a protein is copied. This mechanism called transcription begins with the formation of a pre-messenger RNA. Then, the latter must undergo post-transcriptional modifications (on the 5′ and 3′ regions) and a splicing in order to be stabilized and become a mature messenger RNA transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
Role of messenger RNA in the cell
The messenger RNA carries the arrangement plan of the protein towards the organelles located in the cytoplasm and responsible for their production. A complex involving another RNA (thetransfer RNA) and proteins ribosomal associates with messenger RNA to perform code reading. Each sequence of nucleotide triplets (codons) thus recognized will be translated into one of the 20 amino acids existing. The sequence of these amino acids will give rise to a protein necessary for the cell. A transient snapshot of this information, messenger RNA is a labile macromolecule, which rapidly degrades, thereby playing a role in regulating the expression of Genoa by allowing the cell to synthesize proteins as and when needed.
In front of’emergence new viral agents pathogens and the constraints of speed and distribution of effective and appropriate responses, new technologies based on the use of messenger RNA inasmuch as vaccine are currently being developed. Indeed, the injection of a messenger RNA corresponding to the production plan of a protein of the targeted pathogen allows the production ” in situ ” of the’antigen by the cells and solicits a immune response protective.
You will also be interested
Interested in what you just read?