A twin is an association of two or more crystals of the same mineral species, which orient themselves and fit together at the time of their growth following crystallographic rules very strict.
Several closely intertwined crystals
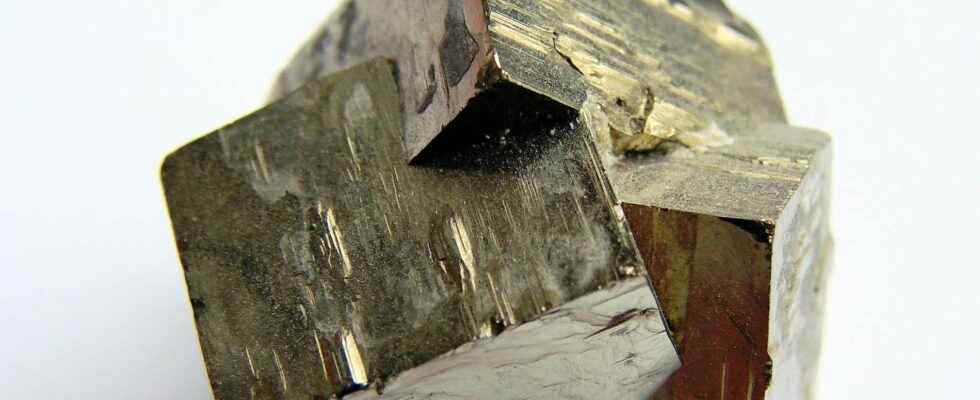
During crystal growthit may happen that a crystal uses part of the crystal lattice from another crystal of the same species. The two or even multiple crystals will thus grow at the same time while sharing a crystal lattice fragment. This twinning operation results in obtaining a single twinned crystal, which comprises several nested individuals according to angles which respect the organization and crystal lattice geometry. Everything is therefore not possible, even if certain mineral species leave many possibilities of orientation, such as pyrite, for which the twin process can give rise to impressive crystals. Others, like the staurolite, will only accept a cross twin.
The feldspars are among the minerals most prone to twins. The Carlsbad twin is characteristic of orthoclase and is defined as a “simple” twin, which includes two individuals. Albite is often characterized by polysynthetic twins, defined by an alternation of several individuals.
A wide variety of twins
More generally, simple twins are defined by the fact that each orientation is occupied by a single individual. Repeated twins are defined, conversely, by the fact that each orientation can be occupied by several individuals. In this case, we can differentiate polysynthetic twins when the different individuals are found side by side, giving a striated appearance to the final crystal, and cyclic twins when the individuals are organized in a circular fashion. This is the case of chrysoberyl for example.
Twins can be classified into three categories, which depend on their origin. Growth twins are thus observed, which form during the crystallization process; transformation twins, which form when a crystal is subjected to a phase transition which alters its symmetry and structure, leaving the possibility of initiating the growth of twinned crystals; or mechanical twins, which form when a strong pressure is applied to a crystal in a given direction.
You will also be interested
Interested in what you just read?