During the summer months, as the temperatures rise, the sun’s rays increase their effect.
A similar situation is valid in Europe, the heat wave from North Africa is effective in Western Europe this weekend.
As we enter the hottest times of summer, experts recommend drinking plenty of fluids, wearing light and light-colored clothes, wearing a hat and using high-level sunscreen.
So, what should we pay attention to in order for sunscreens to be effective and protect our skin? How do sunscreens protect our skin?
WHAT SHOULD WE CONSIDER WHEN BUYING SUN CREAM?
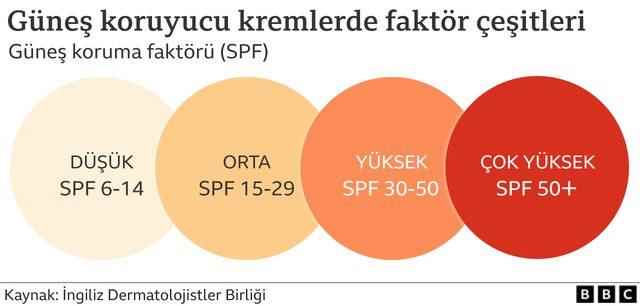
Most of us are familiar with sun protection factor (SPF), it is written in large numbers on the front of the bottle. As the number here grows, it is predicted that the protection will increase.
Many brands add the star number to the bottle in a five-star system; this is actually a data that we need to understand as much as SPF.
SPF tells us how much sunscreen will protect our skin from UVB radiation. The star system shows how much UVA radiation is absorbed by the sunscreen.
WHAT IS UVA AND UVB?
Ultraviolet A and B are used to describe the different wavelengths of radiation that come out of the sun and enter the earth’s atmosphere.
UVA is mostly associated with aging of the skin and cell discoloration that leads to skin cancer of the squamous cell carcinoma type (the second most common skin cancer in the world). UVA can affect the skin even when sunbathing through glass.
UVB is the rays that cause tanning in the sun and cause skin cancer called basal cell carcinoma (the most common type of skin cancer in the world) and harmful melanoma.
Sunscreen doesn’t actually protect us completely from either of these types of radiation; For this reason, for the highest protection, it is the best solution to stay in the shade during the hours when the sunlight is most effective and to protect our skin by covering it.
WHAT DO THE NUMBERS MEAN?
The SPF ratings on sunscreens show how much UVB the cream allows; not how much it blocked.
For example, a 15 factor (15 SPF) sunscreen allows one-fifth of the sun’s light, or about 7 percent, to pass through to your skin. In other words, it blocks about 93 percent of UVB rays. 30 SPF blocks 97 percent of it.
For example, if you can stay under the sun for 10 minutes without burning, SPF will theoretically provide you with 15 times as much protection, so you can stay under the sun for two and a half hours without burning with a factor 15 sunscreen.
The number of stars indicates the percentage of UVA absorbed in proportion to how much UVB is absorbed. The impact rating ranges from one star to five; The five-star cream is the most effective sunscreen.
A sunscreen with a low SPF might have five stars; because the ratio of UVA to UVB protection can be the same as that of a high factor sunscreen.
Ideally, use a sunscreen with both a high SPF and lots of stars.
HOW EFFECTIVE IS THE BEST SUN CREAM?
All these degrees of protection are as effective as written on it if used in ideal conditions.
In reality, most people do not use sunscreen perfectly. When applied while sweaty or out of water and still wet, the cream does not show its full effect. According to experts, the vast majority of users can only apply half of the cream to their skin. This means that half of the cream in the bottle is used.
The British Association of Dermatologists says a factor 30 sunscreen “provides adequate protection in protective clothing and shade.” They also say that regardless of the SPF rating of the sunscreen used, it should be reapplied every two hours.
In the European Union, sunscreens over 50 should be marketed as “50+”; warns that it should not be promoted as a factor of 80 or 100 as it is sold in some countries. These numbers can be misleading. Because 50 SPF provides 98 percent protection, while 100 SPF provides a little less than 100 percent protection.
No product provides 100 percent protection from the sun’s rays.
HOW PROTECTIVE ARE ‘Once A DAY’ SUN CREAM?
There are also many sunscreens on the market that say “once a day is enough”. These products are marketed as being effective for eight hours if used correctly.
However, some dermatologists say that products marketed this way should also be reapplied every two hours; He warns that the cream may be wiped off in some areas and lose its effect if sweating or rubbing it somewhere.
In a report made at the end of a research conducted in 2016, it was revealed that the protection rate of these products decreased to 74 percent after six hours.
