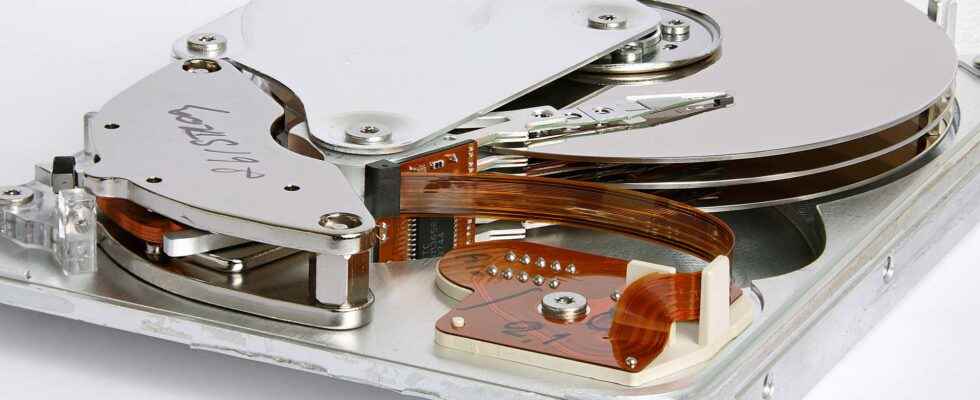
A hard drive is a magnetic medium of digital data storage. The hard drive differs from RAM, the “RAM” of the’computer, whose data is erased when the latter is turned off. Hard disk storage is permanent and has a much higher capacity (up to several terabytes). Hard drives are found in computers, but also in recorders DVD or video game consoles. They can be internal or external.
How a hard drive works
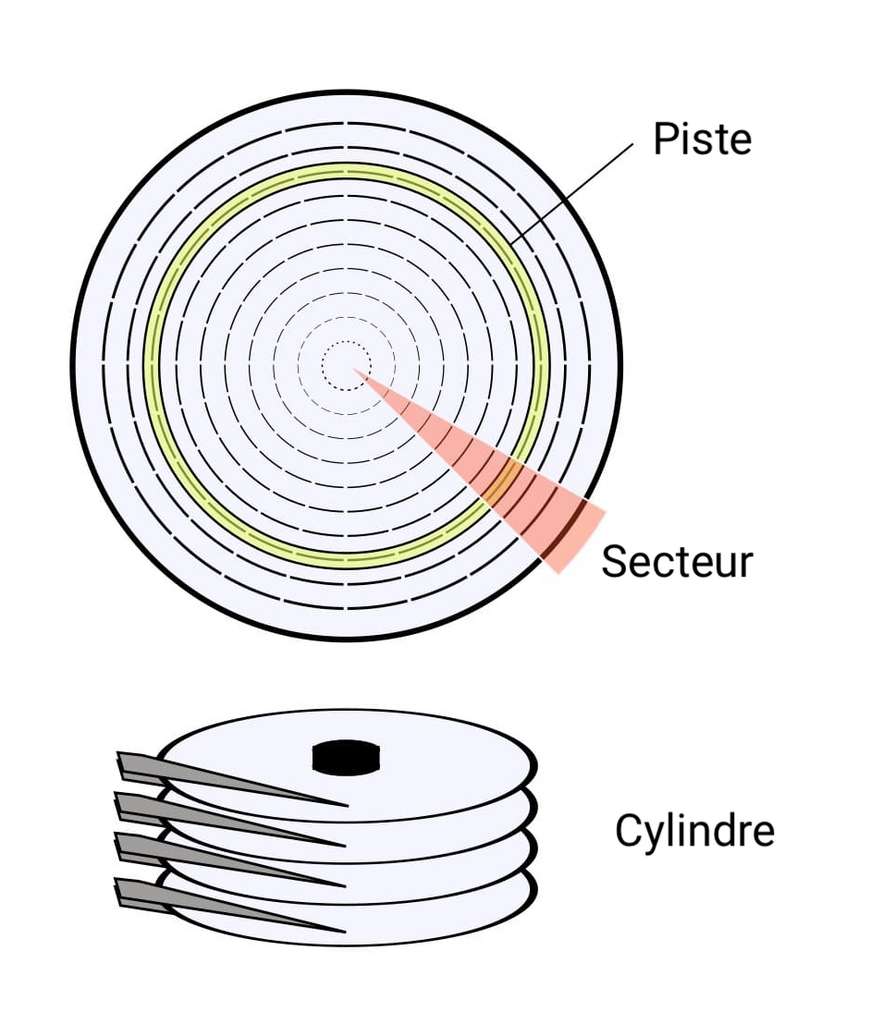
One Hard disk contains several discs in aluminum or glass (called trays) which are covered with a thin layer of material magnetic, on which the data is written digital. Following the Electric power passing through the read head, the data is encoded in the form of bits (1 or 0). The read head begins writing data at the periphery of the disc, then gradually advances towards the center. To read the data, the read head detects the direction of the magnetic field
Characteristics of a hard drive
- The format : expressed in inches, it indicates the size of the magnetic plates. The 2.5 ” format is the most common for internal hard drives while the 3.5 ” format, which is more cumbersome, is intended for desktop computers.
- The access protocol : it concerns the connectors and cables used to route data. Since the 2000s, the SATA (Serial ATA) is the most commonly used.
- The capacity : expressed in bytes, it indicates the amount of data that can be burned to the hard disk.
- The transfer rate (debit): Indicates the amount of data that can be read or written to the disk per unit of time and is expressed in bits per second.
- Rotational speed : expressed in revolutions per minute, it indicates the rotation speed magnetic disks around the central axis. The higher it is, the faster it is to write and read, but the more it consumesenergy and tends to heat the material. The standard is 5,400 rpm for a 2.5 “external hard drive and 7,200 rpm for a 3.5” external hard drive.
- Interface : for the external hard disk, it indicates the transfer intermediary between the hard disk and the computer. Most hard drives work with a USB 2.0 or USB 3.0 interface, but there are also interfaces Firewire or Thunderbolt.
- The file system : it represents the way in which files are stored and retrieved (directories and sub-directories). The best known are FAT32, exFat and NTFS. Note that the system can be changed by formatting the disc on your computer.
Conventional hard drives today tend to be replaced by hard drives SSD, which work as a flash memory and are much faster, more compact and less sensitive to shocks due to the absence of elements mobile.
You will also be interested
Interested in what you just read?
.
fs2