A viral infection which mainly affects babies and children under 5 years old, but not only.
Very contagious, it occurs in small epidemics in spring, summer or early autumn, in temperate climates such as mainland France. It is benign and caused by several types of viruses, usually a coxsackie-type enterovirus.
What is hand, foot and mouth syndrome?
Hand-foot-mouth syndrome (or hand-foot-mouth syndrome) is a childhood infectious disease, most often benigncaused by different types of viruses of the genus enterovirus. We also talk about “vesicular stomatitis with exanthema“. This contagious disease particularly affects children aged 6 months to 4-5 years. He is rarer in adults (the majority of adults are immune). Hand, foot and mouth syndrome usually occurs in small outbreaks, from spring to fall.
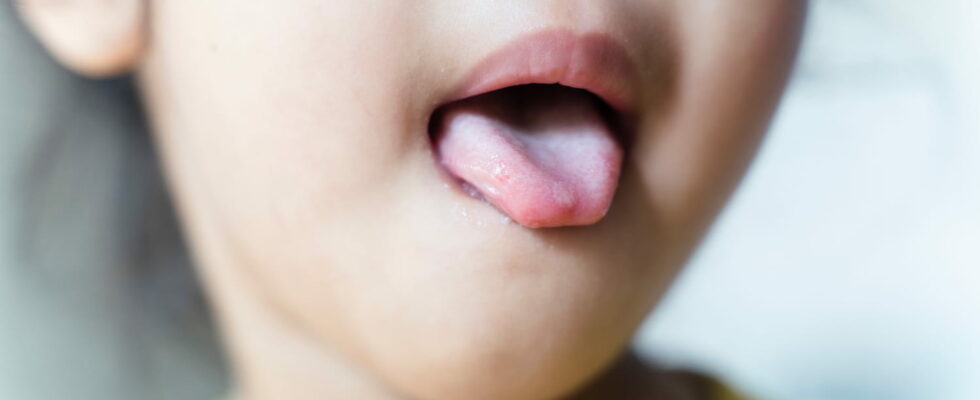
Photo: What do foot-hand-mouth pimples look like?
What is the virus causing foot, hand and mouth?
Hand, foot and mouth syndrome is a viral infection caused by an enterovirus, usually Coxsackie. Enterovirus infections are common and take very varied symptomatic forms.
Transmission: how do you get hand-foot-and-mouth disease?
Transmission of the virus occurs by person-to-person contact (droplets from the nose) or via objects (toy…) Or contaminated food from viruses excreted at the level of nasopharynx or in the stools. Other modes of transmission are also possible: via saliva (droplets in the mouth) and at contact with skin lesionsbut also by maternal-fetal transmission causing neonatal infections. Community settings are particularly conducive to its transmission, this is particularly the case for nurseries, canteens and paddling pools in swimming pools. Once the virus enters the mouth, it passes down the throat and then reaches the digestive tract.
Can an adult get hand-foot-and-mouth disease?
Hand, foot and mouth disease mainly affects children but an adult (most adults are immune) can also get it. by person-to-person contact (droplets from the nose) or via objects Or contaminated food, in stools, via saliva…
What is the incubation period for hand-foot-mouth disease?
L’incubation lasts 3 to 5 daysa period after which different symptoms appear.
How long are we contagious?
Hand, foot and mouth disease is very contagious. The virus persists 1 to 4 weeks in the oropharynx and 1 to 18 weeks in the weeks.
What are the symptoms of foot, hand and mouth?
Foot-hand-and-mouth disease causes lesions, generally less than a hundred, in the mouth, hands and feet.
► First symptoms of foot, hand and mouth
- a slight fever (38.39°C),
- a lack of appetite,
- of the abdominal pain,
- sore throat,
- headaches
- a runny nose
► Symptoms in the mouth
- Pharyngeal erythema, redness of the mouth and throat, like mouth ulcers
- papules around the tongue (small red dots) which turn into fluid-filled blisters. These blisters usually resolve within 4 to 7 days.
► Symptoms in the feet and hands
- rather elongated blisters on the palms of the hands (papulovesiclesthe most typical symptom) and the soles of the feet
- sudden eruption of small, scattered or linear red spots (papules), which may become vesicles and small blisters
- risk of skin superinfection due to scratching (impetigo)
Hand-foot-and-mouth syndrome leaves no after-effects.
How long does foot, hand and mouth last?
The symptoms last about ten days and then the person recovers.
What are the risks of foot, hand and mouth?
Hand-foot-mouth disease is linked to complications such as:
- Dehydration: especially if the oral damage is significant or if the child refuses to drink.
- L’onychomadesis: nails become detached and fall off a few weeks after illness. Then the nails grow back normally. There are no after-effects.
- Of the lung damage (viral pneumonia) or neurological (meningitis, encephalitis) observed in Asia.
What are the risks in case of pregnancy?
If it is a benign illness, hand, foot and mouth syndrome, if contracted during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, can be dangerous. In fact, it increases the risk of spontaneous miscarriage. This is why pregnant women should avoid contact with affected children.
The diagnosis of hand, foot and mouth syndrome is established based on a range of clinical signs. The attending physician will discuss the diagnosis when faced withappearance of blisters on the hands and feet, and after examination of the mouth. No additional examination is necessary.
What are the treatments for foot, hand and mouth?
Treatment is essentially symptomatic and is based on taking antipyretics, such as paracetamolmaking it possible to improve the comfort of the child. Of the Antiseptics may be prescribed to disinfect lesions following the eruption of vesicles. A gargling with baking soda can relieve oral lesions when they interfere with the child’s eating. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice. The fact of eat cold is more bearable in case of lesions in the mouth. Finally, know that antibiotics are useless to treat this infection since a virus is involved, not a bacteria.
What prevention tips to avoid hand-foot-and-mouth disease?
Like any contagious viral disease and even if it is benign, hand and foot syndrome requires strict hygiene measures to avoid epidemics. THE hands should be washed thoroughlyespecially after a trip to the toilet. A washing surfaces, toys and objects within reach of sick children is necessary in order to limit contamination. It is also advisable to avoid sharing bath towels.