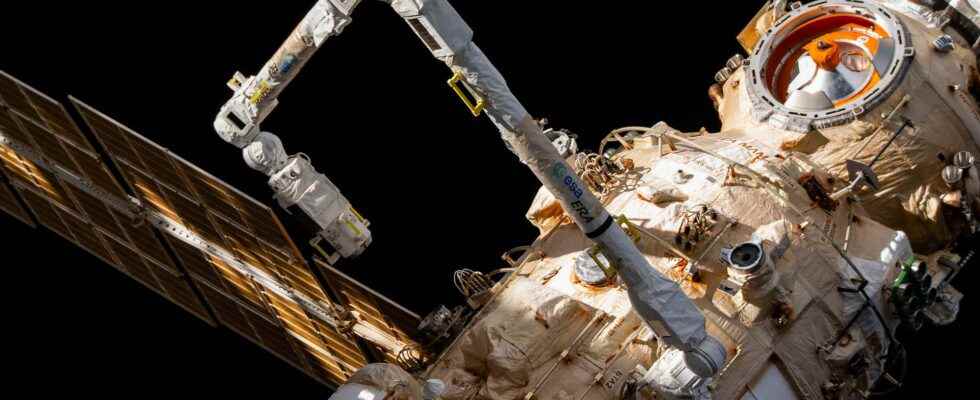
ERA is the arm robotics of the’European Space Agency devoted to the Russian segment of the international space station (ISS). With the scientific laboratory columbus and the Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV), ERA is the third major element of European participation in the construction of the International Space Station. ERA (for European Robotic Arm, in English) was launched in July 2021. Very late on its initial schedule – it should have been launched in 2007 – this arm was built by a European consortium, led by Airbus Defense and Space. It completes the two other arms of the Station, including the Canadarm2 robotic arm, which cannot access all of this part of the ISS. Its commissioning began in April 2022 with the spacewalk of two Russian cosmonauts who unpacked it and gave it a few moves to make sure it was working properly.
A robotic arm inspired by human arms but much more versatile
Although very different from Canardam2, ERA is very complementary. 11.3 meters long and weighing 680 kilos, it can move very large masses, from three tonnes in routine up to eight tonnes in slow mode. This symmetrical, two-handed arm can move forwards or backwards under its own control, from one hand to the other, from one fixed point to another. The Seven joints robust and precise ERA, the light limbs and thecomputer control located in the middle of the arm give the robotic arm its versatility. ERA will be used for a very wide variety of tasks such as replacing solar panelsthe inspection or even the assembly of modules and will facilitate the movement of astronauts going out in the space. With his cameras infraredhe will be able to inspect the outer surface of the station (ageing of the protective coatings, impacts of micrometeorites, verification of the attachments of the modules, of the pallets, etc.).
Depending on the needs of the astronauts, ERA will be controlled from inside or outside the Station, in real time or programmed in advance. With its joints, ERA looks like a kind of human arm. It is operated by motors and cables. It is symmetrical, in the sense that on both sides of the “elbow” there are two “muscles” and two “wrists”. Its extremities are able to cling to the station, which gives it a significant radius of action all around the Russian part. It will move by hooking on one end, then another. Finally, it is equipped with many tools including a platform with footrests and handrails so as to transport astronauts during their extravehicular outings.
You will also be interested
Interested in what you just read?