As part of the gastrointestinal disorders eosinophils (EGID), eosinophilic esophagitis is an increasingly recognized condition. It more often affects men (ratio 1/3) and is characterized by inflammation of the mucosa esophagus with massive infiltration of eosinophils resulting in swallowing dysfunction.
The causes and symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis
It’s a pathology chronic that can occur at any age.
The symptoms are triggered by a allergen dietary or environmental resulting in a massive intake ofeosinophils on the mucosa. These cells involved in allergic reactions are found infiltrate in the epithelium leading to a inflammatory reaction and narrowing of the esophagus. Supported by a predisposition hereditary, this pathology causes in the child a refusal to feed, a loss of weight which can be associated with vomiting and pains thoracic and abdominal. In adults, it is manifested by difficulty in swallowing, sometimes associated with the symptom of reflux gastroesophageal.
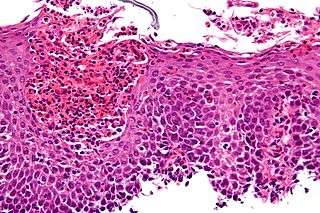
the diagnostic is difficult, as patients get used to it and adapt their diet according to the severity of the symptoms. Generally, it is based on an endoscopy (presence of furrows, rings and a narrowing of the esophagus) accompanied by a biopsy showing eosinophil infiltration (>15 eosinophils/field).
Treatments for eosinophilic esophagitis
The treatment is based on a proton pump inhibitor (IPP) or in case of failure of corticosteroids. A food exclusion diet targeted by tests ofallergy or empirical elimination of foods that trigger an immune reaction (milk, eggs, soy, peanuts, corn, shellfish) is an alternative treatment. A dilation of the esophagus is performed in cases where the narrowing is too great and the symptoms are resistant to treatment.
You will also be interested
Interested in what you just read?