the encryption is a way to scramble data so that only authorized parties can understand the information. It is the process of converting plain text that anyone can read into incomprehensible text, also known as cipher text. In other, simpler words, encryption takes readable data and alters it to appear random.
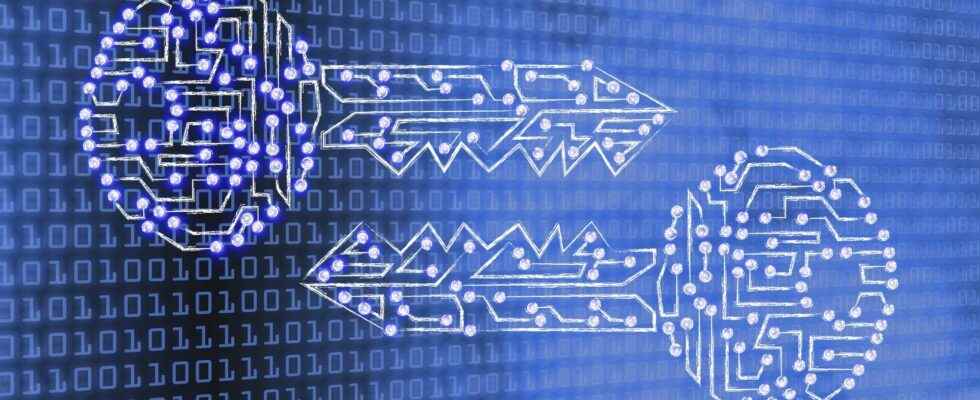
the encryption requires the use of a key: a set of values mathematics that the sender and receiver of an encrypted message agree on. Although the encrypted data looks random, the encryption proceeds in a logical and predictable way, allowing a party that receives the encrypted data, and has the correct key, to decrypt the data and turn it back into plain text.
Truly secure encryption uses keys that are complex enough that it is highly unlikely that a third party can decrypt or crack the ciphertext by brute force, i.e. guessing the key through completeness. Data can be encrypted locally, while stored, or in transitwhen they are transmitted elsewhere for example with a protocol vpn.
What are the different types of encryption?
The two main types of encryption are symmetric encryption and encryption asymmetric. Asymmetric encryption is also known as encryption with public key.
In the case of symmetric encryption, there is only one key, and all communicating parties use the same (secret) key for encryption and decryption. In the case of asymmetric, or public key, encryption, there are two keys: one key is used for encryption and another for decryption. The decryption key remains private (hence the name ” private key ), while the encryption key is shared publicly, so that anyone can use it (hence the name “public key”). Asymmetric encryption is a fundamental technology for many secure web browsing protocols.
Why is data encryption necessary?
If this has not always been the case, today we find encryption in a lot of softwarewebsites and apps. Here are the reasons:
Encryption ensures that no one can read communications or stored data except the intended recipient or rightful owner of the data. This prevents attackers, advertising networks, service providers Internet and, in some cases, governments to intercept and read sensitive data.
Encryption helps prevent data breaches, whether data is in transit or simply stored. If a device containing sensitive information is lost or stolen and its Hard disk is properly encrypted, the data it contains will be always secure. Similarly, encrypted communications allow communicating parties to exchange sensitive data without disclosing it.
- Data integrity:
Encryption also helps prevent malicious behavior such as attacks on the way. When data is transmitted over the Internet, encryption (along with other integrity protections) ensures that what the recipient receives has not been modified or overwritten in transit.
Public key encryption, among other things, can be used to establish that the owner of a website has the private key in the certificate Site TLS. This allows website users to be sure that they are connected to the real website.
For all of these reasons, many industry and government regulations require companies that process user data to keep that data encrypted. Examples of regulatory and compliance standards that require encryption include Hipaa and GDPR.
You will also be interested
[EN VIDÉO] Kézako: how is data encrypted on the Internet? Cryptography is the oldest form of encryption. There are traces of its use until 2,000 BC. This technique still used today, especially on the Web, reveals its mysteries on video thanks to the Kézako program from Unisciel and the University of Lille 1.
Interested in what you just read?