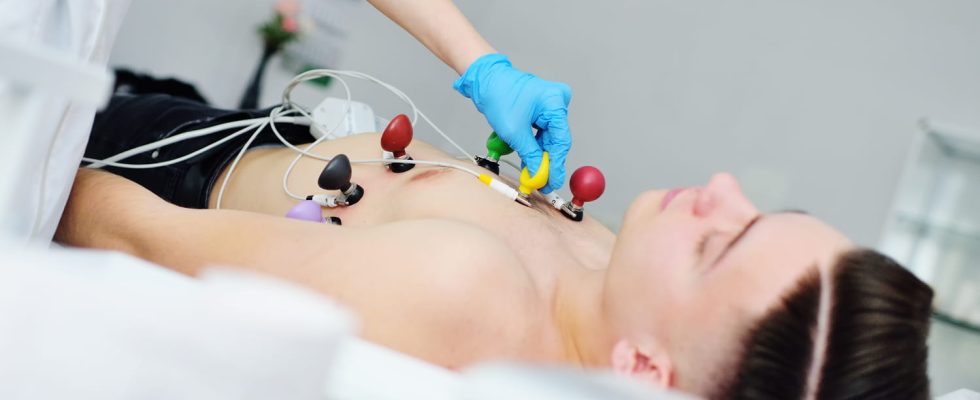
Electrocardiography (electrocardiogram or ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart muscle. A useful test to detect a rhythm disorder or a heart attack for example.
The electrocardiogram (ECG) and an examination to detect a rhythm or cardiac conduction disorder, auricular hypertrophy, pericarditis, myocardial infarction… thanks to electrodes placed on the skin which record the electrical activity of the heart. The exam usually lasts about ten minutes.
What is an electrocardiogram (ECG)?
An electrocardiography (ECG) designates the examination allowing therecording of the electrical activity of the heart. An electrocardiogram is the trace obtained by recording and transcribing the electrical currents that run through the heart during a cardiac contraction. It’s a must-have cardiology testwhich is complementary to clinical examination and echocardiography.
What is the principle of an ECG?
This examination is done at rest: the patient is lying on his back, without anesthesia. THE electrodes which are connected to an electrocardiograph (recording device), are applied to bare skin (which requires, in case of significant hairiness, to shave certain areas of the torso), previously coated with a conductive paste. 4 electrodes are applied to the wrists and ankles of the patient and 6 electrodes are arranged at specific points on the surface of the chest. The electrodes register either a difference in electric current between two points (bipolar leads with two electrodes) or directly the electric current by means of a single electrode (unipolar leads). For each derivation, an ECG tracing is saved. 12 leads are typically recorded on the ECG trace and can be extended to 18 leads under certain circumstances. The recording is made on graph paper. These curves are interpreted by a general practitioner or a cardiologist.
Do you have to be fasting to do an ECG?
Not necessarily, on the other hand, it is advisable not to smoke just before.
Where to do an electrocardiogram?
An ECG is systematically performed in consultation with a cardiologist, as well as when a patient is referred to an emergency cardiology department. More and more general practitioners are also equipped to be able to make early diagnoses in particular in patients with chest pain or cardiac arrhythmias. The electrocardiogram is a quick review, for ten minutes and painless. It can be done during a consultation, in a hospital environment, at home or on the public highway during emergency situations.
When to do an ECG?
Urgentlythe electrocardiogram is indicated in patients with symptoms such as:
In these situations, the ECG can be used to diagnose many cardiac pathologies:
→ The appearance of a chest pain associated with characteristic changes in the electrocardiogram makes it possible to immediately diagnose a myocardial infarction, to locate the artery of the heart which is clogged and to determine the type of infarction and its location: the heart attack anterior, inferior infarcts and infarcts of the lateral wall of the heart.
→ The ECG makes it possible to evoke other causes in the presence of chest pain such as acute pericarditis or thepulmonary embolism ;
→ The ECG makes it possible to diagnose a heart rhythm disorder for example a fibrillation atrial, or a disorder of the electrical conduction of the heart.
“Apart from emergencies, the ECG makes it possible tostudy the impact on the heart of cardiac pathologies such as heart valve damage or signs of cardiac distress in a patient with cardiovascular risk factors, including high blood pressure and diabetes. Finally, the ECG is performed regularly in the monitoring of all cardiac patients“, indicates Professor Alain Furber, head of the Cardiology department at the University Hospital of Angers.
What is stress electrocardiography?
An electrocardiogram can also assess the body’s reaction to sustained exertion (this is called a stress test) or to measure the effects of sports training on the capacities of the heart.
What is a home electrocardiogram?
It is a holter, a portable device that can continuously record an electrocardiogram, for 24 to 48 hours on average. This device is put in place by the cardiologist. It is a useful tool for detect disturbances in the electrical conduction of the heart and arrhythmias, especially if they are intermittent. But also to evaluate the effectiveness of a given treatment against a heart disease or that of a pacemaker.
It is the general practitioner or the cardiologist who interprets the curves. The ECG trace will make it possible to record the electrical activity linked to the depolarization of the right and left atria, this is the first wave called the P wave, then the electrical activity linked to the depolarization of the ventricles is the QRS complex, finally the electrical activity linked to the repolarization of the ventricles is the T wave. “There are normal values which allow the results to be interpreted. For example, if the P wave is higher and wider, this indicates an anomaly in the atrium which is dilated. In the same way, when the QRS complex is too large this is a sign of thickening of the wall of the ventricle (hypertrophy).We analyze all of these complexes and the overall morphology of the complex will direct us towards this or that pathology.When the wave P normal disappears, there is a rhythm or electrical conduction disorder”, relates Professor Alain Furber.
What are the conditions for an ECG to be normal?
For an ECG to be normal, several points must be met:
► The normal heart rhythm (coming from the sinus node located in the right atrium) is a regular rhythm with a heart rate between 50 and 100 beats per minute. Below 50/minute, we speak of bradycardia and above 100, we speak of tachycardia.
► Each P wave must be followed by a QRSthis is what makes it possible to detect possible disturbances of conduction between the atria and the ventricles.
► The space between two QRS must always be the samethis indicates that the heartbeat is regular.
► Atrial P wave and ventricular QRS complex morphologies should be normal.
What are the conditions for an ECG to be abnormal?
If one of the signal sequences mentioned above does not respect the standards (for example an elongation of the duration which separates the point Q and the top of the wave T), one can consider that an ECG is not normal . However, a normal ECG does not mean the absence of heart disease, and an abnormal ECG may be harmless.
How much does an ECG cost? Is it reimbursed?
The ECG costs 14.26 euros and is reimbursed by Social Security.
Are there any side effects?
The electrocardiogram is a non-invasive examination devoid of any side effects.
Thanks to Professor Alain Furber, head of the Cardiology department at the CHU d’Angers.