Each application installed on your Android mobile has permissions to access certain data or functions. Get into the habit of checking the permissions granted to verify their relevance.
On Android, the rule imposed by Google implies that each application you install requests permissions when it wants to access certain data or functions of the device – including those associated with its various sensors or modules. This may be to obtain your location for mapping or GPS applications for example, to be able to access the microphone, the camera or the multimedia elements saved on the mobile, access to the telephone application, contacts, calendar, SMS, etc. However, very often we hasten to press the “Allow” option when installing a new application without necessarily being interested in the authorizations granted. Then we forget. Except that the installed application retains the granted accesses, even if it is unused… until the system revokes them by itself after a certain period of non-use.
Nevertheless, nothing prevents you from checking on your side who has access to what. Especially since this control also makes it possible to detect strange apps, even malware which have surreptitiously granted themselves rights to the device, sometimes by hiding their icon so as not to be spotted… Since Android 8, Google has had no stop simplifying Android’s privacy settings to make data usage more transparent. With Android 12, managing permissions is even easier with a very readable dashboard. Here’s how to use it.
How to control app permissions in Android?
Regardless of the software overlay applied by the manufacturer of your Android smartphone, the options for managing application permissions remain easily accessible.
► Go to Android’s settings, for example by tapping the cogwheel icon normally displayed with standard apps on the home screen. Find a menu Privacy Where Private lifethen open it and select the section Permissions Where Authorization manager. Sometimes this section is located in the menu Apps. If you can’t find it, type the word permissions in the search field at the top of the settings window and select the appropriate result.
► Then press Authorization manager.
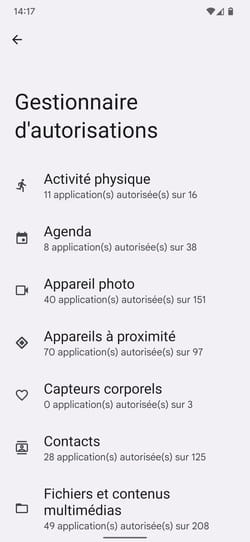
► Several areas are then revealed from which applications may require authorizations: Physical activity, Diary, Camera, contacts, etc Under each of these items is the number of applications that have access to it. Press one of the menus. Camera for example.
► All apps that have permission to use the camera are displayed here. Scroll down the list to verify that an app listed should not have this access.
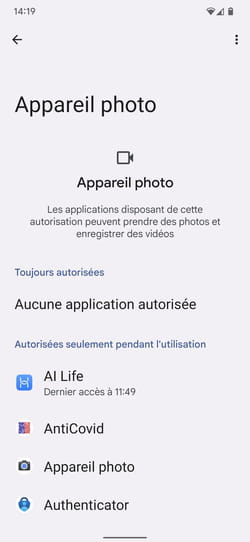
► If you feel that an application has no valid reason to be able to use the camera, tap on its name. In the menu that is then displayed, choose from the proposals presented: Allow only if app is in use, Always ask Where Not to allow. Then press the arrow at the top left of the screen to return to the list of applications.
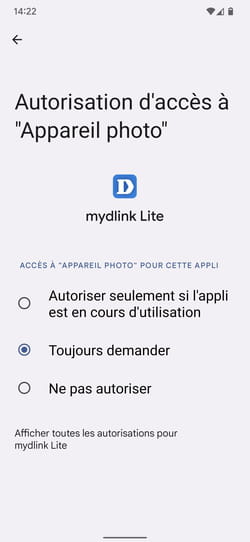
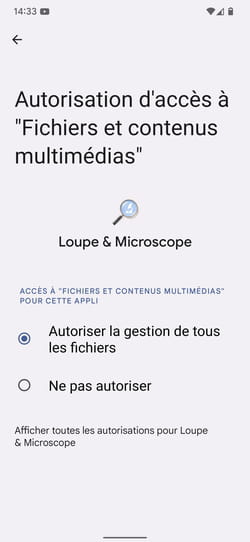
► Repeat the verification operation for the other areas of activity, in particular geolocation (Position) where the Multimedia files and content. You may be surprised by some results such as this Magnifier and Microscope application (which allows you to use the mobile’s camera as a magnifying glass) which grants itself, by default, access to all the files on the mobile.