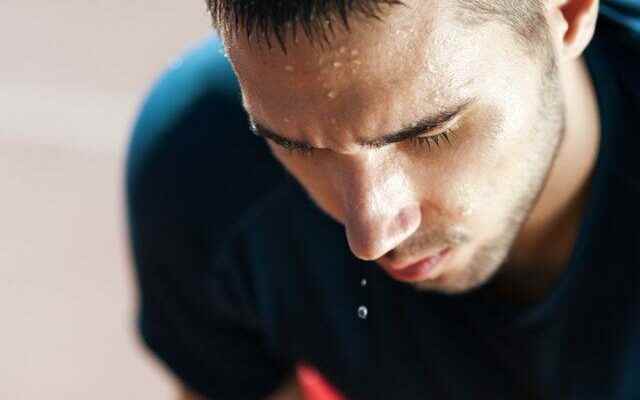
Although sweating is thought to be irritating in terms of smell and appearance, sweating can be a warning sign of dangerous diseases. There are a wide variety of health problems under the sweat experienced without heat and hot weather, without exercise. Experts warn about cold sweats.
WHAT IS COLD Sweating?
Sweating is typically a natural, beneficial bodily function: When we’re very hot, we sweat to keep our body temperature in check. But sometimes we sweat even when we’re not hot at all. It differs from hot sweats in that it usually does not affect the whole body and often occurs with chills at night. Therefore, cold sweats can be defined as profuse sweating accompanied by a drop in body temperature followed by often chills.
CONDITIONS CAUSED BY COLD Sweating
HYPERHYDROSIS
If water flows from our forehead, armpits and back without a single drop of sweat, the cause of the problem is hyperhidrosis. However, although it can be annoying for those who suffer from it, it is rarely a health issue. The most commonly affected areas of the body are the armpits, palms and soles, rarely the face, scalp, and groin. If the sweating stops during sleep and is not accompanied by other symptoms, it does not require medical treatment.

The changing hot flashes associated with menopause are another possible cause of excessive sweating. It is important to note that cold sweats are not limited to menopausal women. Middle-aged women may also be affected and may also experience changes in their menstrual cycles, night sweats, and tremors. According to some studies, the body temperature of menopausal women can drop drastically after a heat wave, resulting in chills as well as cold sweats.
MEDICINES
Cold sweats can also be a side effect of many drugs, and here we should also consider various over-the-counter preparations. Research shows that the main cause of cold sweats or excessive sweating are antidepressants, drugs that affect estrogen and androgen levels, and drugs used to treat diabetes.
LOW BLOOD SUGAR
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, occurs when blood sugar levels drop below normal levels. The body reacts to a lack of blood sugar in a similar way to a lack of oxygen, one of the symptoms of which is the body’s cold sweat. Studies have shown that type 1 and type 2 diabetes are associated with decreased body temperature regulation in both heat and stress. This means that diabetics have trouble regulating their body temperature.

INFECTIONS
Many autoimmune or bacterial infections can cause cold sweats. According to doctors, the following infections may be behind the cold sweat: tuberculosis, HIV, Covid, pneumonia, mononucleosis or hyperthyroidism, which can lead to sweating of the whole body.
Cold sweats can be a symptom of several types of cancer. Sweating is most commonly associated with lymphoma, but sweating has also been associated with leukemia. But it can also indicate liver, bone, and breast cancer.
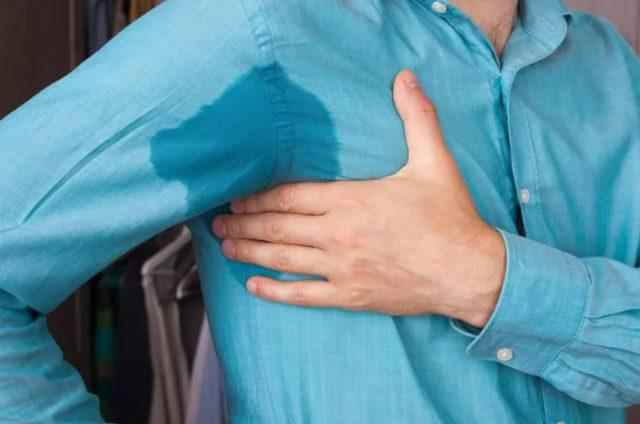
HEART ATTACK
Cold sweat can also be a sign of a heart attack. Immediate medical attention is required if the following symptoms occur in addition to sudden cold sweats: oppressive pain in the chest, stomach, back or neck, difficulty breathing, dizziness.
