You will also be interested
[EN VIDÉO] Radio astronomy catches distant galaxies giving birth to stars Thanks to the International Low Frequency Array (LOFAR), a large network of 70,000 radio telescopes spread over Europe, astronomers have obtained breathtaking images of the youth of our Universe. Tens of thousands of galaxies captured as they formed stars. This video proposes to fly over a part of the studied sky. © Jurgen de Jong, Leiden University
In Greek mythology, Alcyoneus was one of the greatest Giants, son of Ouranos (Heaven) and Gaia (Earth), and one of the leaders during the Gigantomachy, the battle between the Giants and the Olympian gods for supremacy over the Cosmos. It is now also the name of a newly discovered giant radio galaxy at 3 billionlight years from U.S. This 16.3 million light-year-long “monster” is the largest structure of galactic origin known to date.
A giant among giants…
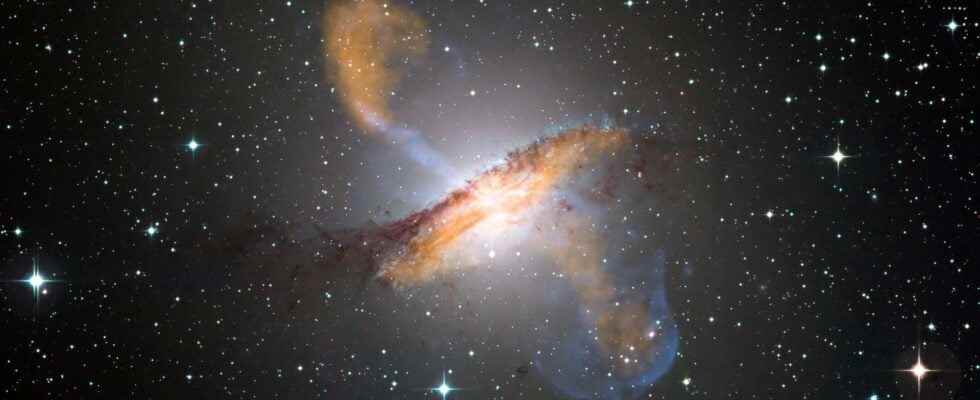
Giant radio galaxies are still very mysterious objects. They consist of a host galaxy as well as jets and colossal lobes that spring from the galactic center. These jets and lobes, in interaction with the intergalactic medium, act like a synchrotron which accelerates electronswhich emit radio waves.
The matter from accretion disk that surrounds the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy does not necessarily end beyond theevent horizon : a small fraction of it is “channeled” from the inner region of the accretion disk towards the poles, where it is projected into space in the form of jets of ionized plasma at gears equal to a significant percentage of the speed of light. These jets can travel huge distances before spreading into giant wave-emitting lobes radio. The Milky Way itself has such radio lobes. However, it is not really understood why, in some galaxies, they reach gigantic sizes of millions of light years.
The most extreme examples of these giant radio galaxies could hold the key to understanding what drives their growth. The international team led by Martijn Oei, doctoral student at the Leiden Observatory (Netherlands), explains in its article that, ” if there are features of host galaxies that are an important cause of the growth of giant radio galaxies, then the hosts of larger giant radio galaxies are likely to possess them. Similarly, if there are particular large-scale environments that are highly conducive to the growth of giant radio galaxies, then the largest giant radio galaxies are likely to reside there. “.
They then reprocessed the data collected by the Low-Frequency Array (Lofar), eliminating compact radio sources that may interfere with radio lobe detections diffuse and correcting optical distortion. According to the researchers, the resulting images represent the most sensitive search ever conducted for radiogalaxy lobes. They then used their own eyes to locate their target, Alcyonée: We have discovered what is projected to be the largest known structure made by a single galaxy: a giant radio galaxy with a projected proper length [de] 4.99 ± 0.04 megaparsecs [16,28 ± 0,13 millions d’années-lumière]. True proper length is at least 5.04 ± 0.05 megaparsecs [16,44 ± 0,16 millions d’années-lumière] “.
…but a surprisingly typical giantess
Then using the Sloan Digital Sky Surveythe researchers found that the host galaxy is a elliptical galaxy fairly typical, integrated into a filament of the cosmic webwith a mass stellar mass equal to about 240 billion times the mass of the Sun (4 to 5 times the mass of all stars of the Milky Way) and a supermassive black hole at its center of about 400 million solar masses (about 100 times the mass of Sgr A*the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way).
” Apart from the geometry, Alcyonée and its host are surprisingly ordinary: the total density of brightness low frequency, the stellar mass and mass of the supermassive black hole are all lower, though similar, to those of the mid-giant radio galaxies. Very massive galaxies or central black holes are therefore not necessary to produce large [radiogalaxies] giants and, if the observed state is representative of the source on its duration life, high radio power is also not “.
It could be that Alcyoneus is in a region of space with lower than average density, which would allow its expansion, or that interaction with the cosmic web plays a role in the object’s growth. Regardless, however, researchers believe that Alcyonée continues to grow in size.
What you must remember
- The largest galaxy ever observed has just been discovered 3 billion light-years from Earth.
- This giant radio galaxy, called Alcyonea, is 16.3 million light-years long.
- This discovery sheds light on our poor knowledge of these colossi and what drives their incredible growth, but could provide a path to a better understanding, not only of giant radio galaxies, but also of the intergalactic medium.
Interested in what you just read?