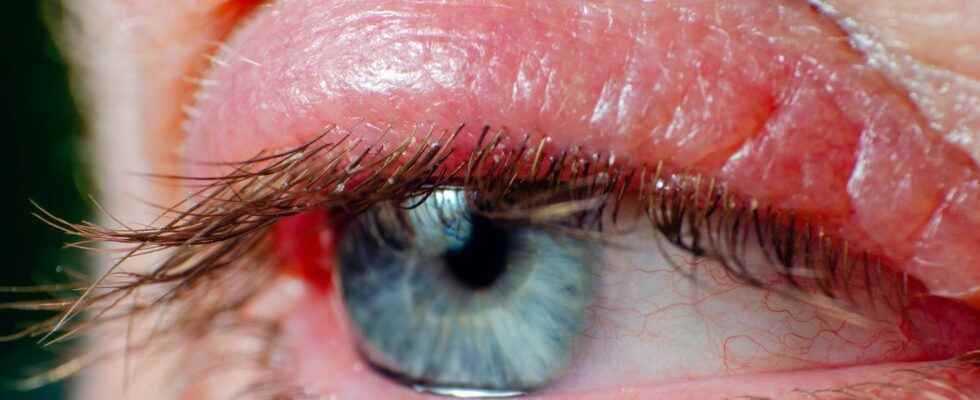
Blepharitis is a inflammation of the eyelid, which results in redness, swelling and a burning sensation. There are two main types: acute blepharitis, the most common and of infectious origin, and chronic blepharitis, of unknown origin.
Common symptoms of blepharitis
- itching (pruritus);
- burning sensation of the rim of the eyelid;
- conjunctival irritation;
- feeling of “grain of sand in the eye;
- tearing;
- photosensitivity.
Causes and symptoms of acute blepharitis
Acute blepharitis is most often due to a bacterial infection, mainly of the staphylococcal type. More rarely, it is caused by a virus Of type herpesof the varicella and shingles, by a mushroom or a parasitic infection (mite, lice). Apart from infection, acute blepharitis is sometimes linked to a allergic reaction (pollencosmetic products…)
- In acute ulcerative blepharitis, small pustules appear on the follicles ciliary, with the formation of scabs and small surface hemorrhages when these scabs come off. The eyelids stick together during the sleep because of the secretions dry.
- Viral infections generate fewer scabs but more abundant serous discharge.
- Recurrent ulcerative blepharitis can lead to scarring of the eyelid, misdirection (trichiasis) of the eyelashes or even their fall.
- Blepharitis of allergic origin causes intense pruritus with the urge to rub the eyes. The edges of the eyelids become edematous and erythematous, and the eyelashes are invaded by liquids dry serous.
Causes and symptoms of chronic blepharitis
Chronic blepharitis is generally linked to a dysfunction of the glands of Meibomius, localized at the level of the eyelid, and which produce lipid secretions in order to ensure a good hydration and eye lubrication. In chronic blepharitis, the composition of lipids is abnormal, causing occlusion of gland ducts where waxy plugs form solid and yellowish. The lack of lipid secretion increases the evaporation of tearswhich results in a keratoconjunctivitis secondary dryer. Patients experience foreign body sensation in the eye, visual fatigue, and intermittent blurring with prolonged eye strain.
Chronic blepharitis is frequently associated with seborrheic dermatitis of the face or scalpor a acne rosacea.
Treatment of blepharitis
Acute ulcerative blepharitis is treated with an ointment antibiotic to be applied for 7 to 10 days, accompanied by thorough cleansing of the eyelids. When the infection is of viral origin, antivirals are administered orally.
The treatment of chronic blepharitis is essentially based on the management of symptoms : hot compresses, tears artificial, ointment ocular to apply at night, gentle eye massages. There are also products to facilitate the dissolution of waxy plugs.
Good eyelid hygiene is essential to avoid recurrences and complications, such as washing your hands before handling and never neglecting the make-up removalor even stop using it if you have a tendency to blepharitis.
You will also be interested
Interested in what you just read?