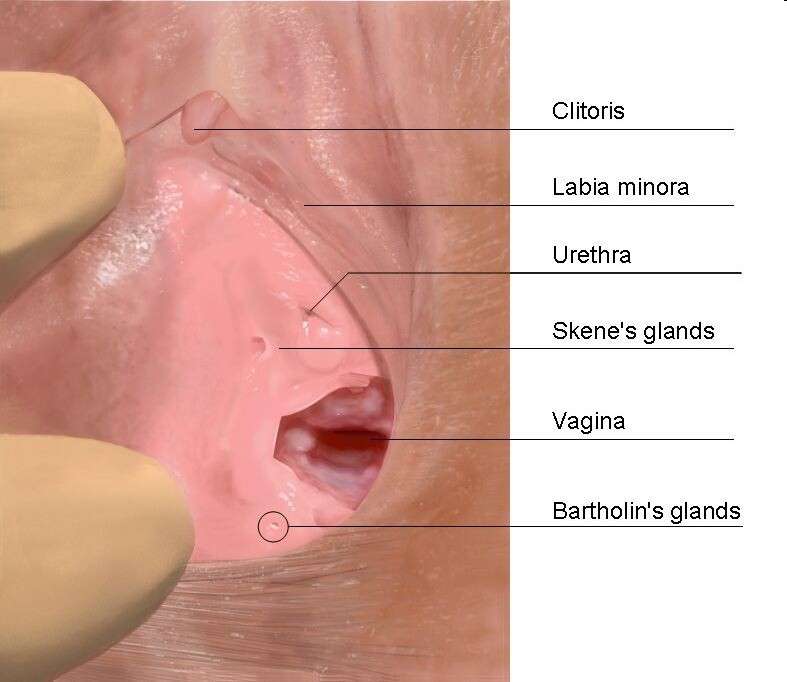
Described for the first time by a Danish anatomist in the XVIIand century (Caspar Bartholin the Younger), the Bartholin’s glands or major vestibular glands are two small secretory organs located on either side of the vaginal opening in women (male equivalent: bulbourethral glands or Cowper’s glands). Functional of the puberty to the menopausethey produce, following stimulation sexuala mucus allowing the lubrication of vagina.
Located in the thickness of the labia majora, they measure the size of a pea and have an excretory duct through which mucus can flow. It happens that the orifice of the duct of the Bartholin’s gland becomes clogged. The accumulation of mucus leads to a inflammation painful: bartholinitis. This inflammation can look like a cystor even an abscess, if it becomes infected, and lead to fever.
Anatomy of the vulva: location of Bartholin’s glands. © Nicolasolan, Wikimedia CommonsCC by-sa 3.0
What are the causes of bartholinitis?
Bartholinitis concerns 2% of women who will develop a cyst or an abscess (three times more common than cysts) during their lifetime.
Before the menopausethe cause of Bartholin’s duct obstruction can be attributed to different factors such as too tight clothes, sportthe sweat or too thick mucus. When the cyst becomes an abscess, certain infectious agents of digestive origin (Escherichia coli) or respiratory (streptococcus) are then involved. In some cases it is a sexually transmitted infection (gonorrhea Where chlamydia). In postmenopausal women, the Bartholin glands naturally involute and a hypertrophy requires excluding a malignant cause.
What is the treatment for bartholinitis?
In first intention, the treatment is based on antibiotic therapy accompanied byanti-inflammatories. A drainage abscess can be performed with, in case of recidivismexcision of the gland.
You will also be interested
[EN VIDÉO] Organ transplantation revolutionized by stem cells? Each year more than 5,000 people benefit from an organ transplant in France. These patients are subjected to heavy treatment to prevent rejection following their operation. Discover in video and thanks to Discovery Science a technique based on stem cells which could make it possible to counter this problem.
Interested in what you just read?