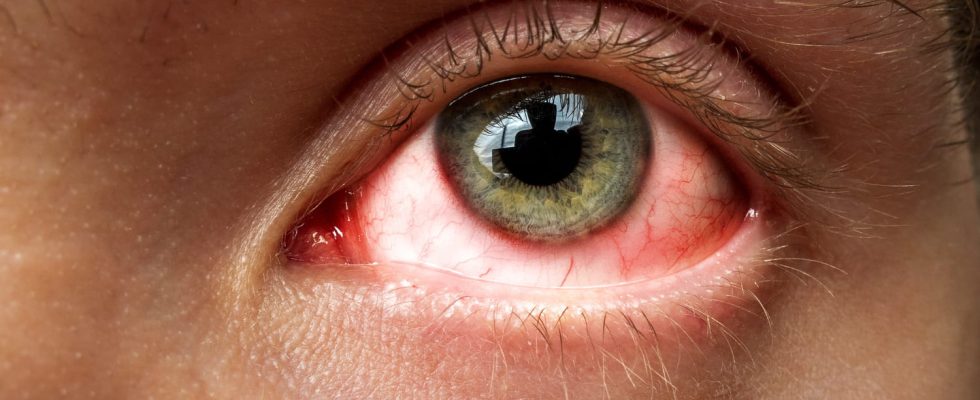
A new variant of Covid called XBB.1.16 or Arcturus is being monitored by the authorities, as it would be more transmissible and responsible for unexpected symptoms such as conjunctivitis (pink eye). It is the majority in India and circulates (little) in France.
[Mis à jour le 11 mai 2023 à 8h56] The XBB.1.16 variant nicknamed Arcturus because of the brightest star in the constellation Bouvier, is closely monitored by health authorities. This new variant of the Covid is particularly rife in India (it has been detected in this country since January 9, 2023 and is now the majority)but it is also present in other countries such as UNITED STATES and a little in Europealerted theWorld Health Organization on March 30, 2023. This variant would be very similar to XBB.1.5 (Kraken), the majority Omicron sublineage currently in France and in the United States. However, it would be equipped with additional mutations, which would make it (again) more transmissible and more resistant to vaccines. XBB.1.16 has been placed in the variant list “under supervision” by the WHO. It would cause conjunctivitis (“pink eye”), especially in children. “No worrying signal in terms of severity has been associated with XBB.1.16 in the countries where it circulates“, would like to reassure Public health France.
What is the new XBB.1.16 or Arcturus variant?
From its official name XBB.1.16, Arcturus is a new mutation of Covid which was first detected in India in early February 2023. It then spread to other countries. Arcturus (in reference to the brightest star of the constellation Bouvier) or XBB.1.16 is a recombinant of the Omicron BA.2.10.1 sublines And BA.2.75 and owns 3 additional mutations in the tip of the Spike protein (E180V, F486P and K478R) compared to its parent line XBB. The F486P mutation is shared with XBB.1.5, meaning it has a similar transmission and symptomatology profile, the WHO report reads. Despite low circulation globally, XBB.1.16 has been placed on the Variants to Watch (VOI) list, reports the latest risk analysis related to emerging variants of Sars-CoV-2 of Public Health France (as of April 24, 2023), following the presence of mutations that may affect its characteristics and its detection on the rise in several countries in very different epidemic contexts.
Here is the family tree of the original Covid strain:
What are the (specific) symptoms of the Arcturus variant?
Dr. Vipin Vashishtha, a pediatrician in India, former head of the Indian Academy of Paediatrics Immunization Committee and a member of the World Health Organization’s Vaccine Safety Network, observed an increase in Covid cases in children under 12 (for the first time in 6 months) as well as a “infantile phenotype that seems to emerge“probably in connection with this new variant, he describes on his Twitter account. The symptoms he observes in children since the arrival of the Arcturus variant would be the following:
- A high fever
- A cough
- “Itchy” conjunctivitis (which is characterized by a pink eye without pus, but with “sticky eyes”), a symptom which had not been observed in previous waves in India, specifies the doctor.
In addition, an Indian study published in preprint analyzed the clinical presentation of patients from a pediatric hospital in northern India. Over the study period (early April 2023), the authors assume that the majority of cases correspond to XBB.1.16, but they did not verify this by genotyping. Of the 90 cases tested for SARS-CoV-2, 25 were positive and none showed severe signs. These pediatric cases mostly presented with mild respiratory symptoms and fever. Among the 22 confirmed cases less than 5 years old, 9 patients had conjunctivitis, or 41%. If the authors make a link between XBB.1.16 and the identification of conjunctivitis, the data of the study do not allow to conclude to such an association. Indeed, there is no evidence that the 25 cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection were indeed due to XBB.1.16.
Map of the Arcturus variant: where is it present in the world?
As of April 24, 2023, Arcturus has been detected mainly in India and in 23 countries in the worldaccording Dr. Raj Rajnarayanan’s Variant Tracking : in the United States, in Singapore, in Japan, in the United Kingdom, in Canada… In India, it contaminated about 1,500 people to date. In this context, the Ministry of Health of India has organized mock exercises to ensure that hospitals are prepared for the increase in Covid cases, reported the bbc on April 10, noting that some states have again made it mandatory to wear masks in public places. However, there are currently no access restrictions for India. In the United States, Arcturus circulates weakly and remains rare: none of the new variants accounted for enough sequences (1% nationally) to be listed in the updated COVID forecasts of the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Is it present in France?
Yes, Arcturus has been detected in mainland France (and Guyana) and represents around 0.3% of the interpretable sequences of the Week 14 Flash survey, according to Public Health France. It is particularly observed in Normandy, in the Centre-Val-de-Loire, in the Grand-Est, in Ile-de-France and in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, according to variant tracking based on GISAID data. Note that this variant also has a sub-variant named XBB.1.16.1 which also circulates in France. For now there is less than 10 cases (XBB.1.16 and XBB.1.161 combined), which does not pose a threat.
Of particular concern is the K478R mutation in this variant.
Is it more dangerous than the others?
The Arcturus variant would be very similar to the XBB.1.5 variant. However, it would present “additional mutations in the virus’ spike proteinwhich can attach to and infect human cells, which have the potential to make the variant more infectious and even cause more severe disease“, can we read in the WHO weekly report of March 30, 2023. One of the 3 mutations (the mutation K478R) is of particular concern and is thought to be associated “to a decrease in neutralizing antibodies (a neutralizing antibody is an antibody that defends a cell against a pathogenic agent or an infectious particle by neutralizing its biological effects, editor’s note), increased transmissibility and pathogenicity”, writes the WHO. However, while mutations seem concerning in theory, they are not always so in reality due to the very complex nature of population immunity, said Ryan Gregory, professor of biology at the University of Guelph. in Ontario, Canada, fortune magazine.
Is Arcturus resistant to Covid vaccines?
According to the WHO, the K478R mutation may help the virus overcome antibodies from previous infection and vaccination. Nevertheless, vaccine boosters should offer “some protection if the dose is recent”reassured Dr. Rajendram Rajnarayanan, at the origin of the Tracking of XBB.1.16.
Sources:
– Epidemiological Weekly Bulletin of Covid-19, March 30, 2023, World Health Organization
– Tracking XBB.1.16* Lineage Over Time by Raj Rajnarayanan
– Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Covid Data Tracker