“People with cancer are more at risk of having blood clots,” said Dr. Marc Carrier, head of the hematology department of Ottawa Hospital.
A clot is a heap of blood that forms in a blood vessel – most often a vein, more rarely an artery. Most of the time, the clots are small and harmless, but it happens that the clot becomes large enough to block the circulation of blood and cause serious or even fatal health problems (pulmonary embolism, stroke …). “”Due to several risk factors that doctors today know well, people with cancer are more likely to have blood clots “, explains Dr. Marc Carrier, head of the hematology department of the Ottawa hospital and president of Thrombose Canada. Scientific data estimate that around 1 person with cancer in 200 will develop a Caillot.
A person who has active cancer (who is not in remission, nor healed) or who has spread to other parts of the body (metastases) is more likely. “”Tumor cells can release substances that stimulate blood coagulation, which leads to the formation of clots in blood vessels. Cancer can also cause chronic inflammation which will cause the secretion of pro-coaglant substances, thus activating the “coagulation cascade”. Sometimes some larger tumors can compress blood vessels, slowing blood flow (blood stasis) and increasing the risk of caillots forming“.
A person under anti -cancer treatment is also more likely for clots. “”Chemotherapy can promote the formation of clots (for example, those based on platinum or certain targeted therapies). Other treatments, such as surgical interventions and the use of intravenous catheters, can damage the walls of blood vessels, thus promoting the formation of clots“, continues our interlocutor. Finally, cancer associated with other medical conditions such as obesity or history of venous thrombosis increases the risks.
Rapid growth tumors are more at risk
Cancers associated with the highest risk of clots are those affecting the ovaries, pancreas, stomach, brain and lung. These are cancers that spread quickly and we know that rapid growth tumors are associated with a higher risk of blood clots formation, while specifying that the risk can also vary depending on the cancer stadium (the more it is advanced , the higher the risk, editor’s note). “”Although breast cancer is associated with a lower risk of blood clots compared to cancers mentioned beforehand, its strong incidence in the female population means that clinicians observe a significant number of caulots in these patients“, wishes to specify Dr. Carrier.
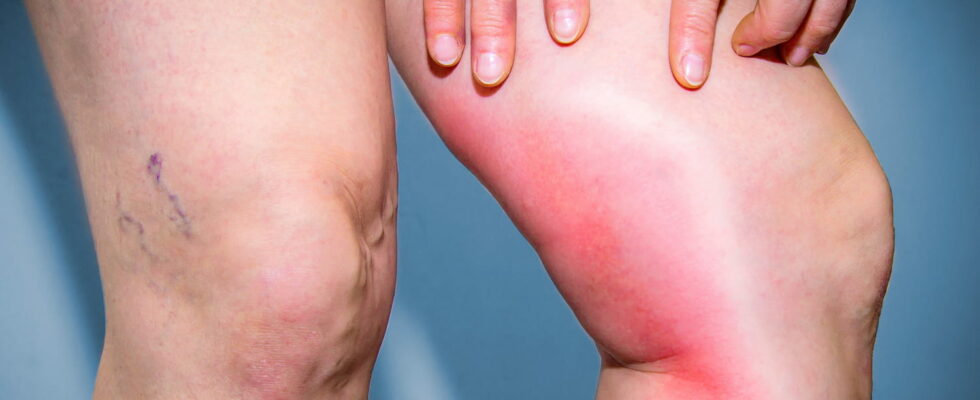
The ideal would be that all people with cancer know the signs of alert of a clot. A clot located at the lower limbs can cause swelling of the ankle or calf, a cramp or contracture in the calf, redness or change in the color of the leg, a feeling of heaviness. More seriously, a clot that moves to a pulmonary artery can cause difficulty breathing, lively chest pain, a feeling of pressure on the chest, dizziness or dizziness.
“”If you feel one of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a doctor immediately or go to the emergency room, because these conditions can endanger your life“, insists our expert. The treatment generally implies the administration of anticoagulants, either by injection (low molecular weight heparin) or by oral route (direct oral anticoagulants or warfarin). The duration of treatment is determined by your doctor as a function The evolution of your cancer and your tolerance.