Does your PC slow down, freeze or stop reacting to the point of becoming unusable? It is worth looking at the CPU, RAM, and disk load to identify the cause of the problem and find the solution.
A PC that sluggish is quite common, especially when it is not regularly maintained (see our practical sheet to bring a slow computer back to life). But when it becomes anemic, unresponsive, the mouse only moves jerkily, or its fans blare loudly for no apparent reason, there’s something wrong.
Most of the time, the culprit is none other than software or a task that monopolizes all the resources of the processor (CPU), occupies most of the available random access memory (Ram) or monopolizes the disk (HDD or SSD) for endless data transfer. It can be a completely legitimate program like a web browser. For example, when you try to open a web page and it contains multiple elements or it is difficult to display due to scripts, the browser may then begin to slip and request more resources. Ditto when many tabs are open. It could also be a Windows process running in the background. the famous svchost.exe (netscvs) is thus often singled out: it is a system process requested by many programs and services, for example involved when it comes to downloading and installing Windows updates (your our practice on the subject). Finally, the problem can also come from a virus or malware that runs more or less discreetly. An overconsumption of resources can thus reveal its presence.
To get to the bottom of it, the most effective tool is Task Manager. This utility provided with the system draws up an inventory of active processes and allows you to close those that cause problems. There are several methods to access it as we describe them in our practical sheet. It then remains to apply the right methods to find the culprit and put an end to his execution.
It is through the Windows Task Manager that you can not only identify processes that are hogging too many PC resources but also put an end to them.
► Open Windows Task Manager by right-clicking on the menu To start up and choosing their name from the list. If your PC is really slowed down, you can use one of the other methods that we describe in our practical sheet to access it.
► By default, Task Manager opens on the tab Process. At the top of the list are currently active applications. At the top of the window, the occupation rates of the processor (CPU), RAM, storage space (disk), network and graphics processor (GPU) are indicated. For each active process, the occupancy rate of each of these resources is specified.
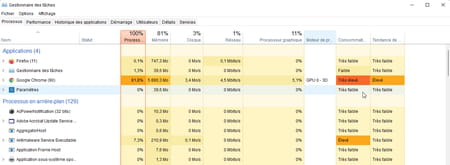
► Processes that use too many resources are easily identifiable since the load they cause is indicated on a red background.
► If the faulty process is linked to a Web browser with, for example, a page that is difficult to display, click on the arrow next to its name (Chrome in our example). All web pages opened in this browser each represent a process. Right-click on the problematic one. From the menu that appears, choose end of task. The page will be automatically closed in Chrome without other open pages being affected by the maneuver.
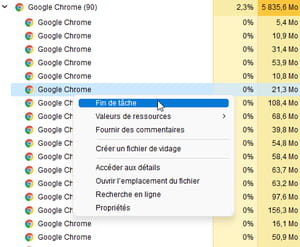
► If the faulty process lies with another open application, carry out the same manipulation in order to force the application to close (be careful, if a job is in progress, it will not be saved).
Svchost processes are related to Windows. Many of them are active in the background and can sometimes malfunction and cause abnormal CPU or memory load. They should therefore be restarted.
► Open Windows Task Manager and click on the tab Details.
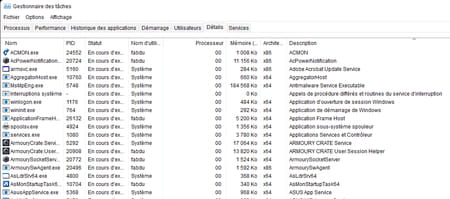
► Click on the column header Processor Where Memory (according to the resource which is saturated) in order to easily find the offending process which will then be displayed at the top of the list.
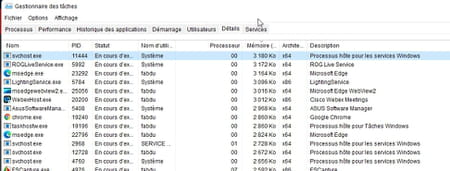
► Right-click on its name and choose Access services.
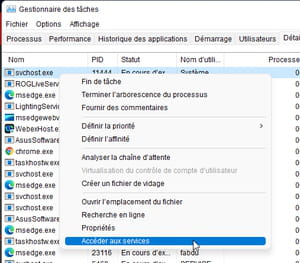
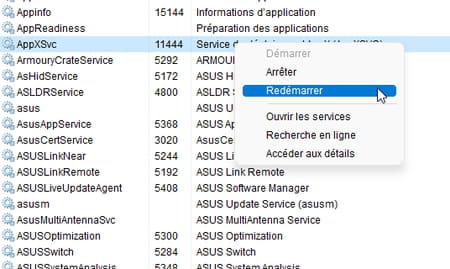
► The tab Services opens and immediately points to the service associated with the Svchost file in use. Two reasons can be attributed to the overconsumption of resources. The currently active service may be performing a task normally but which requires a lot of resources. Wait a few moments for the task to complete on its own. But if time passes and the service remains in the red, it may have crashed. In this case, right-click on its name. From the menu that appears, choose To restart.
Viruses, malware and other cryptojacking tools (malware that mines cryptocurrency without your knowledge) can cause exceptional CPU load. They may not appear in the processes listed by Task Manager. However, you can still unmask them… and delete them.
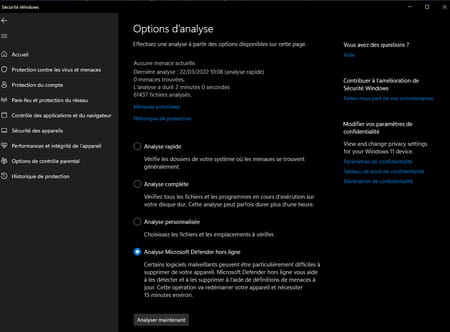
► Start by performing an antivirus scan on your PC using the suite installed on your machine. If it’s Windows Security, the antivirus suite installed by default with Windows, open the taskbar drawer and click Windows Security. In the window that appears, click on the menu Protection against viruses and threats in the left column then on Analysis option.
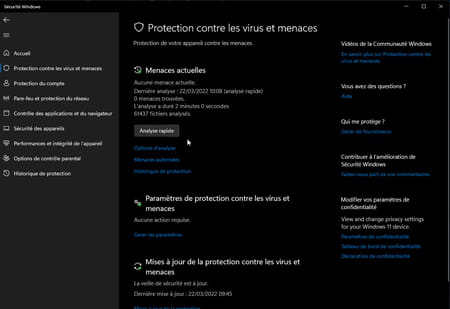
► Then choose the option Microsoft Defender Offline Scan. You can then carry out a deeper analysis of your storage space to detect malware that would slip through the meshes of the Windows Security net. Validate with a click on the button Analyze now. Your PC will restart and perform a scan which can take a good quarter of an hour.
► You can also entrust the analysis to other tools such as Microsoft Safety Scanner or AdwCleaner for example. To do this, follow the advice in our practical sheet.
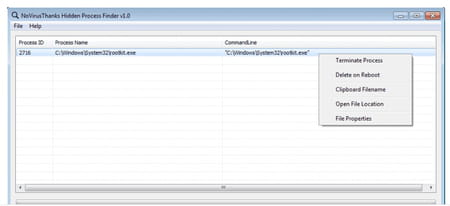
► Another solution, rely on a tool specialized in the search for hidden processes: Hidden Process Finder. Free, this small program in English will analyze the active processes on your PC and identify those that hide their activity. Start by downloading Hidden Process Finder. It comes in two versions: one to install, the other, portable, which does not require installation. Both work the same way.
Download Hidden Process Finder
Download Hidden Process Finder Portable
► Launch the program then click on the button scan at the bottom left of the window.
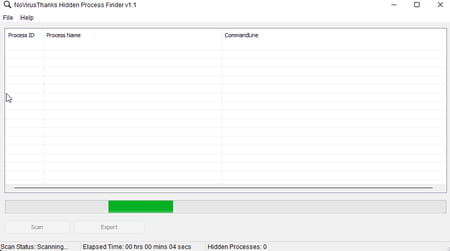
► After a few seconds, the result is displayed. If no suspicious process is detected, the table remains blank. If, on the contrary, the tool has detected a suspicious element, it is displayed. Then click on its name using the right mouse button and choose Terminate process. You can also locate its location in the PC storage space and clicking on Open file location or just delete it on next reboot by choosing Delete on Reboot.