With a prevalence increasing in industrialized countries (5 to 10% of the European population will experience an episode in their lifetime), renal colic is a syndrome which manifests itself by pains intense, unilateral in the lumbar and abdominal regions. Usually appearing at night or in the morning, these pains acute, brief but repeated, are born in the back to then diffuse towards the abdomen, theelder and the genitals. During the seizure, which can last a few minutes to a few hours, no position analgesic is not possible. Nausea and vomiting can complete this picture.
What are the causes of an attack of renal colic?
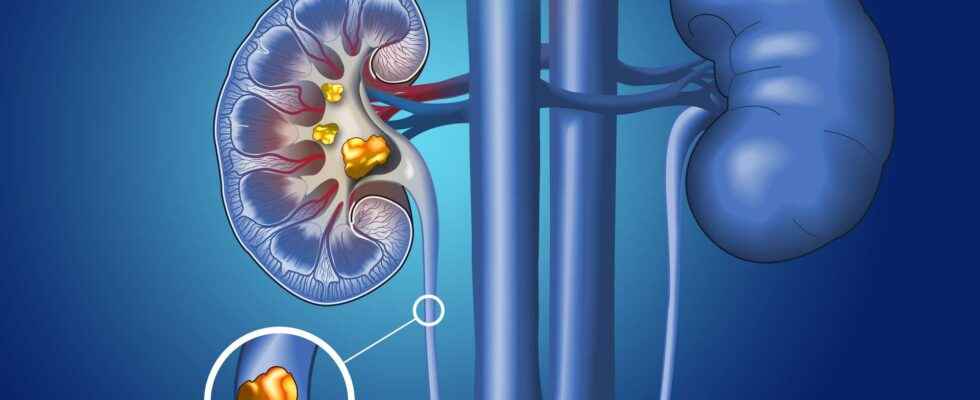
The presence of an obstacle in the urinary tract increase the pressure and leads to this severe pain. In 90% of cases, the obstruction is due to the formation of an oxalate stone of calcium (lithiasis) which appears thanks to an excessively concentrated urinary environment. Excessive excretion of solute, associated with a diuresis insufficient causes precipitation and the formation of crystals, then by aggregation of a stone. The latter, located in the urinary tract (ureter) can be latent and well tolerated for years. But he can also move, cross the bladder, then the urethra to be evacuated in the urine either spontaneously or through treatment.
The origin of this crystallization mechanism is multifactorial. Even if a predisposition genetic promotes the process, the role of food is far from negligible. A diet rich in protein animals and overconsumption of certain foods rich in oxalate such as chocolate are factors that promote the occurrence of an attack of renal colic.
What are the treatments for an attack of renal colic?
The initial treatment is medical, mainly for analgesia. It promotes the use of anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs (NSAIDs) because they decrease the filtration glomerular, smooth muscle tone andedema inflammatory at the level of the obstruction. They are sometimes combined with morphine. In order not to increase the pressure, overconsumption of water is not recommended.
In cases where stone excretion is not spontaneous, there are procedures physical allowing its dislocation. Outside of the surgery, extracorporeal lithotripsy is based on the use of ultrasound to generate shock waves aimed at disintegrating the calculation.
You will also be interested
[EN VIDÉO] What does the color of urine say about your health? Normally, urine is always yellow in color. In some cases, however, the urine is brown, red, green or fluorescent yellow. What does this mean and should we be concerned?
Interested in what you just read?
.
fs7