It is very rare but it can be very serious. The Directorate General of Health (DGS) announced, this Tuesday, September 12, one death in Île-de-France, out of a total of ten cases, suffering from a neurological condition: “botulism”. All would have eaten artisanal canned sardines in the same restaurant in Bordeaux last week. What causes this neurological condition? Elements of answers.
Where does botulism come from?
This toxin develops particularly in poorly preserved foods, and the disease generally results from food poisoning, specifies the Pasteur Institute. The pathogen involved in botulism is a bacteria called Clostridium botulinum (C. botulinum). It is the extremely powerful toxin that it synthesizes that is responsible for the disease. Of the seven types of botulism known today, four (types A, B, E and more rarely F) affect humans.
In France, botulism is rare: the average incidence has stabilized since 1980 at around 20-30 outbreaks per year, most often involving one to three patients each. In the majority of households, this concerns food botulism linked to the consumption of family preserves, but also of artisanal or mass-market products that have not undergone an extensive sterilization process: cured meats, cold meats or even preserved meats. family or artisanal origins.
Other forms of botulism (infantile, due to colonization of the intestine by C. botulinum or by injury, following contamination of a wound by C. botulinum c) are rarer.
Botulism is a serious neurological condition
© / AFP
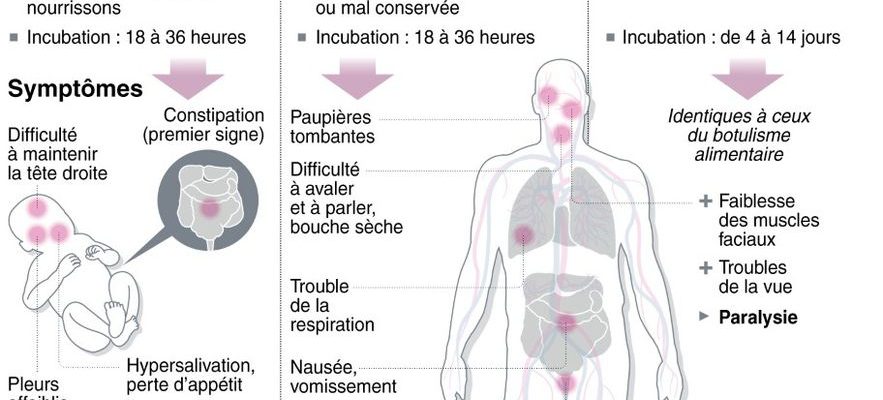
What symptoms?
Botulism occurs after an incubation of a few hours to a few days, depending on the mode of contamination. In general, people who have shared the same foods show identical symptoms, but with varying severity. These begin with eye damage (failure to accommodate, blurred vision), dry mouth accompanied by difficulty swallowing or even speech.
In advanced forms, they progress towards descending paralysis of the limbs and respiratory muscles. It is this respiratory failure that leads to death, explains the Pasteur Institute.
What treatments?
Treatments are essentially symptomatic, that is to say, they aim to reduce the intensity of symptoms. For severe forms, intensive respiratory care with assisted ventilation is necessary. The administration of anti-botulinum toxin in the hours or first days after the onset of symptoms can shorten the hospitalization time, underlines Public Health France.
The vast majority of patients treated without delay recover without after-effects, but the duration of treatment and convalescence can last several months, adds the health agency.
In Bordeaux, 10 cases were reported among people who all attended the same restaurant (Tchin Tchin Wine Bar) between Monday September 4 and Sunday September 10. The health authorities recommend that people who ate in this establishment during this period consult a doctor urgently or contact 15, mentioning cases of botulism, in the event of symptoms appearing after this attendance.