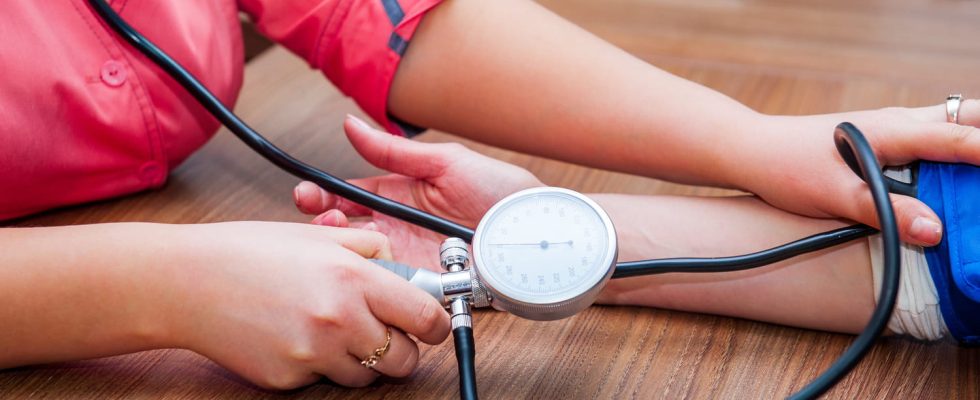
A flare-up (or hypertensive flare-up) is a sudden rise in blood pressure. Although it causes characteristic symptoms, it remains rare and not serious in people without hypertension.
A pressure surge (or hypertensive surge) is a large and abrupt rise in blood pressure. In people without known hypertension, it is very rare and not serious. In a hypertensive person, it is a risk factor for an aneurysm. What causes a hypertensive flare-up? What are the symptoms of a pressure surge? How to react ?
What is the definition of a voltage surge?
Blood pressure surge is different from chronic high blood pressure. “A hypertensive crisis is an acute event that designates a sharp, sudden rise in blood pressure. We speak of a pressure surge when a patient has a blood pressure of at least 21 at rest. Hypertensive attacks are infrequent and only represent a risk in people with hypertension. A patient who has a normal blood pressure (13-14) and who suddenly has a surge in blood pressure to 20-21 generally has little arterial risk. On the other hand, a patient who already has high blood pressure (17-18) and who suddenly rises to 25-26 has a much higher risk.“. explains Dr. Teddy Assulin, cardiologist. The surge of tension can also be the mode of discovery of hypertension in a patient“
What are the risks of a flare-up?
The major risk is ruptured aneurysm. “During a surge of tension, there is a large shock wave which is created brutally on the arteries. And a weakened vessel that receives a strong shock wave has a risk of rupture. A ruptured brain aneurysm is one of the causes of stroke haemorrhagic which can be fatal”, says our expert.
What are the symptoms of a pressure surge?
A surge of tension does not go unnoticed. She is usually symptomatic and is manifested by:
- A sudden headache, called a throbbing headache (the patient has a feeling of “hammering in the head”)
- Palpitations
- The feeling of having flies flying or fog in front of the eyes
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Nausea
- Digestive signs, even vomiting in the event of a major hypertensive flare-up
What causes a blood pressure surge?
► In a hypertensive person:
- Incorrect intake or sudden discontinuation of a treatment for hypertension
- Eating a very salty meal
- Increased emotional or surgical (before an operation) stress/A heavy adrenaline rush
- Taking medications that promote tension flare-ups such as anti-inflammatories, particularly corticosteroids.
- Unknown high blood pressure
► In a person without hypertension: the risk of having a blood pressure flare-up is very rare, except when taking supportive medications such as anti-inflammatories or certain illnesses (hyperthyroidism or very rare diseases such as pheochromocytone)
► In a person without hypertension, tension flare is very rare and does not require treatment. The blood pressure eventually returns to normal.
► In a hypertensive personhypertension should be controlled. In the absence of signs of complicationtreatment of a possible cause, rest and measures to decrease the patient’s stress are often sufficient to lower blood pressure.
► A surge of tension that does not return to normal after a few hours despite rest may require initiation of hypotensive therapy
► A voltage surge above 22-23 (at rest) Or the presence of signs of complications (aneurysm, etc.) are an emergency and may give rise to urgent treatment.
Prevention: what are the recommendations?
- Never stop your hypotensive treatment abruptly and without the advice of a doctor
- A hypertensive person should normally follow a low-sodium diet (low in salt), especially if he takes a treatment that promotes the retention of salts.
- If there is any doubt about the presence of hypertension, consult a doctor and carry out the necessary diagnostic tests.
- People with a family history of aneurysm should have their blood pressure monitored.
Thanks to Dr. Teddy Assulin Cardiologist.
- French Society of Emergency Medicine
- Hypertensive flare in an adult” Rev Prescrire 2018; 38 (414): 285-287