Published on
Updated
Reading 3 mins.
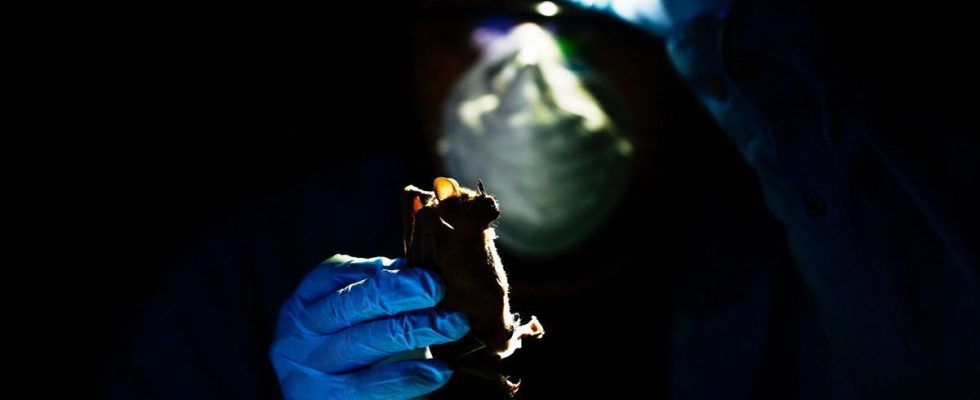
At nightfall in a forest in Yucatan (southeastern Mexico), veterinarian Omar Garcia collects fluids from a bat using a headlamp as part of a research program on zoonoses , these diseases that pass from animals to humans, like perhaps Covid-19.
Caught in nets, motionless in the hands of the veterinarian, the bat is a species considered to be a virus reservoir.
500,000 to 800,000 viruses of animal origin could affect humans
Omar Garcia collaborates in a Franco-Mexican scientific research program on zoonotic pathogens (viruses, bacteria, parasites) at the origin of numerous epidemics in recent decades in tropical areas, such as Ebola for example.
Regarding Covid-19, scientists widely believe that the pandemic started because an animal transmitted the virus to humans, probably in the Chinese market of Huanan, in Wuhan.
Researchers and US officials, however, defend the hypothesis of a laboratory leak, which China disputes.
In any case, the threat and the risks have not disappeared: it is estimated that between 500,000 and 800,000 viruses of animal origin could affect humans.
On the strength of this figure, scientists from the Institute for Research and Development (IRD) and the National Autonomous University of Mexico (Unam) chose Yucatan, a tropical zone at risk like elsewhere in the world (Central Africa, Asia southeast).
“A region very emblematic of the risks of zoonosis emergence”
With major deforestation problems, two hours by plane from a megalopolis connected to the whole world (Mexico City and its 26 million inhabitants on the outskirts included), Yucatan presents itself as “a region very emblematic of the risks of emergence of zoonosis“, underlines Benjamin Roche, researcher and director at the IRD. “In Yucatan, we are trying to design a prevention strategy that can serve as an example for everyone“.
Mr. Roche is the co-director of the Franco-Mexican Eldorado laboratory based in Mérida. In theory, the laboratory can share its “experiences and best practices” with other research centers elsewhere in Latin America (Costa Rica), Central Africa (Gabon, DRC) or in South-East Asia. This is in any case the goal of the French initiative Prezode (to prevent emergence of zoonotic diseases) which includes 22 countries.
The objective of the Franco-Mexican mission is to understand how pathogens, which circulate between animals, birds, rodents and mosquitoes, can potentially affect humans, explains Audrey Arnal, researcher at the IRD.
West Nile virus reservoirs
It is “understand what the consequences of contact between humans and wild fauna could be, and understand what the next epidemic likely to emerge from nature could be“, she adds.
“We have a lot of questions“, adds Maria José Tolsa, biologist at UNAM, stressing that the Covid-19 pandemic has highlighted the research she has been carrying out for ten years.
Fieldwork begins in the early morning with the laying of nets to capture birds and bats.
Then comes the taking of blood or other fluids by the scientists who identify the animal and record data, before releasing it.
Then comes the time for analysis, on site in Mérida in the Franco-Mexican Eldorado laboratory, or in Mexico City.
“Among the birds, we found species identified as a reservoir for the West Nile virus (Editor’s note: arbovirus mainly transmitted by mosquitoes that can cause neurological damage in humans)“, explains in Mexico Rosa Elena Sarmiento, of the virology laboratory of the veterinary faculty of the UNAM.
Exchanges favored by the extension of agricultural and tourist areas
In a later step, the team plans to take blood samples from local populations to determine if they carry a virus of animal origin.
In the meantime, the project includes visits to these rural communities and interviews on social and environmental themes, against the backdrop of the extension of agricultural and tourist areas.
“We can’t arrive and impose ourselves“, explains Erika Marcé Santos, of the NGO Kalaankab which liaises with the communities. “We need an exchange of knowledge with the communities“.
At the end of December, beginning of January, 1.7 million poultry carriers of avian flu were sacrificed in Yucatan, had indicated the local responsible for Rural Development, Jorge Andrés Diaz Loeza, according to whom the situation was under control.
In the peninsula, thousands of trees have also been cut for the construction of the Maya train, a construction site with a length of 1,554 km which is to be inaugurated in December.
Under the fire of criticism from environmental activists, the government claims to have compensated by planting other trees.