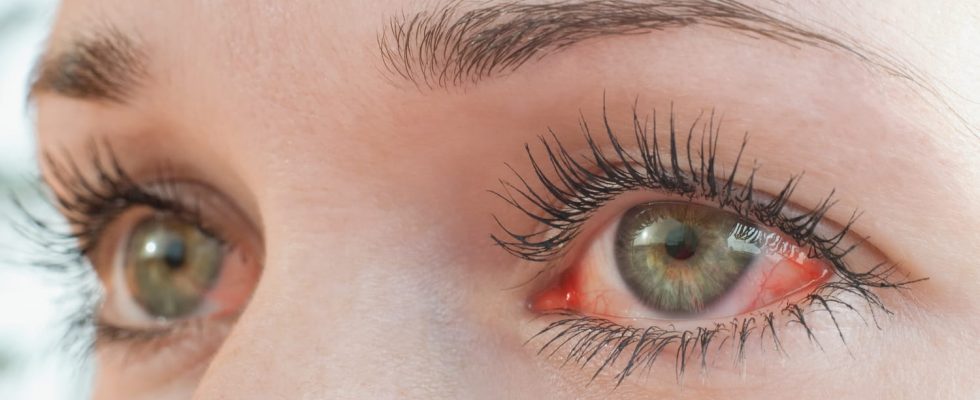
The red eye is a very common reason for “emergency” consultation. Conjunctivitis, glaucoma, keratitis, uveitis… Several causes can give red eyes. When to consult? How to treat the white of the red eye?
Have the white of the eye red requires consulting a healthcare professional, especially if the symptoms are painful. Several causes can cause red eyes. Why do I have red eyes? When to worry? How to cure red eyes?
What are the symptoms of a red eye?
“Redness of the white of the eye may be accompanied by tingling, itching, pain, tearing or decreased visual acuity. Sometimes even associated secretions“explains Dr. Karen Bitton, ophthalmologist. “These symptoms can have a wide variety of causes” says Doctor Pablo Gomez, medical director. from the Ophthalmoexpert Clinic, Mérignac.
What causes a red eye?
► When the eye is red, but this redness is not accompanied by a decrease in visual acuity, it is most often conjunctivitis or subconjunctival hemorrhage, two simple pathologies which do not threaten vision. Red eye, when painful or accompanied by loss of vision, is much more worrying. In these cases, it is generally the sign of a more severe pathology.
► The redness predominates in the periphery of the eye and in the conjunctival sac. Conjunctivitis can be of bacterial, viral or allergic origin. The ophthalmologist recalls that we also observe “traumatic, inflammatory or toxic conjunctivitis, when the eye has been in contact with a toxic product”. During conjunctivitis, the redness is mainly located on the periphery of the eye and in the conjunctival sac.
- allergic conjunctivitis associates redness, tingling, tearing and other allergic signs such as allergic rhinitis most often but also asthma or eczema.
- Bacterial conjunctivitis caused by a bacterium causes redness characteristic of conjunctivitis and purulent discharge that can stick the eyelashes especially in the morning on waking.
- Viral conjunctivitis which is most often accompanied by nasopharyngitis is often very contagious and can be transmitted by contact between the eyes and the hands.
► Impressive but most often not serious, subconjunctival hemorrhage generally does not have specific causes. It is necessary to consult urgently in order to eliminate an underlying sceral wound or an ocular contusion.
► Brutal, unilateral accident, with very intense ocular and peri-ocular pain, semi-dilated and fixed pupil. As its name might suggest, acute glaucoma is not a complication of chronic glaucoma (GAO), but an event that occurs on an anatomical predisposition (narrow iridocorneal angle).
► The keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea accompanied by pain, photophobia, tearing. Several causes are possible: trauma (contact lens accident), infectious, UV (electric arc, snow blindness), dry eye.
► Doctor Gomez specifies that the etiologies of uveitis are also very diverse:The cause of uveitis can be an infectious or inflammatory disease, but also an autoimmune disease”.
When to worry about a red eye?
While the redness as such is not a warning sign and can have a large number of perfectly benign causes, Doctor Gomez reminds us that “Redness accompanied by loss of vision, pain or after shock” East a reason for urgent consultation. Treatment will of course depend on the cause of these symptoms.
“In first intention, you have to consult if your eye is red and especially if it is painful, because usually the absence of pain means that it is benign” emphasizes Dr. Karen Bitton. The treatment then depends on the cause. If it is a hemorrhagic cause, there is no treatment. If the eyes have reddened as a result of trauma, corneal healing ointments are recommended. “If red eyes are related to drought, artificial tears will relieve. If it is an inflammatory cause, we prescribe aanti-inflammatories and if it is due to an infection, antibiotics. In the case of conjunctivitis, apply an antiseptic. In all cases, you have to clean the eye. In addition, a patient who wears contact lenses and suffers from a red eye must remove them and replace them with glasses until the consultation” recommends the ophthalmologist.
Prevention is also important. In order to avoid the appearance of viral or bacterial conjunctivitis, it is advisable to wash hands thoroughly before any contact with the eyes, especially if someone close to you has this type of conjunctivitis. Also think about wear sunglasses that protect against ultraviolet rays, but also wind and dust. As for the swimming pool, a sensitive place due to the presence of irritating chlorine products, it is essential to protect the eyes with swimming goggles or a mask. In the event of allergic conjunctivitis, an allergological assessment carried out by an allergist is essential. An allergy to dust mites, animals or pollens, for example, may be the cause.
Thanks to Dr. Pablo Gomez, Chief Medical Officer. from Clinique Ophtalmoexpert, Mérignac and Dr. Karen Bitton, ophthalmologist.