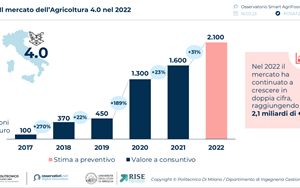
(Finance) – 2022 was a complex year for the agri-food sector. The increase in the cost of raw materials, together with the severe drought that has hit all of Europe, have put a strain on the whole sector which has also used digital technologies to face new challenges. The Agriculture 4.0 market, in our country, in 2022 it grew further, going beyond the wall of €2 billion (2.1)registering a growth of +31% compared to 2021. It grows there too area cultivated with 4.0 solutions, from 6% in 2021 to 8% in 2022. 65% of the market value is made up of connected machinery and monitoring and control systems for vehicles and equipment. The remote monitoring systems of crops, land and infrastructures are also growing strongly, +15%. This is what emerges from research carried out by the Smart Agrifood Observatory of the School of Management of the Milan Polytechnic and the RISE Laboratory (Research & Innovation for Smart Enterprises) of the University of Bresciapresented today during the conference “From adoption to valorisation: the challenge of Smart agrifood”.
Between needs that are most satisfied by Agriculture 4.0 solutions, according to user farms, those linked to efficiency stand out, with the reduction in the use of the main production inputs. More than half of user farms implement more than one solution; on average, 3 solutions are adopted per company, a figure showing strong growth compared to 2021 (+21%). With regard to agri-food processing companies, the research reveals that 82% of these realities have used or experimented with at least one digital solution. Of these, almost half have implemented four or more at the same time, recording a 30% increase compared to 2020. And it is above all food traceability, production, logistics and quality control (both of the raw material and of the product finished) the areas where companies are most innovating.
“Technological and digital innovation applied to agricultural production processes is an increasingly relevant and topical issue – he says Andrea Bacchetti, director of the Smart AgriFood Observatory –. In the very difficult context we are facing, digital technologies can help manage the scarcity and rising costs of production inputs and energy in agriculture. Agrifood now faces the greatest challenge, that of moving from the adoption, which is constantly growing on various fronts, to the real and complete valorisation of digital solutions”.
“Among the enabling technologies in the agricultural sector, those aimed at collecting, storing and analyzing data prevail, with technological solutions that are transversal to the various sectors and processes – he continues Chiara Corbo, director of the Smart AgriFood Observatory –. In this context, the interoperability of solutions becomes increasingly relevant and a priority. It is essential to allow the integration of data collected from different systems, internal or external, and in fact for some years the number of collaborative initiatives and projects that go in this direction has been growing. It should not be forgotten that data sharing is proving to be increasingly important to ensure visibility throughout the supply chain, for increasing traceability and sustainability of agri-food production”.
Digital in agriculture – In 2022, the world Agriculture 4.0 market continued to grow at a rate of more than 10% and is estimated to reach a value of around 30 billion by 2027. Signs of ferment also emerge by observing international startups: 28% of innovative companies in the field of digital innovation for agrifood, it has a proposal dedicated to agricultural and zootechnical companies, in most cases offering Agriculture or Animal Husbandry 4.0 systems (23%). Today, in an even more difficult context than the one experienced during the pandemic, digital technologies in agriculture can help manage the scarcity and higher costs of production inputs – thanks, for example, to solutions for the variable rate and for the precision irrigation – and energy, thanks to parallel guidance systems.
The evolution of the market – In 2022, the Agriculture 4.0 market grew significantly as did the area cultivated with 4.0 solutions, going from 6% in 2021 to 8% in 2022: a share, however, still limited, which shows a large margin of evolution for the market. In fact, it should be considered that a significant portion of the investments in 2022 was made by farms that already have experience in this area and that are continuing their path of innovation, going to acquire new solutions or services, which however act in fact on the same surface cultivated. There is therefore still a significant potential associated with farms that to date have not yet approached Agriculture 4.0.
Digital in the Italian agri-food industry – In 2022, 82% of processing companies used or experimented with at least one digital solution; of these, almost half implemented four or more at the same time, recording an increase of 30% compared to 2020. If we do not consider business management software, the first places among the most used solutions are those based on cloud computing technology (58 %), QR Codes (56%), those enabled by mobile technology (for example apps for tablets and smartphones for monitoring the journey of vehicles, for controlling the cold chain and for checking the quality of final products, 45%), ERP and MES (37%) and advanced automation solutions such as robots and cobots (34%). Precisely the latter, together with the cloud, have recorded significant growth compared to 2020, highlighting the need to use digital solutions to archive large quantities of information and have large computing resources, but also an impact from the Covid-19 pandemic, which has accelerated the need to automate some internal processes.
Digital for food traceability – 82% of food processing companies have used or experimented with at least one digital solution. The areas where companies are innovating the most are those relating to food traceability, production, logistics and quality control (both of the raw material and of the finished product). 88% of companies, in particular, are innovating in the traceability area, using or experimenting with technological solutions, such as integrated management software (56%), mobile solutions (26%) and cloud (21%) to reduce the time required for the traceability of products in case of critical issues and streamline data entry processes, reducing the margin of error. Furthermore, these systems make it possible to enhance the characteristics of the product towards the final consumer, precisely in terms of traceability, especially through the use of QR Codes, and to make relations and verification and control processes with public bodies easier . The trend towards innovation is also confirmed by looking at the technological offer: in Italy, 75% of digital solutions for food traceability are enabled by innovative technologies and 17% of these are proposed by startups, which mainly offer solutions in this area based on Blockchain technology.
Despite the positive numbers on adoption, and the development opportunities for all those technologies that are still little used and known, little less than 30% of companies declares its intention to invest in new solutions within the next three years. 80% of companies that do not intend to invest have already implemented one or more digital solutions; therefore, he probably wants to measure the benefits now, before proceeding with new investments. Among the solutions in which 28% say they want to invest are traceability (33%) and business intelligence (26%) software, but also solutions based on QR Codes (23%).