Published on
Updated
Reading 2 mins.
Caused by bacteria, syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease. It can be passed from mother to child. The number of babies treated has jumped 900% in the last five years in the United States. The point of view of Pr Eric Caumes, infectious disease specialist and consultant at the Hôtel-Dieu.
It’s an impressive number: the number of cases of babies treated in the state of Mississippi in the United States for congenital syphilis has jumped 900% in five years, according to an analysis of hospital billing data shared by Dr Thomas Dobbs , medical director of the Mississippi State Department of Health’s Crossroads Clinic in Jackson.
Growing numbers in the United States
In 2021, in the state of Mississippi in the United States, 102 newborns were therefore treated for this pathology, compared to only 10 in 2016. Nationwide, preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that cases in the country have more than doubled, from 941 in 2017 to at least 2,677 in 2021.
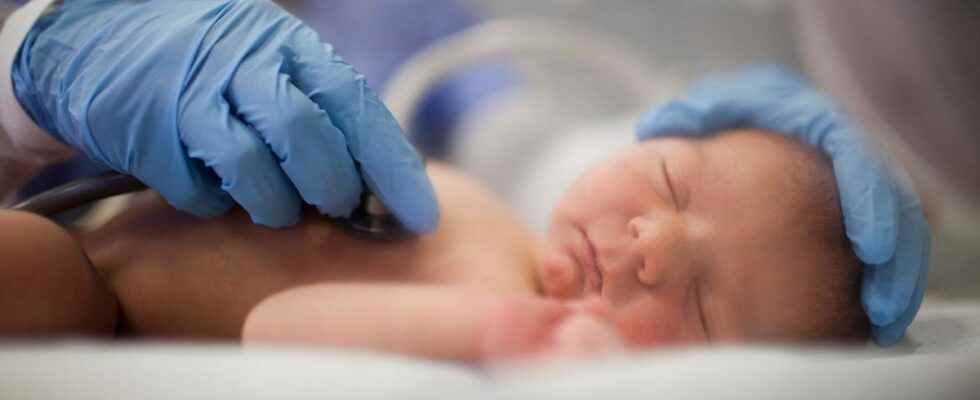
What is congenital syphilis?
Congenital syphilis is caused by bacteria called Treponema pallium, which is transmitted from a pregnant woman to her baby, before she has received effective treatment. If left untreated, a pregnant woman with syphilis has an 80% chance of passing it on to her baby.
Babies infected with syphilis may not initially show symptoms. If left untreated within three months of birth, syphilis can damage a baby’s organs.
The disease can strike a child’s nervous system, in particular its vision and hearing, but also cause anemia, meningitis, jaundice, facial malformation, hypertrophy of the liver and spleen… In the most serious cases, newborns die. The Mississippi State Department of Health does not officially track deaths from congenital syphilis, but said at least one baby died from it in 2021.
A person can contract the disease during sexual contact if they are in direct contact with a contagious patient. Symptoms of syphilis are: genital ulceration (or oral or anal depending on sexuality), skin rashes, possibly fever, weight loss, muscle pain and fatigue. The disease can be effectively treated with two antibiotics. Syphilis can also be present in a latent form in the body, without visible symptoms.
A real public health problem
“It seems like something that should have happened a hundred years ago, not last year.“says Dr. Dobbs, to our colleagues from NBC. “There is really a kind of shock”.
Asked, Professor Caumes is not surprised by these figures. “Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease on the rise. The abandonment of safer sex, including the use of condoms among gays, people most at risk of syphilis, in favor of other practices has something to do with it. And as often, a sexually transmitted infection spreads outside risk groups, after a while, that’s what happens. It is possible in the USA that this is linked to prostitution too, it is dramatic because the children risk serious malformations“.