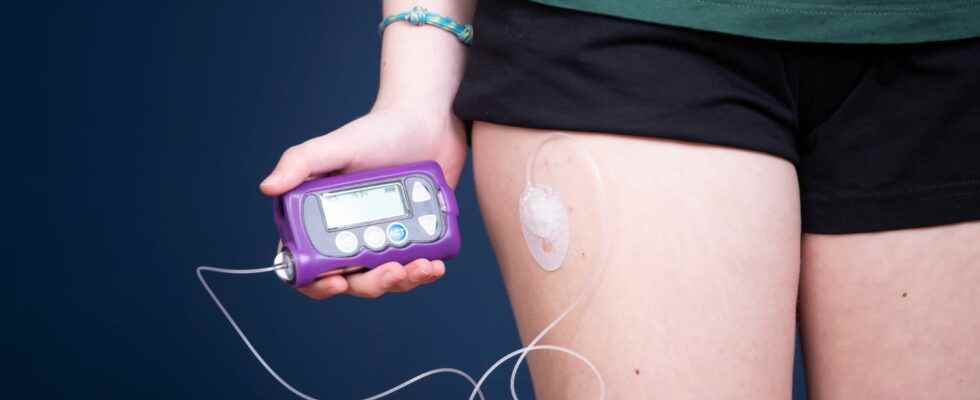
The insulin pump allows people with diabetes a continuous and more precise infusion of insulin, allowing better blood sugar control compared to treatment with multiple insulin injections. Operation, types, reimbursement and prices.
Definition: what is an insulin pump?
The insulin pump is an electronic device who go streaming insulin fast subcutaneously, thus mimicking the activity of the pancreas. It is addressed to people with type I and II diabetes. “The diabetologist programs the device to administer the amount of insulin necessary for the body to maintain the most normal blood sugar possible outside of meals (basal rate), details Dr. Charlotte Condomines, endocrinologist. Additional doses are delivered during meals (bolus). Insulin boluses are adapted by the patient himself, according to his blood sugar levels and carbohydrate intake“. At mealtimes, the diabetic patient sends a bolus of insulin using a remote control or the insulin pump. This system offers great freedom with respect to meal times, food consumed, deviations, sports activity. The insulin pump facilitates dose calculation and improves the patient’s quality of life. “Most patients are still treated with a multi-injection insulin regimen, but recent technological advances are encouraging more and more patients to benefit from an insulin pump.”
What are the indications for an insulin pump?
“The insulin pump is indicated for patients type I and II diabetics for whom the therapy by multiple injections does not allow an optimal balance diabetes, ifsevere hypoglycaemia or a unstable blood sugar balance“, continues the doctor. The insulin pump allows a reduction in the number of injections which can thus drop from 150 to 10 per month.
From what age should an insulin pump be used?
The age varies according to the systems used. “A simple insulin pump and patch system can be installeds at any age, thus allowing the treatment of diabetic newborns and children, underlines our interlocutor. The closed loop is for the moment reserved for type 1 diabetic patients and only arises‘Starting from 7 years old”.
“There are several types of insulin pumps, specifies the doctor. The choice will be made according to the lifestyle and the preferences of the patient (aesthetics, ease of use, remote control, possibility of associating a sensor, sealing)”. The pump can be used with a sensor, coupled or not to the pump. To set up pump treatment, the regulations require:
► An initiation in an insulin pump initiation center by a specialized team comprising at least 2 doctors specializing in endocrinology and/or a pediatrician experienced in diabetology and a multidisciplinary paramedical team trained in diabetology and therapeutic education.
► One regular medical and nursing follow-up with 24 hour telephone support.
► The intervention of an approved service provider for the logistical aspects (pump, catheters, batteries, reservoirs), equipment maintenance and part of the education.
► One hospitalization is necessary in order to initiate the treatment, thus making it possible to train the patients and ensure monitoring by the medical teams. The handling of the pump requires education and adaptation to this technology.
“The traditional insulin pump is connected to the wearer’s body through an infusion set (a tubing). This infusion set should normally be replaced every 2 or 3 days“. Insulin is stored in a cartridge or reservoir that is inserted into the pump. With most models, users have to fill the tank themselves.
The patch pump is attached directly to the skin, for example, on the abdomen, arms or thighs. “It delivers insulin through a cannula at the back of the pump. The pump needs to be replaced regularly, which makes it unsuitable for people with high insulin needs.” Permanently glued to the skin, it requires no infusion tubing.
The hybrid closed loop or artificial pancreas is made up of 3 elements that communicate with each other: a pump, a sensor and an algorithm. “IIt is an automated insulin delivery solution that improves patients’ glycemic control. An algorithm will then determine the insulin needs of the user“. Continuous insulin doses are adjusted if the glucose level detected by the sensor is below or exceeds the set threshold. The closed loop also requires learning functional insulin therapy. “In the initiating center, the patient learns to determine the dose of insulin necessary in proportion to the quantity of carbohydrates consumed during the meal. This requires learning to assess the amount of carbohydrates in the diet and determining the corresponding rapid-acting insulin requirements.”
What are the disadvantages of an insulin pump?
If the insulin pump system improves the quality of life of the patient, it nevertheless has disadvantages. “The main one being the need to carry the device with you at all times, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, recognizes the specialist. It is possible to part with it, two hours at the most”. Moreover, the place where the pump is placed remains visible, especially in summer when you are in a swimsuit. “With a pump, the patient must realize more daily blood glucose checks (at least 4 to 6 times a day) in order to adapt the doses, to detect hyperglycemia accidents”. Pump does not self-regulate blood glucosee and thus requires a perfect mastery of its operation in order to adapt the doses correctly, to know the attitude to have in case of breakdowns, hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia… “Ophthalmic control must be carried out before the installation of a pump in order to rule out any risk of diabetic retinopathy”.
What is the price of an insulin pump and is it reimbursed?
The cost of an insulin pump varies depending on the type of pump. For example, an insulin pump with a sensor costs around 2,000 euros per year. The treatment is reimbursed to 100% by Social Security, under the ALD. He understands :
- pump rental,
- the initial technical training package,
- the daily flat rate (supply and delivery of consumables, accessories, 24-hour technical on-call, home intervention, maintenance).
Thanks to Dr Charlotte Condomines, Endocrinologist at the Clinique du Parc in Castelnau Le Lez (34)