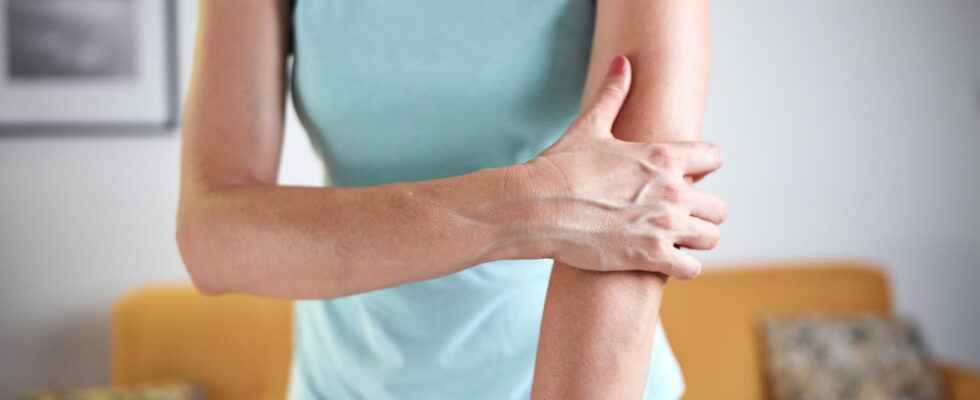
Arm tendonitis is an injury and sometimes inflammation of the tendons that causes severe pain. Its occurrence can prevent gestures of daily life.
What is arm tendonitis?
Arm tendonitis is a musculoskeletal disorder caused by injury or inflammation usually due to the tendon rubbing against the bone. It is often located at the elbowin particular to the external part (epicondylar tendon) or to the internal part (epitrochlear tendon), sometimes at the level of the biceps in the anterior part of the elbow (bicipital tendon).
What are the symptoms of arm tendonitis?
Tendinitis is manifested by more or less acute or chronic pain that descends into the forearm or that rise above the elbow. “These pains will interfere with the use of the wrist and hand. They are felt when the elbow is extended or flexed or during movements that require pronosupination: hand in pronation downwards, hand in supination upwards“, adds Dr. Boullier De Branche. Daily gestures such as shaking hands, raising a glass or a bottle for example, or certain sporting gestures such as holding a racket tennis courts or a golf club, are so difficult.
What causes arm tendonitis?
Tendinitis of the arm is mainly due to inflammation of the tendons of the epicondyle and/or epitrochlea, at the lower end of the humerus. So we’re talking now lateral or medial epicondylitis (epitrochleitis) depending on the tendons affected. This inflammation occurs most often during a excessive and repeated use of the arm. “Tendinitis appears as a result of repetitive strain injuries and rarely suddenly, most often in the 40-60 age group because at this stage there may be histological changes in the tendons”notes Dr. Boullier De Branche.
Who to consult?
We first consult a general practitioner. If the pain does not regress, despite proper management, it is recommended to consult a physical medicine doctor or rheumatologist.
The diagnosis of tendinitis of the arm is made when consultation looking for isometric contraction (against resistance) of the different muscles of the arm or forearm that reproduce spontaneous pain (supinators or pronators). “Palpation at the level of the insertion of the various tendons is essential to confirm the diagnosis“, insists Dr. Boullier de Branche.
The natural evolution of tendonitis at the bottom can last 2 years
How long does arm tendonitis last?
Tendinitis of the arm is “very tenacious” even well treated, with a natural evolution that can last 2 years, or even more in some cases. We sometimes observe disabling recurrences for activities of daily living.
Treatment: what to do in case of arm tendonitis?
“Preventive first: stay well hydrated, especially when playing sports. Use good materialfor example, in tennis, having a good racket with a good head balance, a string that is not too tight…“, says Dr. Boullier de Branche.
► Curative treatment: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) will reduce the intensity of the pain over a period of 8 to 10 days but are often insufficient and cannot be used indefinitely. A daily local massage at the insertion of the tendon is also recommended with an anti-inflammatory gel twice a day.
► Rehabilitation: beyond drug treatment, physiotherapy with deep transverse massages (MTP) and physiotherapy (ultrasound or shock waves) or sometimes even mesotherapy, as well as a work of tendino-muscular reconditioning in eccentric of the epicondylar are proposed. A dozen sessions, 2 or 3 times a week, will be prescribed.
► We also recommend the wearing an epicondylitis bandage to the upper part of the forearm as long as the pain persists in order to reduce stress on the elbow. “This bandage will absorb all the vibrations coming from everyday gestures and gestures of sporting life, and can thus allow or facilitate the resumption of certain sporting activities.. In some cases, in the event of failure of the treatments mentioned above, corticosteroid infiltration can be performed, but despite everything with a risk of recurrence a few months later, obliging to renew the treatment. More recently, injections of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) are proposed but with inconsistent and expensive results (not reimbursed by Social Security).
Can you exercise with arm tendonitis?
Once the acute phase has passed and rehabilitation has been well followed, the resumption of a sporting activity is possible “with continued wearing of the bandage on the forearm for some time to ensure good support.
Thanks to Dr Bernard Boullier de Branche, specialist in physical medicine and rehabilitation in Paris