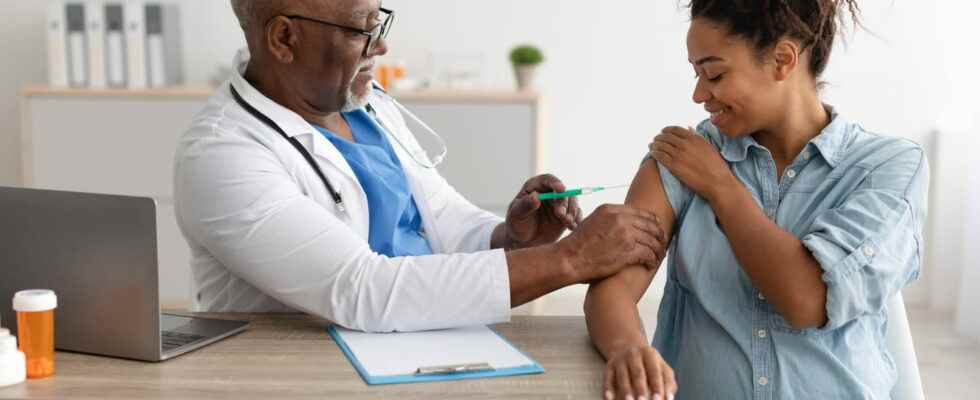
Fragile people, including pregnant women, are given priority for getting the flu shot. Ilana Bénichou, Doctor of Pharmacy, reminds us of the risks of the virus on pregnancy, and the importance of protecting against it when emerging from the Covid crisis.
Each fall, at the opening of the flu vaccination, vulnerable people including pregnant women have priority access to the vaccine. The process is even made much easier for them, as they can now go directly to the pharmacy to print out their receipt and proceed with the injection on the spot. Arrangements more than welcome in view of the risks that the virus can cause on a pregnancy, which can seriously endanger the mother and her fetus. At the end of the covid crisis and especially the wearing of the compulsory mask, Ilana Bénichou explains why in 2022, it is even more essential for pregnant women to be vaccinated against the flu, which this year risks being much more widespread than ” cocooning effect….
Why should pregnant women get the flu shot?
The gestational state weakens future mothers, who lose 50% of their immunities to the benefit of the fetus. They are then much more receptive to viruses, such as that of the flu, which returns epidemically each winter. And in pregnant women, the latter can have serious consequences: “it is not the flu itself that is dangerous, but its main symptom, fever, which is harmful. The flu can cause very strong bouts of fever which lead to spontaneous deliveries, namely miscarriages” explains the pharmacist. Indeed, each year, the flu is responsible for many hospitalizations resulting in premature deliveries, and in the worst cases, deaths. This is why the High Council for Public Health has been recommending systematic vaccination for pregnant women since 2012, regardless of the trimester of pregnancy…. and all the more so this year, explains the specialist: “After two years of Covid and especially of wearing a mask, the organisms have no longer been in contact with the viruses, and the immune systems no longer have the same effectiveness against the affections as when they were used to them. because paradoxically, an immune system is only fully efficient when it is regularly stimulated. With the rebound of respiratory diseases after the Covid episode, everyone is likely to be contaminated… and to be a super a super-contaminator”. Because if an unvaccinated or unimmunized person could previously benefit from the vaccination coverage or the immunities of those around him, he will no longer be able to count on this famous “cocooning effect” this year. Hence the capital importance this year of the vaccination of pregnant women.
“The flu can cause very high fevers that lead to spontaneous deliveries, namely miscarriages”
When should a pregnant woman be vaccinated?
A pregnant woman can be vaccinated as soon as the vaccines are available. Nevertheless, the Doctor of Pharmacy recommends getting vaccinated as closely as possible to epidemiological forecasts. Why ? “Because the antibodies do not stay in the body permanently, and if the epidemic arrives later than expected, as it may have been the case in some years when it hit in March, the vaccine will no longer be as efficient”. To note : it is absolutely necessary to get vaccinated at a time when you are not sick, even slightly. “That way, the body will have plenty of time to focus on the flu antibodies, rather than being mobilized at the same time to fight a cold. And above all, you don’t get vaccinated if you have fever” she adds.
Where can pregnant women get the flu shot?
Pregnant women can get the flu shot from their midwife. Of course, doctors and nurses are also authorized to do so, as are pharmacists.. On a voluntary basis, the latter are effectively able to vaccinate within their own pharmacy the people targeted by the vaccination recommendations. If you have received your health insurance voucher, you can pick up the vaccine on simple presentation of the voucher, or get vaccinated on the spot. And if you haven’t received your voucher, it doesn’t matter: accompanied by your pretty bottle, go to a pharmacy, where your voucher will be issued directly on site!
Is the flu vaccine reimbursed during pregnancy?
To encourage future mothers to come and be vaccinated, the Health Insurance has developed a simplified vaccination circuit: Vaccination is free for pregnant women and therefore 100% covered by Health Insurance. The vaccine can be obtained from a pharmacy on simple presentation of the voucher provided by your doctor or midwife who can then proceed with your vaccination.
Vaccination is free for pregnant women and therefore 100% covered by Health Insurance
Can a pregnant woman be vaccinated against the flu and against Covid at the same time?
No problem, assures us the specialist. “In this case, we will do the flu vaccine on one arm, and the Covid booster dose in the other arm.” And if the flu vaccine tolerance profile has not yet been established, it may cause a little pain in the arm as well as a slight fever “who will respond perfectly to taking paracetamol”. As for the Covid booster, given that it’s the third or fourth dose, there’s no risk of having a big reaction either. “It was especially at the second injection that the biggest reactions could have taken place, but now that the body knows what to expect, it no longer risks getting carried away!” Conclusion: pregnant women can perfectly combine the two vaccinations, and for the most circumspect, Ilana Bénichou invites them to consult the site of the Cratwhich lists in a very current way everything related to taking medication during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Does baby also benefit from the flu vaccine?
In utero, the baby benefits indirectly from the vaccine. If mom is protected, in fact he will be too. But even after birth, the infant will benefit from the flu vaccine, since it will be a winter baby, of course. “If a pregnant woman is vaccinated at the end of October or the beginning of November and her term is in December, the vaccine will protect the newborn until the end of the epidemic” gives us the example of the pharmacist.
Flu in pregnant women: what are the risks?
According to health insurance, hospitalizations are up to 8 times more frequent among pregnant women than in a population of the same age, in particular due to the occurrence of respiratory and/or cardiac complications. This acute respiratory infection usually results in a strong tiredness and an intense fever (about 39°C), as well as a dry cough, aches and headaches. Pregnant women with a higher risk of bacterial infection are then particularly vulnerable. And especially in the face of risk of miscarriage. Therefore, they should not hesitate to consult their doctor or gynecologist if any of these symptoms occur, in order to limit the risk of complications during pregnancy. He will then be able to establish a diagnosis thanks to a nasal swab and offer antiviral treatment to the future mother according to her state of health.
Misconceptions about the flu vaccine
Some received ideas are a brake on the flu vaccination, has noted the Health Insurance for several years. Among the unfounded ideas, some people believe that the vaccine can be harmful for the mother and the baby. An opinion not shared by specialists. Contrary to what one might think, “the influenza vaccine is safe for mother and child”. “It is not associated with any risk of maternal disease, in utero growth retardation, miscarriage, fetal malformation, or disease of the child after birth,” defends the National Council of the Order of Midwives in its communicated. The vaccine even protects the child in the first months of his life.
Another received idea evokes the fact that the vaccine would give influenza to the vaccinated people. False information, because the vaccine is “made from inactivated viruses in order to stimulate the body’s immune response which can sometimes give a few brief symptoms caused by the production of antibodies against the disease. It is without adjuvant, says health insurance.
What to do in case of flu during pregnancy?
There’s no point in panicking. Nevertheless, it is important not to wait too long before consulting your doctor. Indeed, early treatment in the event of flu during pregnancy helps to limit respiratory complications and to treat pregnant women more effectively. This is particularly the case for treatment with Tamiflu, which is prescribed within 48 hours of the appearance of the first flu symptoms. In addition, the High Council for Public Health recommends that expectant mothers get vaccinated against the flu to prevent risks. The vaccine thus makes it possible to prolong the immunity of the pregnant woman while protecting the newborn until the age of six months.
In order to avoid the transmission of the disease, the Ministry of Health recalls some hygiene measures. Sick people are invited to limit contact with the most fragile, to cover their mouth and nose in case of sneezing or coughing and to blow their noses in single-use paper handkerchiefs. In case of pregnancy, it is recommended to avoid crowded areas during a flu epidemic and do not approach contagious people. Wash your hands regularly with soap and water (or failing that with a hydroalcoholic solution), and protect yourself with a surgical mask in the presence of other sick people, make it possible in particular to prevent the risk of transmission of the flu. And the pharmacist recommends wearing a mask all the more this winter for pregnant women, especially in closed and poorly ventilated places, because of the rebound that respiratory-type diseases are sure to cause.
What percentage of pregnant women were vaccinated against the flu in 2021?
Last year, only 52% of priority people were vaccinated, Ilana Bénichou tells us, but among them, many were pregnant women.. According to the national perinatal survey carried out in March 2021 among 12,723 women, the vaccine was offered to 58.9% of women and 30.4% of them were vaccinated, a very large increase compared to 2016. , where this percentage was only 7.4%. The 2020-2021 vaccination campaign was however marked by an unusual demand for vaccination against influenza in general, in the context of the Covid-19 epidemic and at a time when the anti-Covid vaccine was not yet available. .