Is your computer struggling to properly display your games in decent definition? Are the videos you are watching slowing down or stopping mid-stream? Changing your PC’s graphics card to a newer model will breathe new life into it.
One of the advantages of desktop or stationary PCs in tower, mini-tower or “pizza box” format lies in the fact that they remain fully modular and scalable. When a component begins to show weaknesses, it can therefore be easily replaced. Memory, hard drive or SSD, processor or graphics card are immediately accessible after removing a few screws. This is not the case for laptops for which the main developments are limited to adding RAM (Rem) or swapping the hard drive for a faster SSD.
The graphics card is a major element within the PC. Its processor (GPU) is responsible not only for displaying the image on the screen but also for complex calculations for which the main processor of the computer (CPU) is less efficient. This is particularly the case for video encoding and decoding, image processing, etc. Changing the graphics card on a fixed PC can therefore be very useful for reviving a somewhat aging computer, especially when it comes to playing video games. Two players compete today on this ground: AMD and nVidia. If the operation remains quite simple, it is better to respect some precautions. Here are the steps to follow. Warning: the manipulations described below only concern the exchange of the graphics card and not the chipset of the computer. This brings together in the same place the CPU, the GPU and several other components of the PC. It cannot be exchanged. Check if your PC can accommodate a graphics card in addition to this chipset. If this is the case, nothing prevents you from grafting an additional card to it.
Have you set your sights on a new graphics card by carefully checking its compatibility with your motherboard and your power supply? It’s time to part with your old card. But before that, it is of course necessary to prepare its withdrawal by starting by deleting its pilot in order to avoid any conflict with the new model. This operation is only necessary if you change the card manufacturer. For example, if you install an AMD card to replace an nVidia card or vice versa. If you are simply changing model but not brand, installing the new card will remove the old driver. Moreover, if the card comes in addition to a chipset, do not uninstall the present driver.
- Turn on your PC. Type Management in the Windows search box and choose Device Manager among the displayed results. In the window that opens, pull down the menu Graphics Cards.
- Right-click on the name of the currently installed graphics card and choose Uninstall Device. This operation will have the effect of uninstalling the drivers and removing the card from the list of hardware installed on your computer.
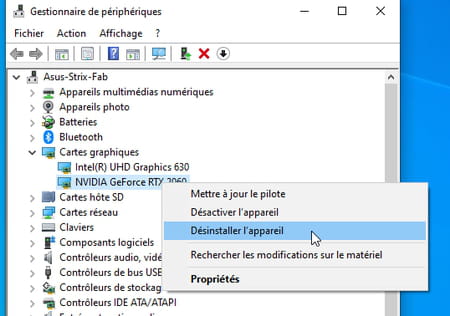
- Warning: never use an uninstall utility other than Windows, or worse, a disk cleaner. Otherwise, you will have every chance of corrupting the system registry in such a way that only reinstalling Windows can get you out of the rut.
Your PC is now ready for trade-in. First, remove the old card. A smooth operation.
- Shut down the PC. Disconnect the power supply and all cables connected to the rear panel. Place the central unit on a table. Remove the side panel to access the expansion cards.
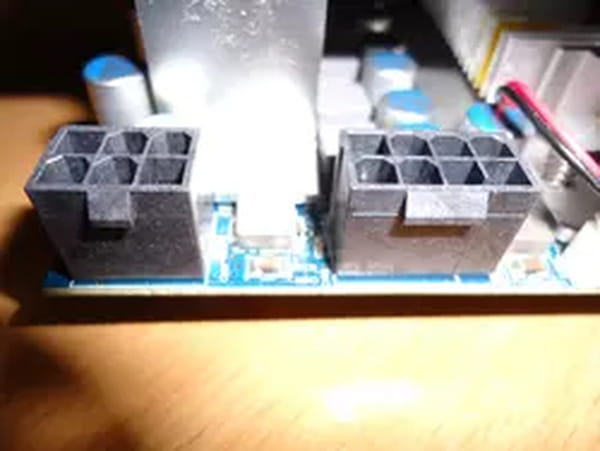
- Before proceeding, check if your new acquisition has one or more dedicated power connectors (such as a 6/8-pin PCI-E connector). If so, check that your power supply has the correct connectors. If not, search through the accessories provided in the box of the new card. An adapter may be provided. If you do not have this adapter, you will have to get one, or even in some cases, change the power supply.
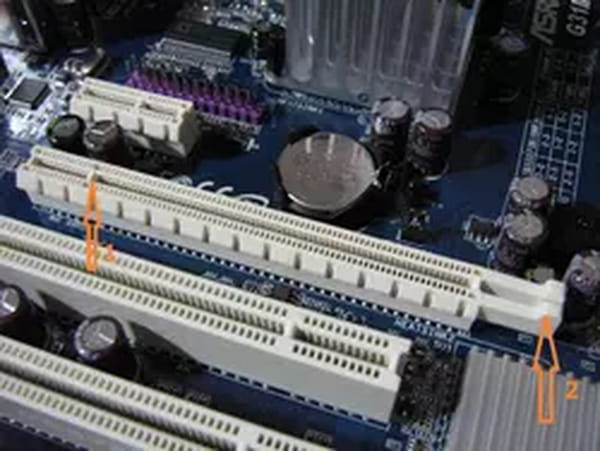
- Before touching your card inside the case, remember to discharge static electricity (just touch the piping of a radiator or a valve). Start by unplugging the 6/8 pin PCI-E connector(s) (if the old graphics card has one).
- Remove the screw securing your graphics card to the PC case, then push back or unlock the locking system at the back of the PCI-Express connector. The majority of motherboards are equipped with a system preventing the graphics card from disengaging from the connector, each manufacturer having its own solution, refer to the motherboard manual for details.
- Now remove the card, without excessive force. It is often easier to lay the case flat for this operation.
The space is now free to accommodate your new graphics card. All that remains is to plug it into its slot, reassemble the PC and install its driver.
- Gently insert the new card into the PCI Express slot by pressing with both hands, again without excessive force.
- Connect the 6/8 pin PCI-E connector to the power supply. This is an essential step if the graphics card is equipped with it since it cannot function without it. If you forget to connect only one of these connectors to the power supply, the card and therefore the pc will not start.

- Replace the card fixing screw on the case and close the central unit. Reconnect the PC and all peripherals.
- Restart the computer. Windows will detect the new card and prompt you for the drivers. Click on to cancel until the dialog box no longer reappears and a message appears telling you “there was a problem during installation and the device may not function normally”. No panic, it’s normal.
- With your web browser, go to the graphics card manufacturer’s website to download the latest drivers.
- Download the driver corresponding to your card and launch the installation. Follow the directions on the screen.
- When the installation is complete, restart the computer, even if no dialog box prompts you to do so. If the screen resolution has changed, right-click on a blank area of the desktop and choose Display Settings. You can then choose the resolution that suits you best.
What to do if the system no longer boots after changing the graphics card?
In some cases, graphics cards that are too recent are incompatible with older motherboards. A BIOS update may also be necessary to support new generations of graphics cards. First check that your PC has the latest version of the BIOS (a visit to the manufacturer’s website should tell you this). If not, reinstall the old card (with its drivers) and check for the presence of a utility branded by the manufacturer of your PC which can inform you of a new version of the BIOS.
