Published: Less than 20 min ago
full screen
Next
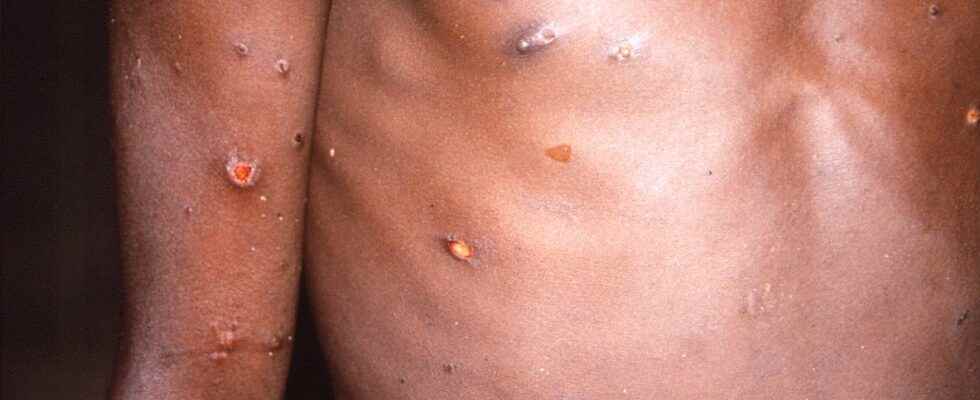
Monkey pox often causes rashes, sores and blisters. Other common symptoms are fever, headache and muscle pain. Archive image.
1 of 2 Photo: CDC via AP/TT
The spread of monkeypox has so far been detected in over 70 countries.
But how big is the risk of a new pandemic? Not that big, but it cannot be ruled out that the virus will become more contagious.
The WHO’s new classification – an international health emergency – of the latest outbreak of monkeypox is due to the organization’s attention to the spread of infection as a potential public health problem and wants to urge countries to reduce the risk of further spread of infection, according to Niklas Arnberg, professor of virology at Umeå University.
It is the seventh declaration of an international health emergency in 13 years, and viruses have been the cause of all of them.
– WHO believes that countries’ infection control needs to review their routines, pay even more attention to the virus and track infections to prevent the spread of infection from escalating, says Niklas Arnberg.
With more than two years of the corona pandemic in the bag, the WHO’s message can feel worrying to many. The risk of the monkeypox virus becoming as contagious as covid-19 is low, but it exists.
Different viruses
For starters, the coronavirus and the monkeypox virus are different types of virus. The monkeypox virus is a dna virus, which mutates much more slowly compared to the coronavirus, which is an rna virus. So far, the monkeypox virus does not appear to be airborne or spread by droplet infection. The risk of the monkeypox virus mutating to become airborne and spread through droplet infection – and thus become as contagious as the coronavirus – is therefore relatively small.
– However, it cannot be ruled out that it can do so. There are other DNA viruses that are airborne, such as chicken pox, says Niklas Arnberg.
Niklas Arnberg considers that similar restrictions and recommendations that were introduced during the corona pandemic – such as for travelers or about wearing face masks and keeping distance – will also be introduced to prevent the spread of monkeypox as very remote, if it will even ever happen.
– This virus is so far bad at infecting people and it requires very close, probably physical contact. That would be if the virus changes a lot, which it could if it multiplies in people with poor immune systems who can’t fight off the infection. Then the virus gets more chances to mutate, he says.
Contagious by close contact
Monkey pox is mainly transmitted through close physical contact with an infected person. The risk of infection is particularly high during physical sexual contact, or other close skin contact, with an infected person, according to the Public Health Agency (FHM). Of the reported cases, 98 percent are men who have sex with men, according to the WHO.
In total, more than 16,000 cases of monkeypox have been detected in 75 countries and five deaths have been reported during the current outbreak, according to the WHO. 77 cases of the infection have been confirmed in Sweden up to and including July 21 this year, according to FHM. The symptoms are often mild but can become serious in people in risk groups.
Around 40 percent of all Swedish cases are estimated to have been infected within the country, the rest in other countries. The disease has previously occurred in western and central Africa, according to FHM. In other parts of the world, few cases have previously been reported.
– The difference between this outbreak and previous ones is that it has spread outside the African continent to many countries, says Niklas Arnberg.
Vaccine for all not so likely
There are drugs that seem to have some effect against the infection and that can be used in serious illness, such as the smallpox vaccine.
This week, Sweden received 2,700 doses of vaccine via the EU. When the vaccine will not be enough for everyone, people who have been exposed to the virus will be prioritized, according to FHM.
– The idea is to give the vaccine fairly quickly after the person has been exposed. It is to have time to develop additional antibodies against the virus before it has made someone really sick, says Niklas Arnberg.
But Niklas Arnberg does not see that the entire population would need to be vaccinated, such as against covid-19, as something that could become relevant.
– It will take a lot in that case. The virus must change radically to become droplet or airborne and become much more contagious.
Facts
Monkey pox
Monkeypox is a disease that can be transmitted between animals and humans. It was discovered in monkeys and was therefore named monkeypox, but it is likely that various rodents in Central and West African rainforests are the reservoir for the virus.
During the spring of 2022, an unusually high number of cases of monkeypox have been confirmed in several countries. Transmission of the virus seems to have mainly taken place via sexual contacts between men who have sex with men.
Monkey pox often causes rashes, sores and blisters. The symptoms are often mild but can become serious in people in risk groups. In older studies conducted in Africa, some mortality has also been reported.
There are drugs that seem to have some effect against the infection and that can be used in severe disease.
All cases of infection with monkeypox must be reported to the infectious disease doctor in the region and to the Public Health Agency.
Source: Public Health Agency
Read more