Fatty liver, which is one of the most important health problems seen in 25 percent of the society, is caused by the accumulation of fat in the liver for various reasons.
SEEN MORE IN MEN
Fatty liver is defined as the liver containing more than 5% of its own weight in fat. Fatty liver is considered to be alcohol-related and unrelated to alcohol use. The form, which is unrelated to alcohol use, can be seen in all age groups and ethnic groups.
Its incidence in the community is around 14-30%. Fatty liver is more common in men. Fatty liver usually does not give any symptoms until it reaches a certain level. It can cause weakness, fatigue, pain in the upper right region of the abdomen and a feeling of fullness. During the examination, mild elevations in liver enzymes may be detected in liver enlargement blood tests.
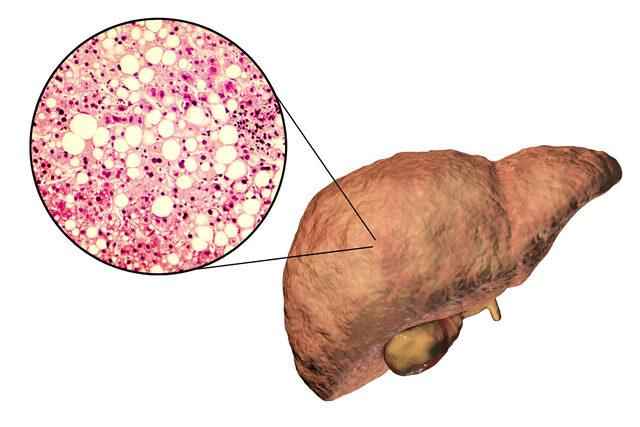
MAY CAUSE SERIOUS DAMAGE
Ultrasonography is the most used method in diagnosis. Treatment should be started when fatty liver disease, which can cause serious damage to the liver, is diagnosed. As the amount of fat increases, inflammation in the liver, decrease in its functions, and damage to the liver cells occur. If the damage is not controlled, serious liver diseases, including liver cancer and cirrhosis, can occur.
IF IT HAPPENS DESPITE TREATMENT…
The first step in the treatment is to determine the cause of the adiposity and to create treatment options for the cause. Concomitant diseases such as diabetes, hyperlipidemia (high blood lipids), exercise, weight loss, liver protective agents such as drugs and antioxidants should be evaluated. In 5% of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease cases, cirrhosis develops in an average of 7 years, and 1.7% may result in death. Regular follow-up is required. Liver biopsy should be performed if liver enzyme elevation persists despite treatment for six months. The stage of the disease and the level of damage to the liver should be determined.